Are There Salt Water Lakes?


Dotted across the globe, amidst arid landscapes and towering mountain ranges, lie salt lakes – fascinating expanses of salty waters that support a unique array of life forms. These saline wonders, characterized by their exceptionally high concentrations of dissolved salts, hold significant ecological importance, providing essential habitats for a variety of plant and animal species. They also play a crucial role in regulating regional climates, influencing temperature and precipitation patterns.
This article by thedailyECO, aims to provide a deeper understanding of salt or saline lakes, their unique characteristics, ecological importance, and the urgent need for their conservation.
What are salt lakes o saline lakes?
Salt lakes, saline lakes, and endorheic lakes are all terms used to describe lakes that have a high concentration of salt.
These lakes are typically found in arid regions where evaporation rates are high and there is little or no outflow of water. As the water evaporates, the salt concentration in the lake increases until it reaches a point where it is no longer possible for the salt to dissolve in the water.
At this point, the salt precipitates out of the water and forms a layer of salt crystals on the lakebed.
The salt content of a salt lake can vary greatly, depending on the climate, the geology of the region, and the amount of water that flows into the lake. Some salt lakes, such as the Great Salt Lake in Utah, have salinity levels that are almost as high as those of the ocean. Other salt lakes, such as Mono Lake in California, have lower salinity levels, but they are still much saltier than freshwater lakes.
What is the most saline lake in the world?
The most saline lake in the world is the Don Juan Pond in Antarctica. This hyper-saline lake is located in the McMurdo Dry Valleys of Antarctica and contains extraordinarily high salt levels. The water in Don Juan Pond has salinity levels nearly ten times greater than that of seawater, making it one of the saltiest bodies of water on Earth.
Curious about the key distinctions between lakes and reservoirs? Delve into our insightful article and uncover the nuances that set them apart.

Characteristics of salt lakes
Key characteristics of salt lakes include:
- High salinity: one of the primary hallmarks of salt lakes is their elevated salinity levels. They contain a significant amount of dissolved salts, often reaching concentrations that far surpass those of the ocean. This high salinity often makes these lakes inhospitable for many forms of aquatic life, yet they provide a haven for specialized organisms that have adapted to thrive in these extreme conditions.
- Endorheic nature: salt lakes are typically endorheic, meaning they don't have an outlet to the ocean or any other external drainage system. Water enters these lakes through rainfall, rivers, or underground springs but doesn't flow out to the sea. Due to the lack of an outflow, these lakes have high evaporation rates, leaving behind concentrated salt and mineral deposits. This closed-basin nature further contributes to the accumulation of salts and the unique characteristics of these ecosystems.
- Unique ecosystems: despite their extreme salinity, salt lakes support specialized ecosystems adapted to these conditions. Some microorganisms, like halophiles, thrive in high-salt environments and give these lakes a unique biological character. Certain species of algae, bacteria, and invertebrates have evolved to survive in these harsh conditions, forming complex and resilient food webs.
- Varied appearance: The salt content often affects the appearance of these lakes. Some salt lakes have crystal-clear, reflective surfaces due to high salinity, while others might have a milky or colored appearance because of the presence of specific types of algae or other microorganisms. The interplay of salt concentration and biological activity creates a mesmerizing visual tapestry across these landscapes.
- Salt deposits: over time, the evaporation of water from salt lakes leads to the accumulation of salt deposits. These deposits can be harvested for commercial use or research purposes, contributing to various industries such as the production of table salt, minerals, and sometimes even cosmetics. The salt deposits serve as a testament to the transformative power of evaporation and the concentration of elements within these unique ecosystems.
- Environmental sensitivity: salt lakes are sensitive to environmental changes. Any alterations in the surrounding environment, such as increased pollution or reduced water inflow, can significantly impact their salinity and overall ecosystem. Human activities such as water diversions and land-use changes can disrupt the delicate balance of these ecosystems, potentially leading to changes in salt concentrations, shifts in biological communities, and even the loss of unique species.
Did you know that lakes can transform into mesmerizing pink spectacles? Unravel the captivating science behind this natural phenomenon in our article.
Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea, the world's largest lake by surface area, is a landlocked body of water situated between Europe and Asia. With no outlets to the ocean, it is considered an endorheic lake. Its defining characteristic is its high salinity, making it a brackish lake with a salt concentration of approximately 1.2%.
Despite its high salinity, the Caspian Sea supports a diverse ecosystem, including over 180 fish species and numerous bird species. The lake has been inhabited for millennia, serving as a crossroads for trade and cultural exchange. It is also a resource-rich ecosystem, with vast oil and gas reserves, fisheries, and mineral-rich waters.

Aral Sea
Once the fourth largest lake in the world, the Aral Sea has shrunk to a fraction of its former size, a stark reminder of the devastating impacts of human actions on the environment. Situated between Kazakhstan and Uzbekistan, the Aral Sea was once a vibrant ecosystem teeming with life, supporting thriving fisheries and providing a lifeline to surrounding communities.
The Aral Sea's demise began in the 1960s when Soviet authorities initiated an ambitious irrigation project to transform the arid region into fertile farmland. Two major rivers, the Amu Darya and the Syr Darya, were diverted to supply water for the newly cultivated fields. However, this massive diversion came at a tragic cost.
As water was diverted for irrigation, the Aral Sea began to shrink at an alarming rate. By the 1990s, the lake had lost over 90% of its surface area and half of its volume. The exposed lakebed became a source of toxic dust storms, affecting the health of local communities and damaging agricultural lands.
The salinity of the Aral Sea has increased significantly as the lake has shrunk, and it is now considered to be one of the most saline lakes in the world.
Do you know the difference between a lake and a lagoon? If not, check out our other article on the topic!

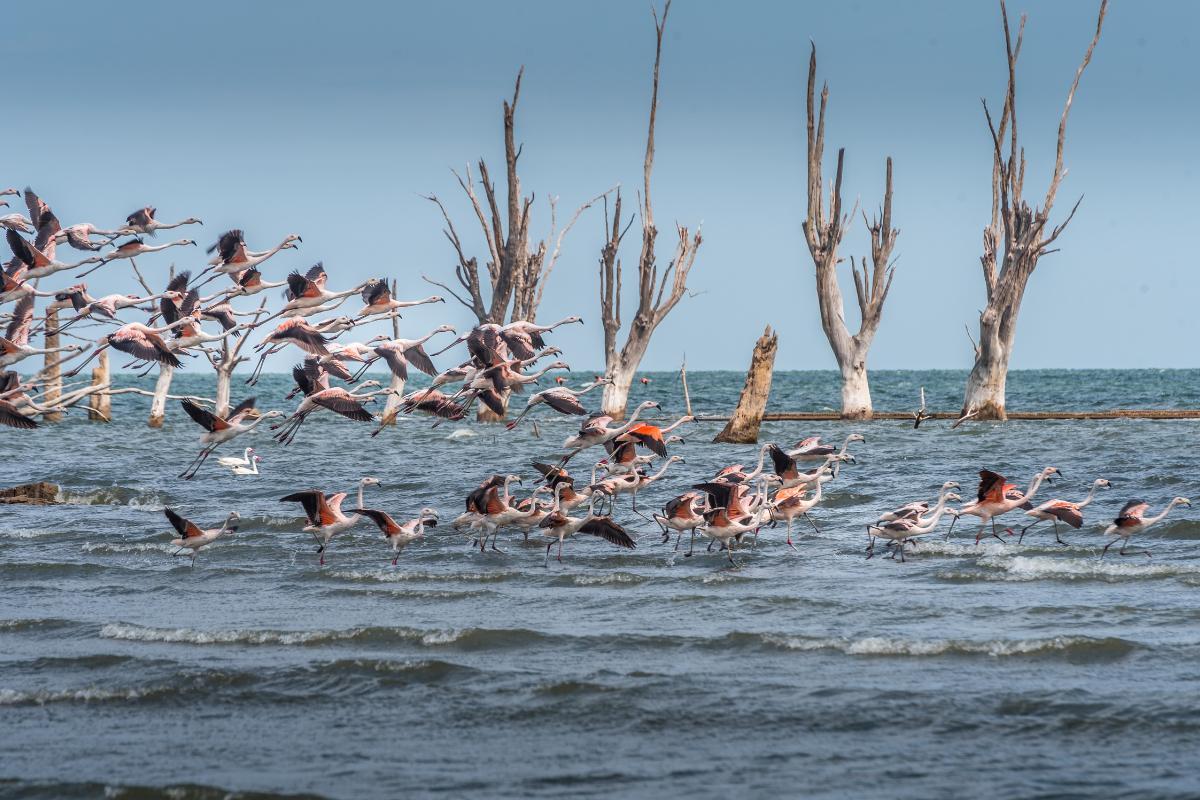
Mar Chiquita or Ansenuza Sea
Located in the northeastern region of Argentina's Córdoba province, the Mar Chiquita, also known as the Ansenuza Sea, is an endorheic salt lake, meaning it has no outlet to the ocean. It is the largest salt lake in Argentina and the fifth largest in the world, covering an impressive area of over 10,000 square kilometers during wet years.
The Mar Chiquita's defining characteristic is its high salinity, with a salt concentration that can reach up to 10 times that of the ocean. This salinity is attributed to the lake's closed-basin nature and the evaporation of water under the arid climate of the region.
Despite its extreme salinity, the Mar Chiquita supports a unique ecosystem adapted to these harsh conditions. Brine shrimp, algae, and other specialized microorganisms thrive in the lake's salty waters, forming the foundation of a complex food web. The lake also provides a critical habitat for migratory birds, attracting over 380 species.

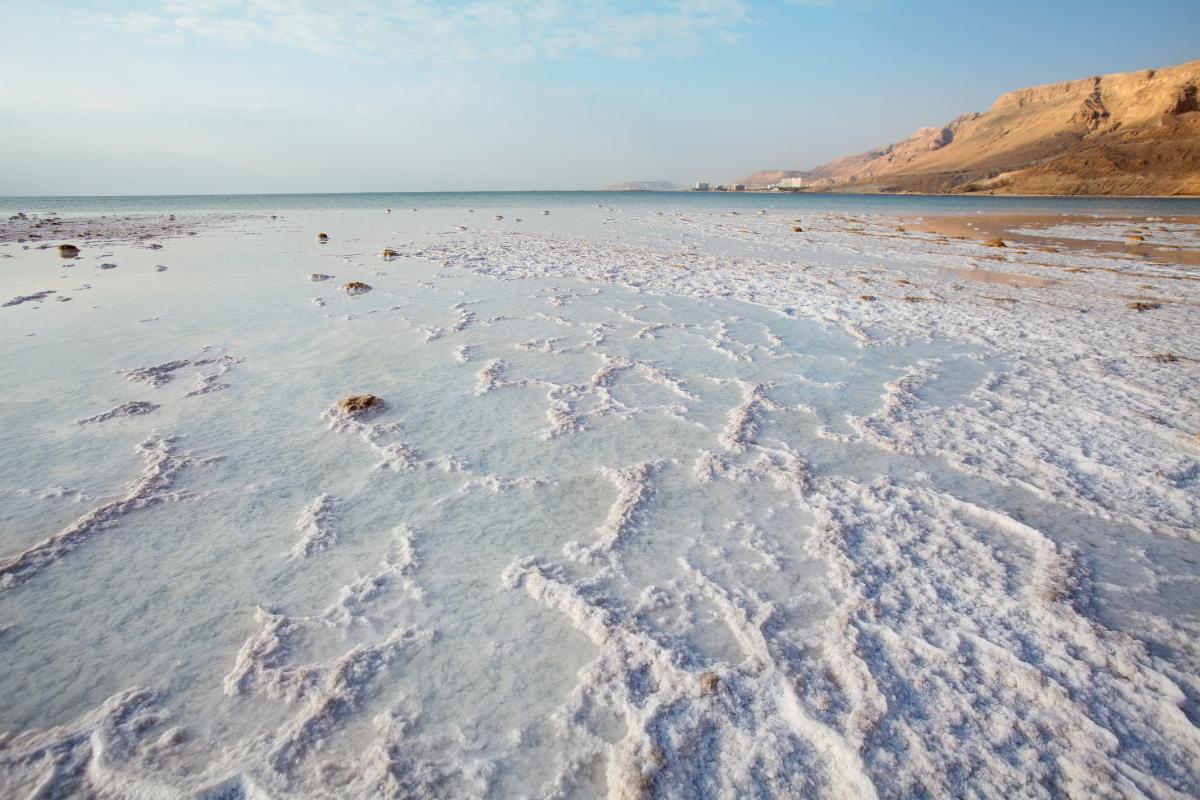
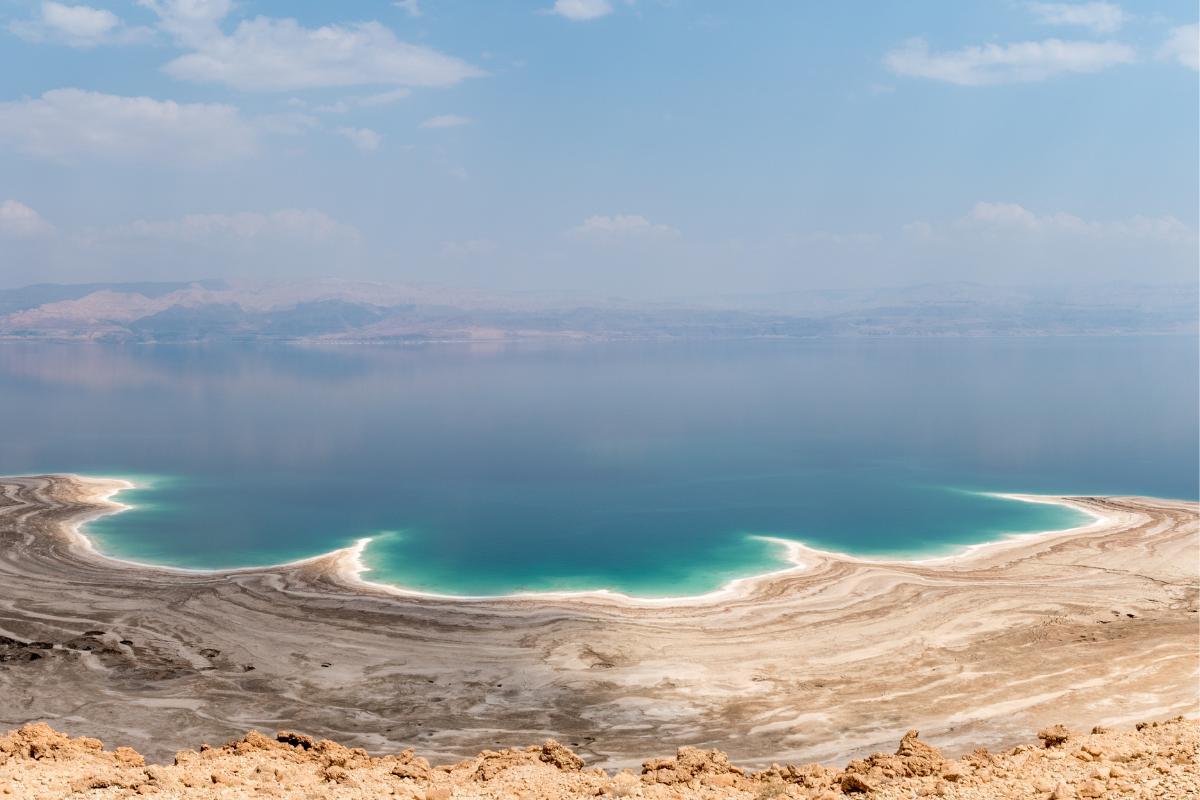
Dead Sea
The Dead Sea, situated between Jordan and Israel, is a remarkable natural wonder known for its exceptionally high salinity and therapeutic properties. Its salt concentration, approximately 8.6 times that of the ocean, makes it the world's saltiest lake. This unique characteristic has shaped its landscape, ecology, and cultural significance.
The Dead Sea's high salinity has long been recognized for its potential therapeutic benefits. The buoyant waters allow effortless floating, easing the burden of gravity and promoting relaxation. The mineral-rich waters are believed to alleviate skin conditions, muscle aches, and joint pain. Spa resorts and wellness centers have flourished along the Dead Sea's shores, attracting visitors seeking rejuvenation and tranquility.
Learn more information about different bodies of water with our guide to inland waters.

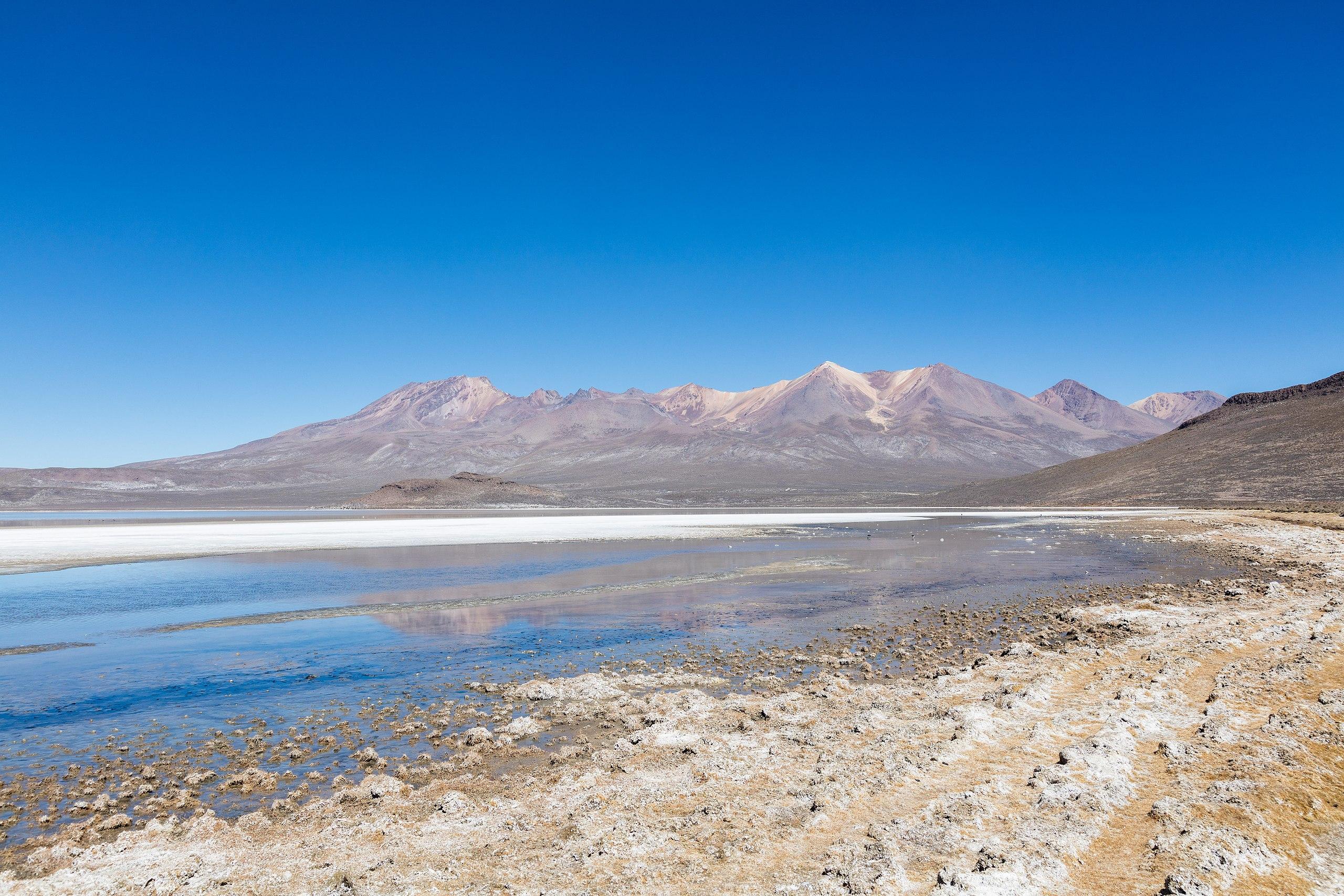
Salinas Lagoon
The Salinas Lagoon is nestled approximately 4,300 meters (14,100 feet) above sea level in the southern reaches of Peru. The Salinas Lagoon is a vast expanse of white salt crystals, contrasting with the surrounding snow-capped peaks.
The Salinas Lagoon formed through the evaporation of ancient glaciers, leaving a deposit of salt minerals.
The lagoon has been a source of salt for local communities for centuries. Traditional salt extraction involves raking salt crystals from the lagoon floor, used for various purposes such as food preservation and livestock feed.

Threats and need for conservation of salt lakes
Distributed globally among arid landscapes and towering mountains, salt lakes are captivating expanses of saline waters housing unique life forms. These remarkable environments, marked by their high salt concentrations, showcase nature's adaptability to extreme conditions.
However, salt lakes confront significant environmental challenges threatening their delicate ecosystems and distinct biodiversity.
Human activities, including water diversions for agriculture and industry, have substantially reduced water levels, altering salinity and disturbing the ecosystems' balance. This decline has led to critical habitat loss, jeopardizing various plant and animal species and overall biodiversity.
Pollution from agricultural runoff, industrial waste, and sewage further intensifies the issues faced by salt lakes. The introduction of chemicals disrupts nutrient cycles, impacting the health of these sensitive ecosystems.
Unsustainable practices like excessive grazing and mining activities degrade salt lake ecosystems. Overgrazing harms vegetation, leading to erosion, increased sedimentation, and habitat loss. Mining activities release harmful substances, disrupting natural processes vital for salt lake health.
Conserving salt lakes is crucial for preserving their unique biodiversity, ecological functions, and economic significance. These environments offer vital habitats, climate regulation, and valuable natural resources.
Protecting salt lakes demands a multifaceted approach. Sustainable practices to minimize water use, reduce pollution, and encourage responsible land management are vital. International cooperation and awareness initiatives play a significant role in promoting responsible behaviors and understanding the importance of conservation.
Delve into our other article for a more in-depth exploration of aquatic ecosystems and their significance.
If you want to read similar articles to Are There Salt Water Lakes?, we recommend you visit our Facts about nature category.
- Bucher, EH, Coria, RD, Curto, ED, & Lima, JJ (2006). “Conservation and sustainable use. “Bathed by the Dulce River and Mar Chiquita lagoon (Córdoba, Argentina).”
- Bucher, E.H., & Bucher, A.E. (2006). “Physical and chemical limnology. Bañados del Rio Dulce and Laguna Mar Chiquita (Córdoba, Argentina)”.
- Red List of Ecosystems of the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). Available at: https://assessments.iucnrle.org/