Echeveria Pulvinata Care - Frosty, Ruby and Other Types


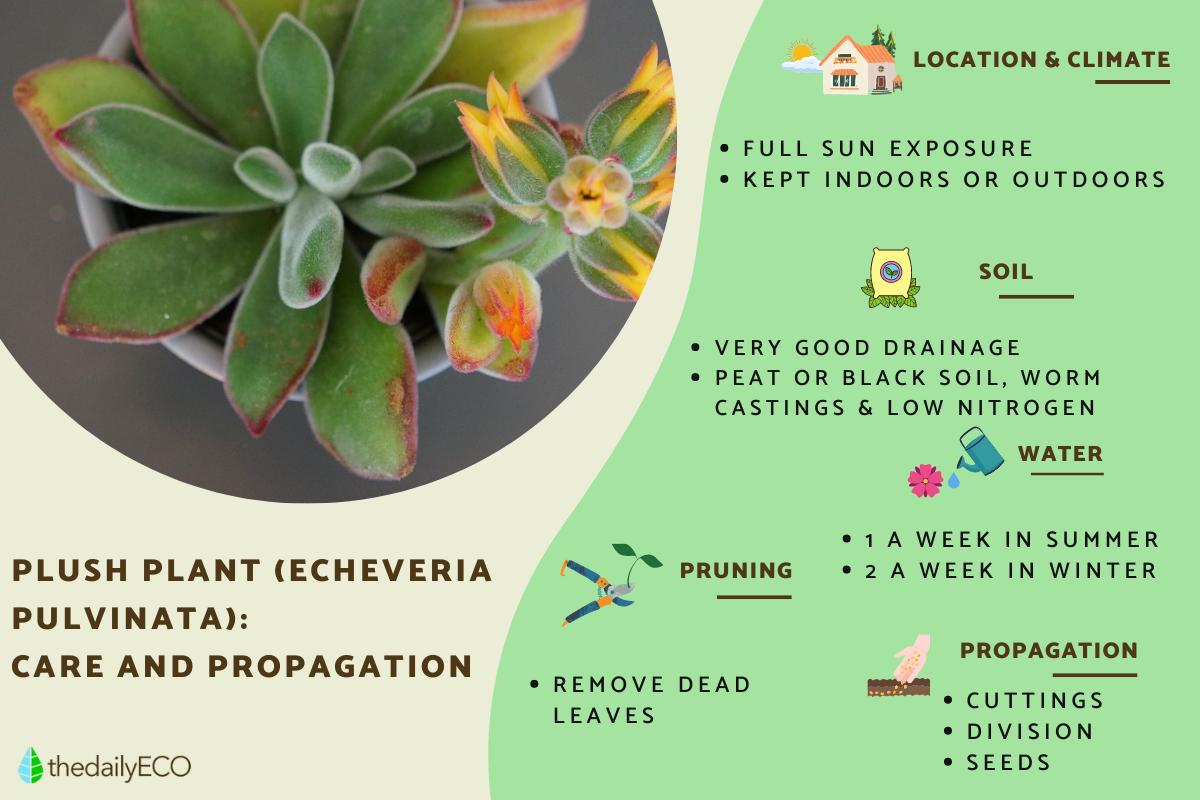
The care of Echeveria pulvinata requires full sun exposure, low irrigation, substrate with good drainage. This applies to all types of Echeveria pulvinata, the most common of which are Echeveria pulvinata frosty and Echeveria pulvinata ruby. These are some of the most beautiful cultivars of this plant, all of which require the same levels of care.
Commonly known as the plush plant, Echeveria pulvinata is popular succulent which can be kept as an indoor or outdoor plant. It is relatively low maintenance, as is common to almost all types of succulent plant. Fortunately, this does not compromise their beauty. At thedailyECO, you can learn everything you need about Echeveria pulvinata care for both frosty and ruby, as well as other varieties.
Echeveria pulvinata characteristics
Before we discover how to care for Echeveria pulvinata, it is best to take a look at its characteristics. This is because these traits will inform their care and help you to decide if they are a good plant for you:
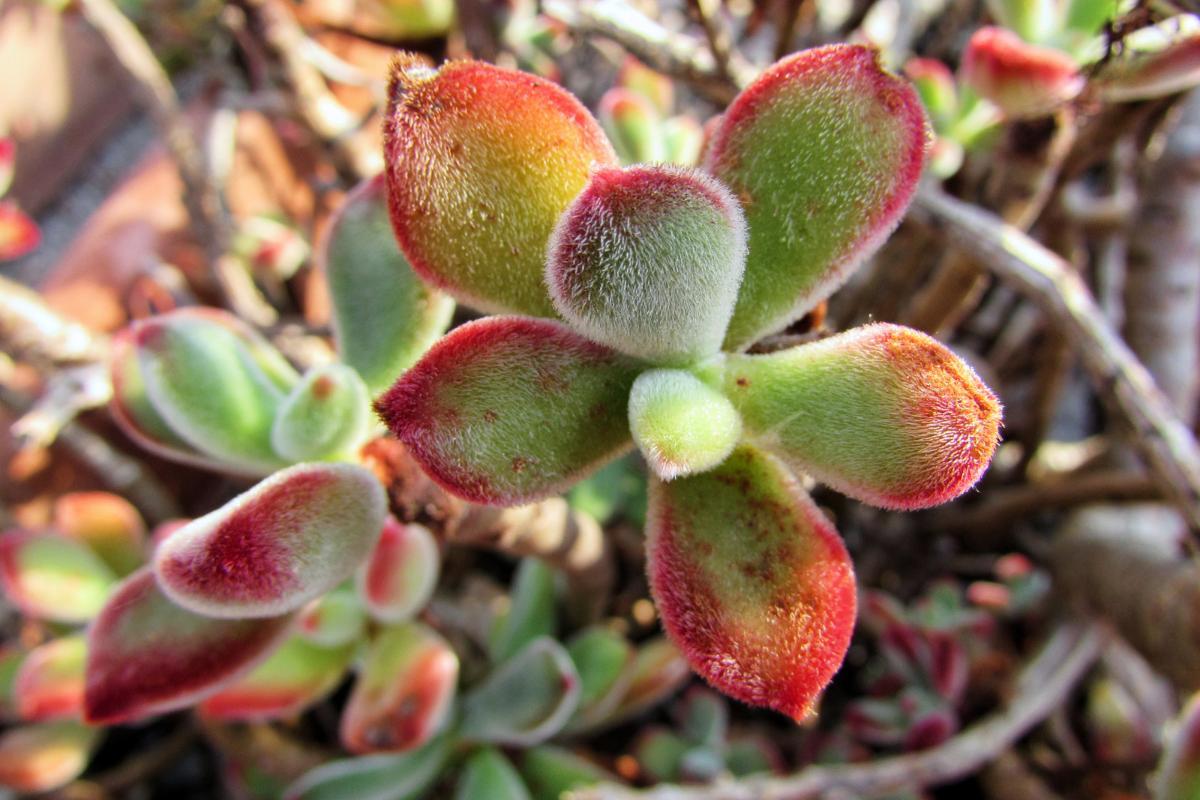
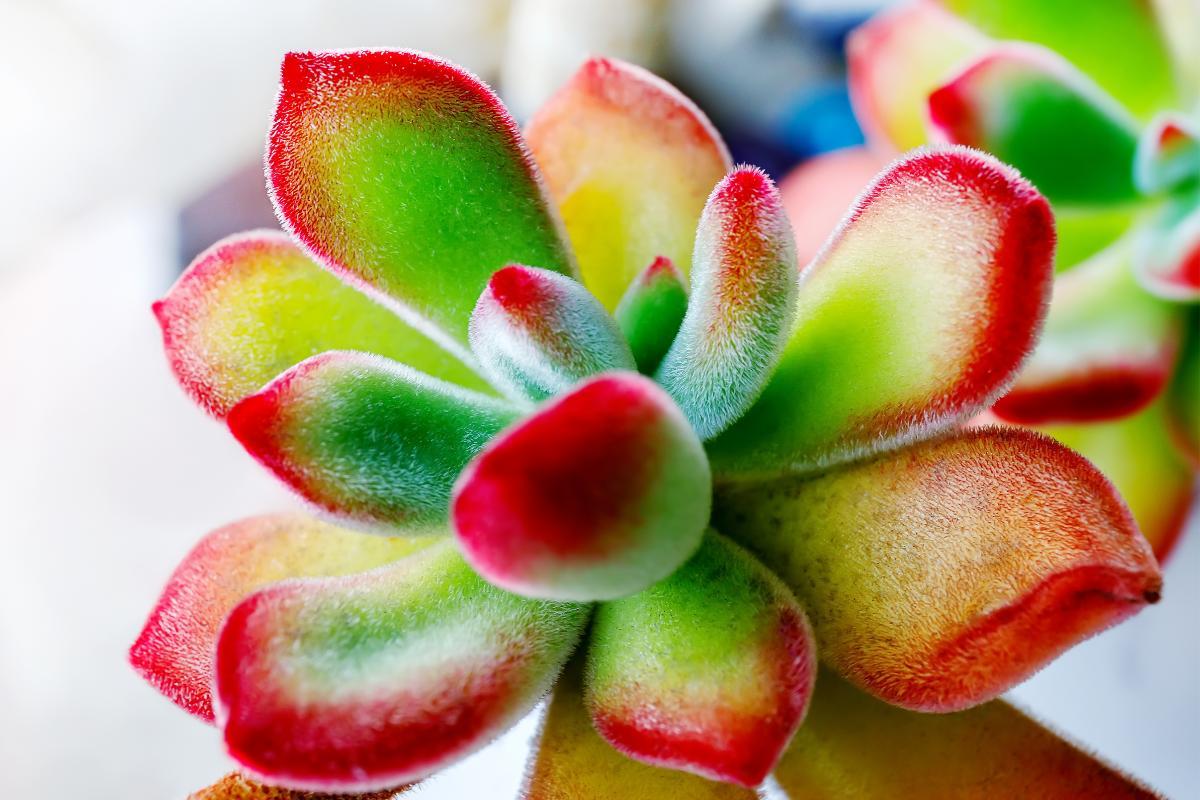
- This species of Echeveria is characterized by appearing to be made of velvet. This is because its leaves are covered by short white hairs. Under these hairs, the bloated leaves are dark green and the tips have a slight tinge of red.
- The leaves are elongated spatulate and grow in the form of a rosette around a stem. The base of these leaves is thin, so often the stem is visible. Several rosettes usually form in a colony. This is a trait common to most types of echeveria succlent plants.
- Plush plants grow upwards, rather than sideways like other echeverias. The maximum height of Echeveria pulvinata is around 12"/30 cm.
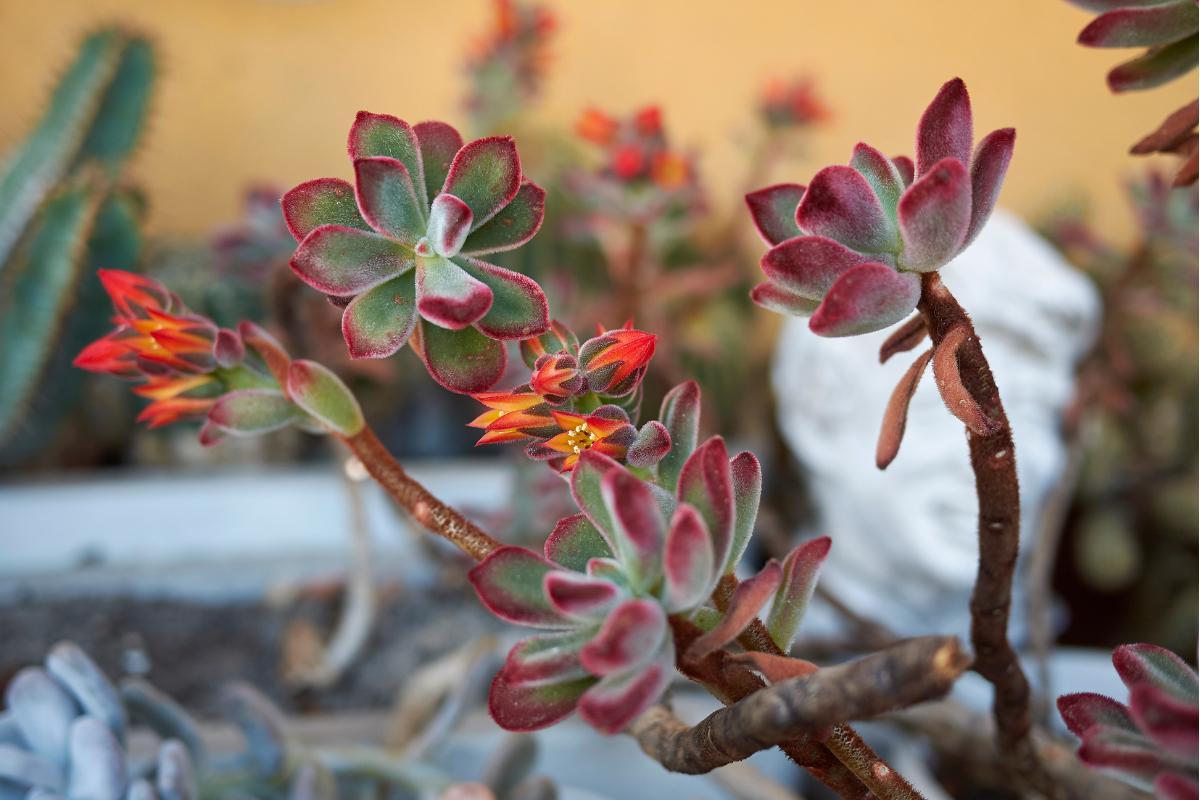
- The Echeveria pulvinata flower grows from a floral stem from which several are arranged in clusters. They are red with yellow markings.
If you would like to grow your own Echeveria pulvinata at home, you can use the affiliate link below to purchase some cuttings:

Types of Echeveria pulvinata
Due to the great attractiveness of this plant, many plush plant cultivars have been created. These cultivars accentuate the special characteristics such as the red tint of the tips and the hairs. The following are some types of Echeveria pulvinata which you might find:
- Echeveria pulvinata ruby: the margins are heavily colored red. They grow to be quite bushy.
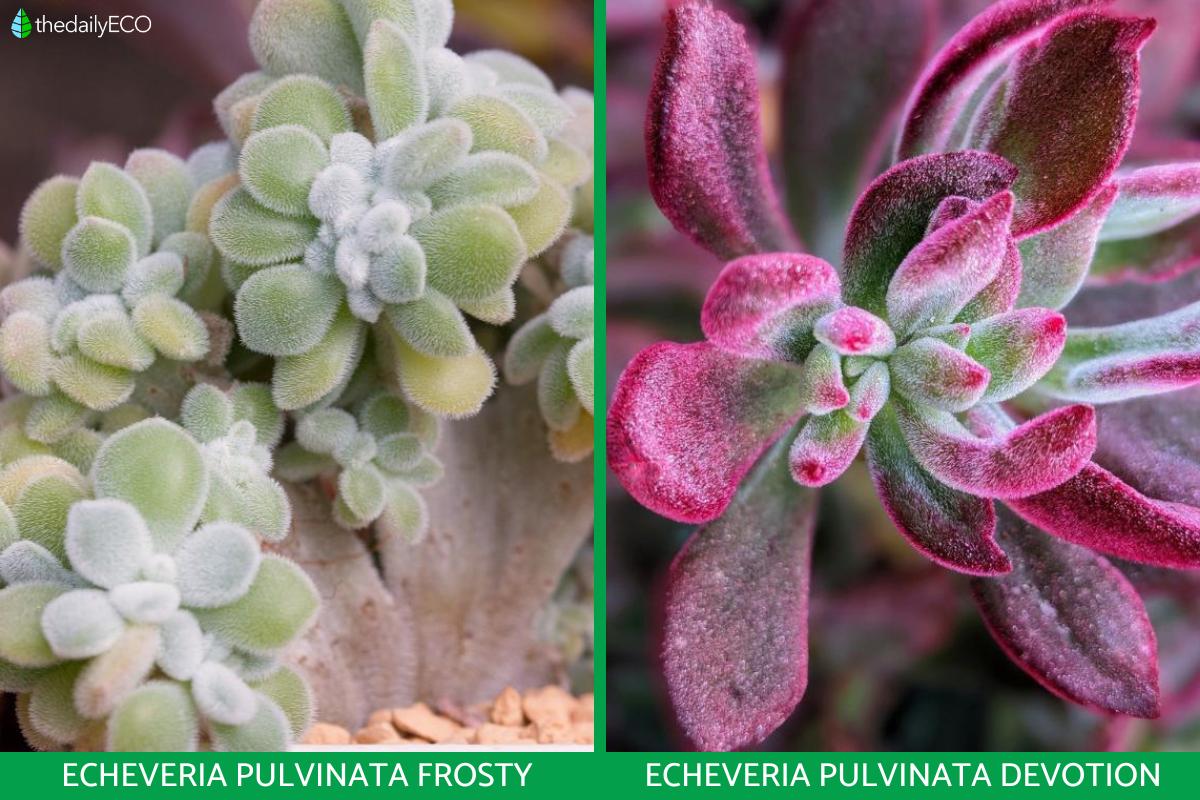
- Echeveria pulvinata frosty: it is known as frosty echeveria because it has a greater number of hairs that give it an appearance as if covered in ice or snow. It does not have red coloring.
- Echeveria pulvinata devotion: grows compactly and does not develop flowers. The leaves are half red. It is a patented variety and won the international award as the best indoor plant of the year in 2020.
- Echeveria pulvinata red velvet: characterized by the fact that the leaves are more fleshy and less spatula-shaped than those of the normal species. They have red tint on the margins.
Although the red coloration gives the plush plant its unique appearance, you may want to discover more plants with colorful leaves in our related guide.

Light, temperature and location
As with most succulents, Echeveria pulvinata thrive when fully exposed to the sun. This is thanks to their adaptations that protect them from high temperatures. It can also be kept in semi-shade if it receives a few hours of full sun during the day or indoors if it is placed near a window.
Soil and compost for Echeveria pulvinata
A good substrate for plush plants is important to keep it in good condition. It must have good drainage so as not to retain excess water. Since the leaves are already in charge of this storage, watering too much will cause the plant to rot. A mixture of substrate for succulents or cacti is prepared with equal parts of worm castings, peat and a porous material such as vermiculite, tepojal or lava rock for plants.
In spring and summer a low nitrogen fertilizer can be applied to promote growth, although it is not essential. Discover the different organic fertilizers you can make at home with our related article.

Irrigation of Echeveria pulvinata
Here we share our guide to watering Echeveria pulvinata and its various cultivars:
- Since it is a succulent that stores water in its leaf tissues, it is low watering and therefore easy to care for, especially for beginners in the world of gardening.
- It should be watered when the first centimeter of the substrate dries up. This means you should let the soil dry between waterings. This will be the best indicator, since the frequency will depend on whether it is outdoors or indoors, as well the temperature in your area. Outdoors it is usually watered once a week and indoors every two weeks.
- It is better to under-water than over-water, because it is very prone to rot if there is stagnation or excess water. Remember that soil preparation is very important in relation to water.
- In winter, irrigation should be lowered to the minimum, doing it every two weeks to prevent the leaves from wrinkling. If they do, it is indicative that more water needs to be added.
- It should not be watered above the rosette because this will cause rot. The best irrigation method is by immersion where the pot is submerged in a planter saucer so that it absorbs what it needs. Another method is to water the substrate, although it is usually more difficult due to the wide growth typical of the species.
Pruning of the Echeveria pulvinata
The leaves at the base of the plant that are aging and dying should be removed. They tend to come off easily. This will help keep the plant healthy and with little chance of rot or fungus settling on the other leaves.

Echeveria pulvinata propagation
- The easiest way to reproduce this plant is by cuttings. This is where a leaf is cut and placed in worm castings. It is constantly watered and soon a new Echeveria will emerge from the end. This method can be done in spring or early summer.
- Another option for this species is to propagate by division. Since they form colonies, it is possible to separate the individuals that form by the roots and replant the divisions to propagate.
- Finally, it is possible to propagate by seed. Due to the ease of asexual propagation, this method is not so common and the seeds are usually difficult to find.
Now that you know the care of Echeveria pulvinata, you can learn more about this type of plant with our guide to the difference between cacti and succulents.
If you want to read similar articles to Echeveria Pulvinata Care - Frosty, Ruby and Other Types, we recommend you visit our Plant care and cultivation category.
Royal Horticultural Society (n.d.). Echeveria pulvinate search. Retrieved from: https://www.rhs.org.uk/plants/31967/echeveria-pulvinata-ruby/details