How Do Icicles Form? - Icicle Formation


We may think that the formation of icicles simply requires water and freezing temperatures, but there is a complex interplay of factors that results in icicles forming. One of these important factors is gravity. It also requires a fluctuation in temperature that allows water to freeze and melt. We can observe icicles in freezing temperatures, meaning they are less than 0 ºC. These temperatures are known to drop most significantly during the night, so we might be greeted by icicles hanging from the eaves of a home or anywhere else. While we associate icicles direct down toward the ground, it is possible to see icicles orientated sideways or even upwards.
At thedailyECO we ask how do icicles form? By looking at the formation of icicles, we can look at how they can develop downwards, upwards and even to the side.
What are icicles?
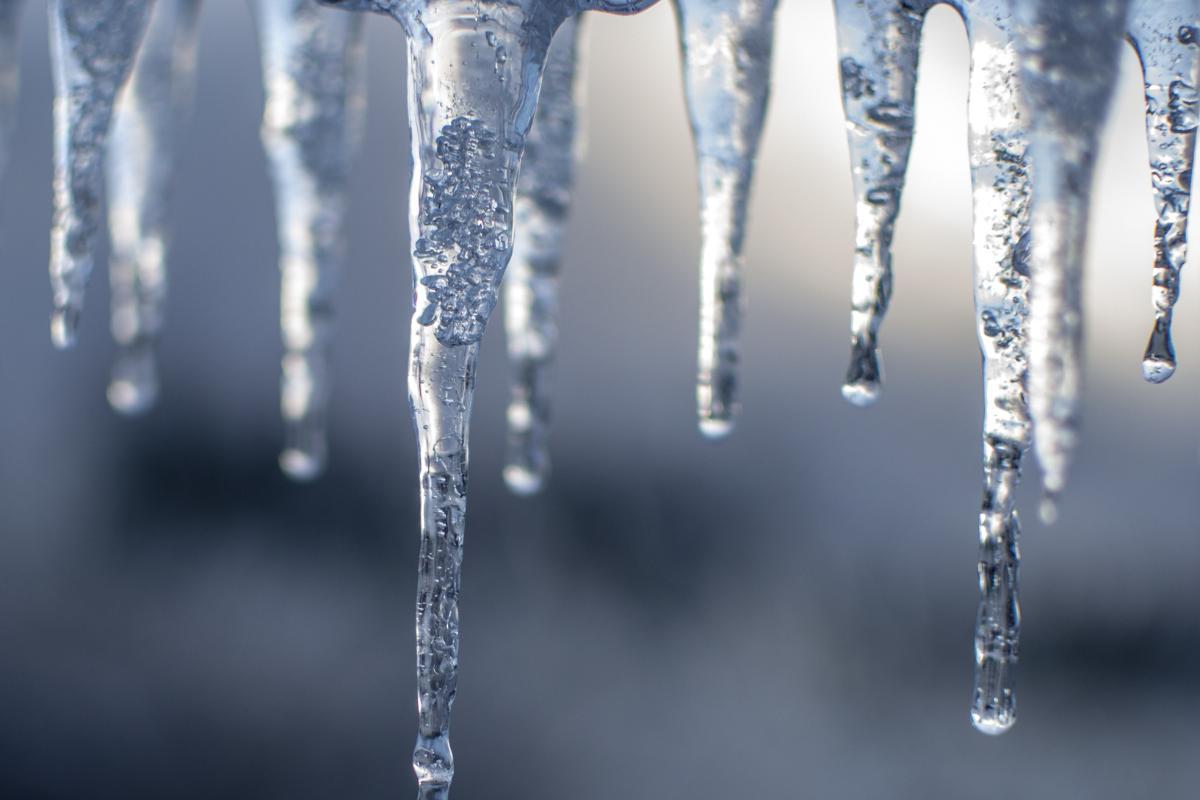
Icicles are ice formations that develop on the ends of objects exposed to cold temperatures during winter. This phenomenon is commonly observed in places where moisture in the air condenses and freezes on cold surfaces. The word ‘icicle’ comes from the French carambole, which means ‘fall’ or ‘crash’, alluding to the hanging types of icicles which often fall from their anchor positions.
Not all icicles are the same and they can vary in structure. Length is one of the most obvious differences between one icicle and another. They have a wider base than tip due to the gradual freezing process we explain in detail below. This phenomenon is more common in areas with cold and wet winters. This is because temperature fluctuations allow the melting and freezing process to repeat.
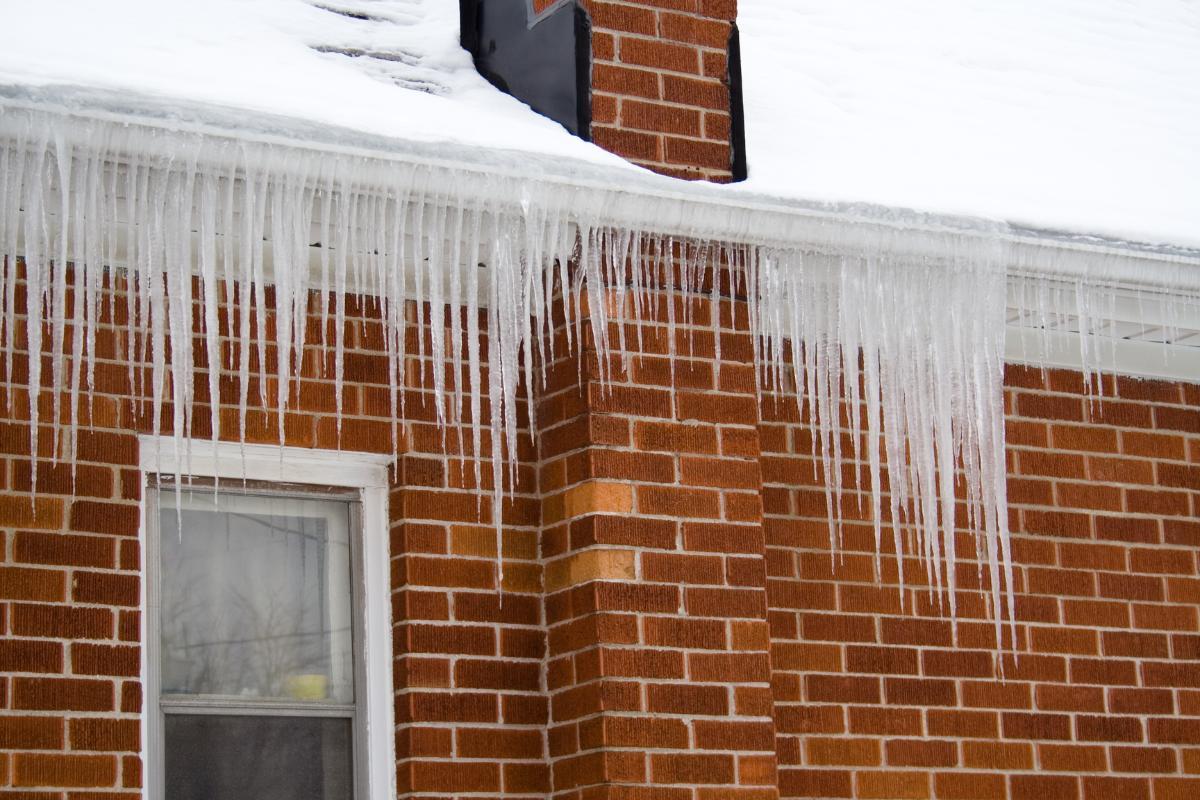
In addition to their attractive visual appearance, icicles can also pose a potential hazard. Their pointy nature makes them sharp objects that can fall and cause damage or injury. For this reason, it is important to use caution when walking under structures with icicles, especially during and after snowfall. The larger the icicle the more danger they pose.
Learn more about freezing water phenomena with our article on what is sea ice and how is it formed?
How icicles are formed
Icicle formation is a process that involves a combination of climatic and physical factors. To better understand how they form, it is useful to observe the cycle of melting and freezing that occurs on surfaces exposed to winter cold.
The formation of icicles generally follows this process:
- The heat emitted by an object melts accumulated snow.
- This meltwater drips and slides to the edges, where the temperature is lower.
- As the water drips and meets cold air, it gradually freezes.
- Icicles are the frozen meltwater structures of different sizes and shapes.
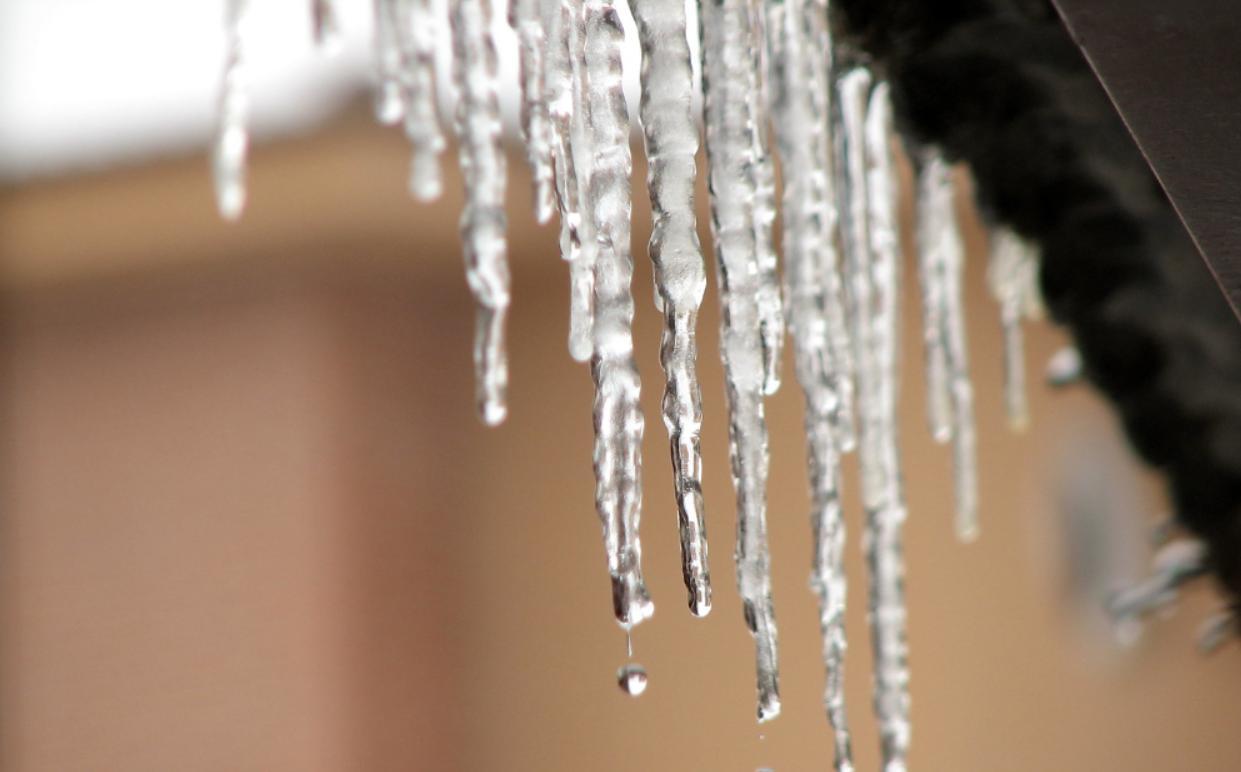
In this way, the icicle formation begins with accumulation of snow on a surface, such as a roof, a tree branch or any object exposed to the cold environment. When the temperature rises slightly, either due to the heat emitted by the object or due to weather conditions, the accumulated snow begins to melt.
The water resulting from melting (known as meltwater) moves towards the edges of the object. Upon reaching areas where the temperature is lower, it encounters the cold outside air. At this point, the meltwater freezes again, forming a layer of ice. As the process repeats itself with successive melting and freezing, the icicles begin to take shape.
The characteristic shape of icicles is of a sharp tip and a wider base. This is due to the gradual freezing and melting of water. The water drips from the end of the icicle where it meets the cold air and freezes into a point. The wider bases is due to the closer proximity to the source of the meltwater.
The length and size of icicles can vary depending on several factors. These include the following:
- Duration of cold temperatures
- Amount of snow accumulation
- Rate of melting and freezing
In environments with more pronounced temperature fluctuations, icicles are likely to be larger and more striking in appearance.

How do sideway icicles form?
When water droplets are present and freeze on a surface, the direction of freezing is influenced by the movement of the water. In the case of sideways icicles, the water source is typically dripping or flowing in a horizontal direction.
This sideways direction is often due to factors like wind, air currents or the angle of the surface on which the icicles are forming. Gravity still plays a role in the downward growth of the water droplets that freeze to create the icicles, but external forces can influence their final orientation.
The freezing process is influenced by the direction of the water movement and the ambient temperature. As water droplets freeze, they adhere to the existing ice in a manner that aligns with the flow of the water. If the water is moving horizontally due to wind, the freezing process follows suit. This results in the formation of icicles that project sideways rather than hanging vertically.
The unique combination of water flow, temperature and freezing dynamics creates the intriguing phenomenon of sideways icicles, adding an extra dimension to the beauty of ice formations.
How do upward icicles form?
The simple answer is that there are no upward icicles. What might appear to be an upward icicle is actually something known as an ‘ice spike’.
An ice spike is a vertical column of ice that can sometimes form in containers of freezing water, especially in the presence of impurities. It occurs when water freezes from the outside in, trapping liquid water in the center. As this inner liquid water expands while freezing, it can force ice to extrude upward, creating a spike-like structure.
While the term ‘ice spike’ doesn't refer to a naturally occurring phenomenon like icicles, it does involve an upward protrusion of ice. In this case, it's a unique occurrence in specific conditions and settings, such as within ice cube trays or other containers. The formation of ice spikes is not governed by the same processes as the icicles that form naturally on surfaces.
Types of icicles
Shape and size are not the only variables in icicles when they are forming. Other characteristics can be used to group icicles into different types, often due to changes in environmental conditions. These include the following:
- Clear icicles: formed when water drips down and freezes quickly, resulting in a transparent appearance.
- Rimed icicles: created when supercooled water droplets freeze upon contact, producing a cloudy or opaque appearance.
- Hollow icicles: formed when liquid water flows through a partially formed icicle, leaving a hollow core.
- Brachiating icicles: develop when icicles branch out due to changes in wind direction or varying water flow.
- Dripless icicles: occur when there's a consistent water source and a steady freezing rate, minimizing the dripping effect.
- Chandelier icicles: characterized by multiple prongs or spikes extending from a central point, resembling a chandelier.
These variations arise from the interplay of temperature, humidity and wind conditions during the freezing process. These contribute to the diverse shapes and structures of icicles.

Dangers of icicles
Although icicles may look beautiful and picturesque, they also carry certain dangers that must be taken into account, especially in winter environments. Here are some of the risks associated with icicles:
- Falls and injuries: since icicles often form on the eaves of roofs, around structures or on tree branches, there is a risk of them breaking off and falling. These sharp objects can pose a threat to people walking under them. A fall from a large or sharp icicle can cause serious injury.
- Property damage: falling icicles can also result in property damage, especially if they fall on vehicles, windows or other structures. The accumulation of icicles on roofs can generate additional weight. In extreme cases, this could contribute to excessive loading and partial or complete collapse of the structure on which they form.
- Clogged drains: when icicles form on the eaves of buildings, they can clog drains and gutters. This can lead to drainage problems, water pooling and ultimately damage to the building structure.
- Road hazard: in areas with heavy snowfall, icicles may form on the edges of bridges and elevated structures. If they become detached, they could fall onto roads and pose a risk to road safety.
- Impact on utilities: excessive accumulation of icicles on power lines and poles can have consequences for public services. The additional ice load could affect power lines and cause power outages.
Now you know all about how icicles are formed and the many different types, you can learn about other freezing weather phenomena with our article on what are the different types of avalanches?
If you want to read similar articles to How Do Icicles Form? - Icicle Formation, we recommend you visit our Facts about nature category.