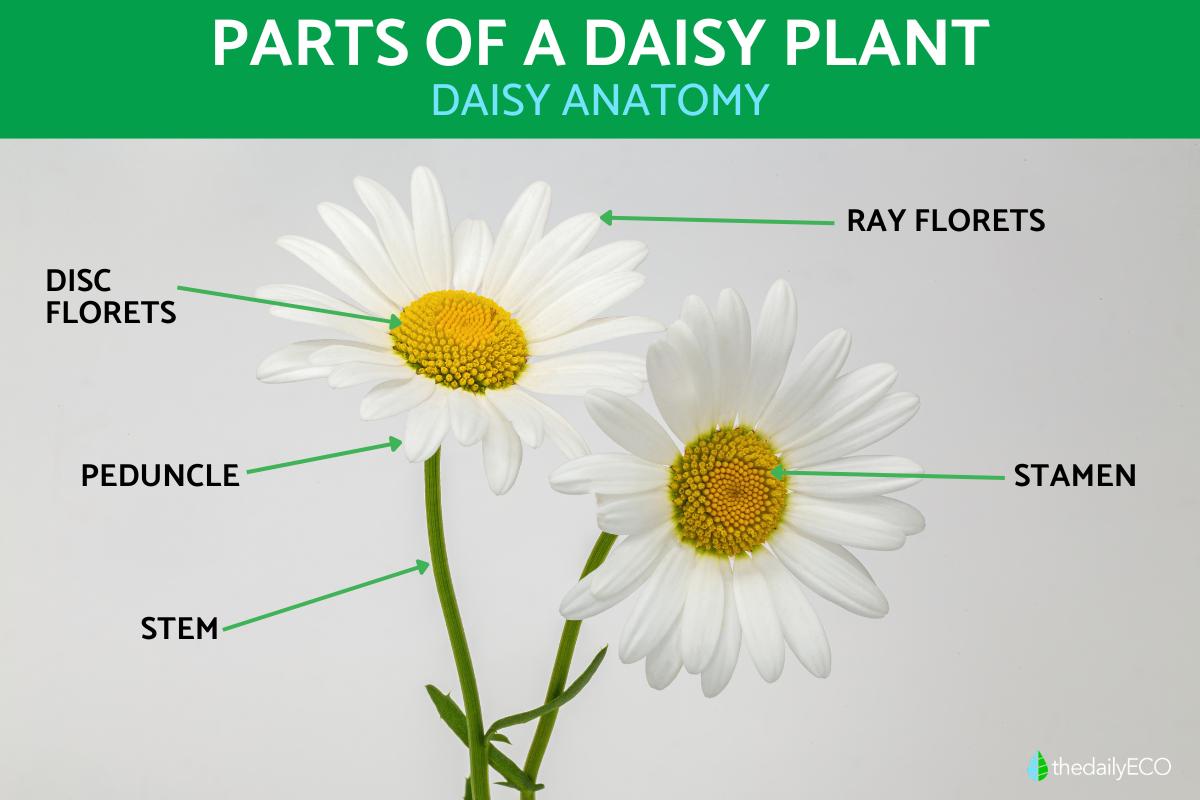
Parts of a Daisy Plant

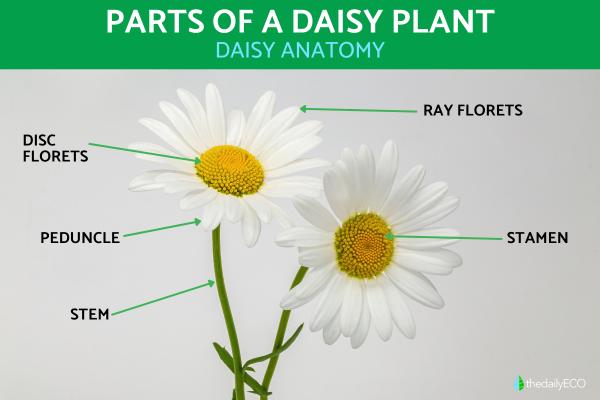
The daisy (Bellis perennis) is a herbaceous flowering plant of the Asteraceae family in the order Asterales. While it is often tolerated in lawns for its lovely white petals around a yellow cluster of stamens, the daisy is considered a weed. This means it often grows where it is not wanted and can use the resources which would otherwise go to other plants. Other people have cultivated them into colorful hybrids, some with very large inflorescences compared to others. Despite variations in cultivars, they all have the same basic daisy anatomy. thedailyECO looks at this anatomy in more detail by sharing the parts of a daisy plant with diagrams.
Inflorescence
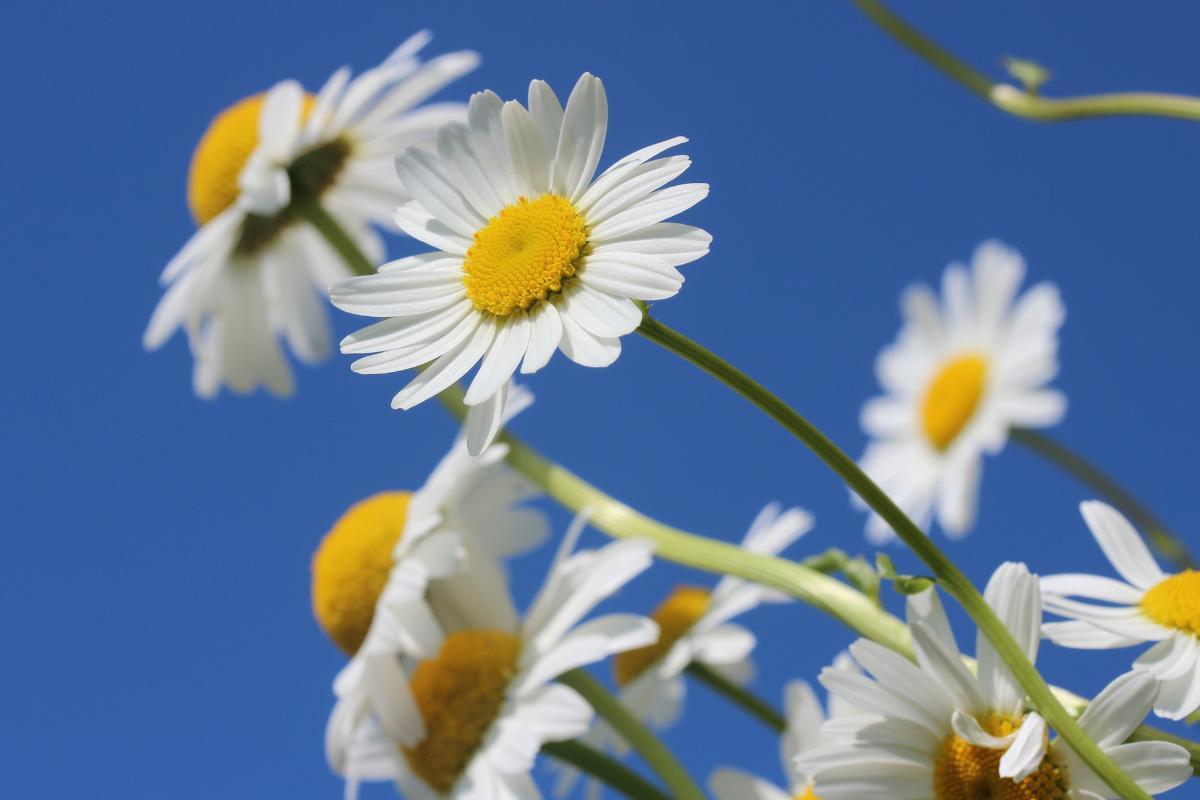
The inflorescence of a plant refers to the part which contains the clusters of flowers. While it may appear to be one single flower, the inflorescence of the daisy is actually a cluster of many individual small flowers. These flowers are known as florets and the daisy has two main types:
- Ray florets: the white petals which are spread around the outside of the inflorescence and form the daisy's characteristic appearance.
- Disc florets: the small yellow flowers which are arranged in a dense cluster in the center.
The combined inflorescence of the daisy is known as a flowerhead. This flowerhead consists of a central disc surrounded by ligule-shaped florets, forming a composite flower. This arrangement maximizes the daisy's visibility, making it easily recognizable and attractive to pollinators.
Learn more about how flower inflorescence can differ with our article asking what are monoecious plants?

Florets
Florets are the individual flowersthat make up the head of the daisy. They can be divided into two types which we have explained above. These are the short disc florets which are yellow and found in the center of the flowerhead, as well as the ay florets which are white and found on the outer edges. This diversity in flower types within the daisy contributes to its reproductive success. Each type plays a specific role in attracting pollinators and producing seeds.

Stamens
The stamens are the male parts of disc flowers that form the core of the flower head. Their main function is to generate pollen. These are the male reproductive gamete cells necessary for fertilization. Pollen is transported by external agents, such as insects or the wind. These facilitate the reproduction process. Without these stamens, the daisy's ability to reproduce effectively would be jeopardized.
You can discover more about the importance of these parts of a daisy plant with our article asking what are the stamens of a flower?

Carpels
Carpels are the female sexual organs of daisies and are also found in the disc flowers. They can be single or multiple ovules. They are located near the stamens, facilitating fertilization due to their proximity. This proximity between the stamens and carpels increases the chances of successful reproduction, as external agents can transfer pollen directly to the ovaries of the carpels.
For example, a bee can land on a daisy flowerhead and pick up pollen from the stamens. If they then do the exact same thing to another daisy, the closeness of the carpels means they will receive pollen more easily.
Ovary
The ovary is located within the carpels, just below the upper disc structures of the flowers. Its function is crucial as it is where the seeds develop after fertilization. Once fertilized, the ovaries begin to produce seeds. In some daisies, the seeds can be so small they are almost invisible. A daisy's ability to produce a large number of seeds is a key factor in its success as a species.
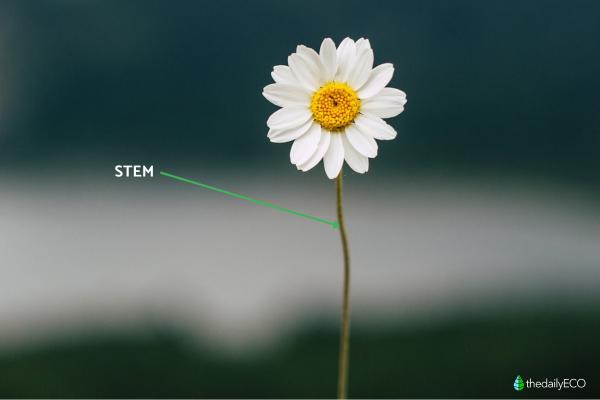
Stem
The daisy stem acts as the plant's structural support, connecting the roots to the leaves and flowers. Typically thin and green, the height of a daisy stem can vary depending on the species. This stem not only supports the plant, but is also responsible for transporting water, nutrients and sugars throughout the plant. This process is vital to maintaining the health of all parts of the daisy, ensuring that each component receives what it needs to grow and flourish.
An important part of the daisy plant, you can learn more about the general importance of plant stem parts and their roles.

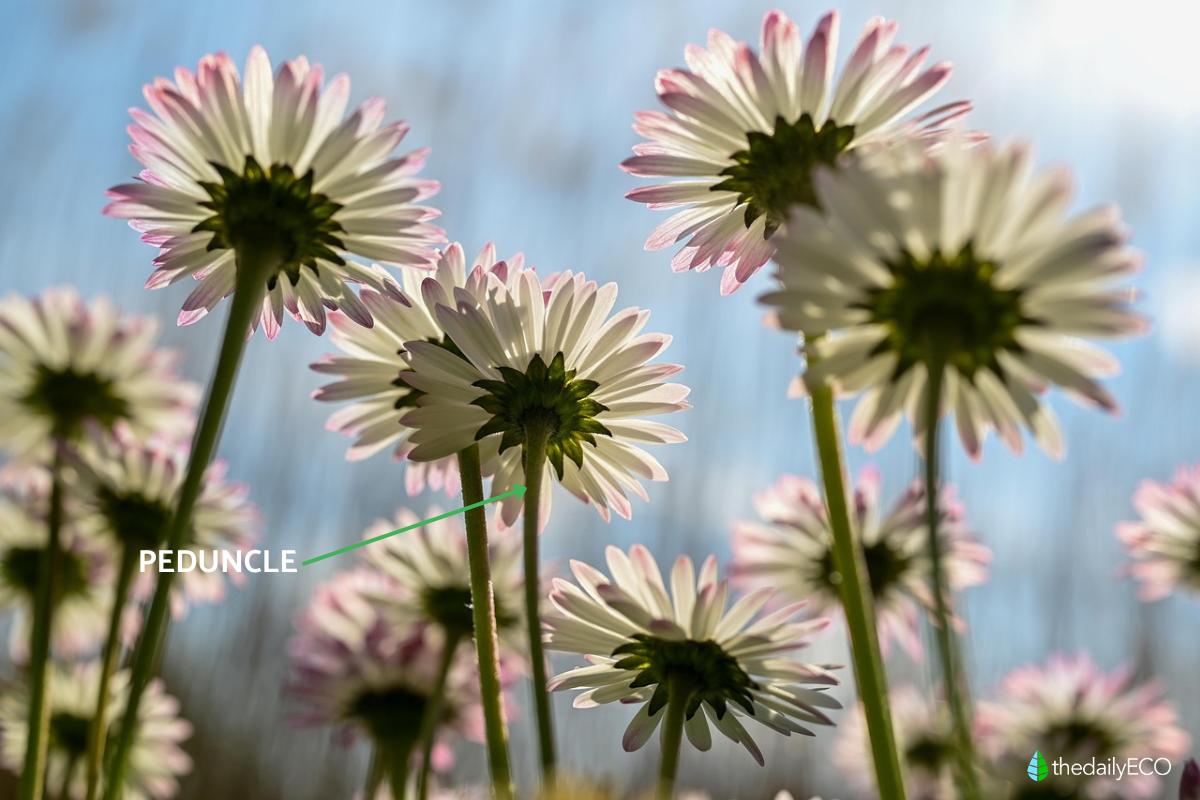
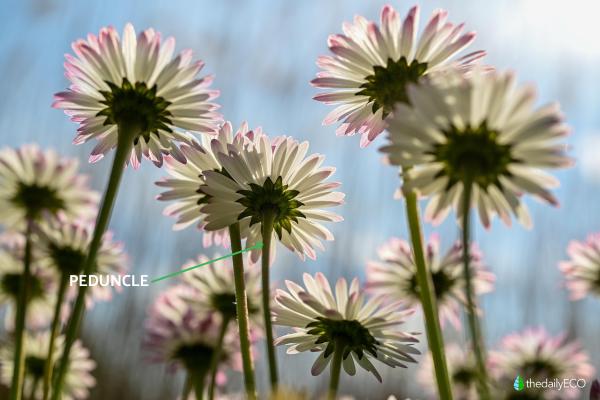
Peduncle
The peduncle is located at the end of the stem and provides a solid base that supports the different components of the daisy. In some varieties, the peduncle may feature green petal-like structures, which originally formed the main flower bud. This structure is not only functional, but also contributes to the overall aesthetics of the plant.

Roots
We finish explaining the parts of a daisy plant with the roots. A daisy's life begins underground with its root system. Roots are fibrous and formed by thin branches that extend horizontally. This system not only anchors the plant to the soil but is also essential for water and nutrient absorption. The health of the root system directly affects the daisy's vitality. Proper nutrient absorption is crucial for its growth and development. Furthermore, these roots allow the plant to adapt to different soil types and environmental conditions, facilitating its propagation.
You can learn more about the parts of roots and their functions in our related guide.

Facts about daisies
We have provided the important parts of the daisy plant, but you can know more with these daisy facts:
- The daisy belongs to the Asteraceae family, known for its diversity of species. This family also contains popular flowers such as dahlias, sunflowers, lettuce and artichokes.
- It is a perennial herbaceous plant with obovate-spatulate leaves and hemi-ligulate flowers that can be white or slightly purple. This purple or reddish color appears more commonly when young.
- Daisies bloom from October to June, being visited by different types of pollinators such as bees and flies.
- These flowers reproduce through achenes that are dispersed by wind, rain and animals, as well as vegetatively.
- It can thrive at altitudes up to 2,451 meters above sea level and withstand temperatures as low as 5 ºF (-15ºC).
- It is used in traditional medicine for its proposed antitussive, diuretic and healing properties, although little scientific evidence supports its efficacy.
- The leaves and flowers are edible, with a flavor that varies from sweet to slightly bitter.
- It is popular in landscaping, often mixed with grass, and can be invasive in some regions.
In addition to daisies, you can discover the best white flower plants for the garden with our helpful guide.
If you want to read similar articles to Parts of a Daisy Plant, we recommend you visit our Facts about nature category.
- Association of Botanical Artists. (2020). The three B's - Complex Flowers. https://www.assocbotanicalartists.com/post/the-three-bs-complex-flowers