What Is the Cause of the Coriolis Effect?


The Coriolis effect is a physical phenomenon that occurs when an object moves in a rotating reference frame. The Earth is probably the most prime example of such a rotating system. Although it may seem complicated, we can understand the Coriolis effect in a simple way. Imagine that you are on a merry-go-round that is spinning very fast. If you throw a ball towards the center of the merry-go-round, from your point of view, the ball will follow a straight trajectory. However, from the point of view of someone outside the merry-go-round, they will see the ball curve due to the spinning motion of the merry-go-round. Essentially, this is the definition of the Coriolis effect.
In this thedailyECO article, we ask what is the cause of the Coriolis effect? We answer this question by looking at a more detailed definition with examples of the Coriolis effect in action.
What is the Coriolis effect?
The Coriolis effect is a consequence of the conservation of angular momentum in a rotating system. When an object moves in a rotating reference frame, it experiences a fictitious force called the Coriolis force. This force acts perpendicular to its velocity. This force causes the object's trajectory to deviate, appearing to follow a curve.
The Coriolis force is a fictious force because there is no actual force on the object. Instead, it is the movement of the rotating frame of reference which creates the movement. When we are on the Earth's surface, it can appear as if inert objects in the air are moving when it is ourselves that are moving.
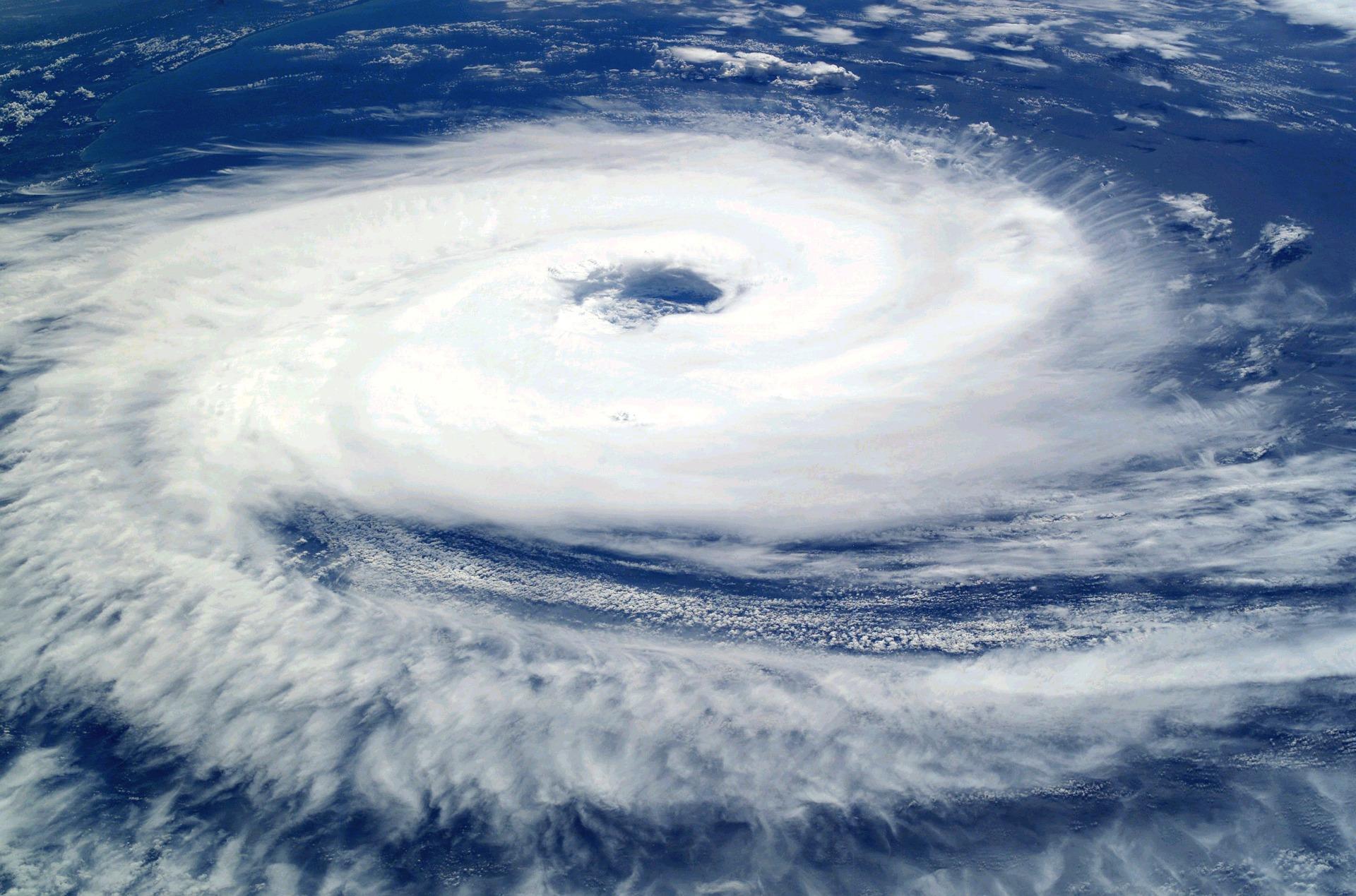
The Coriolis effect has implications in different natural phenomena. For example, on Earth, the Coriolis effect influences the direction of winds and ocean currents. In the northern hemisphere, moving objects are deflected to the right, while in the southern hemisphere they are deflected to the left. They also move faster at different distances from the poles with the fasting movement occurring at the equator.
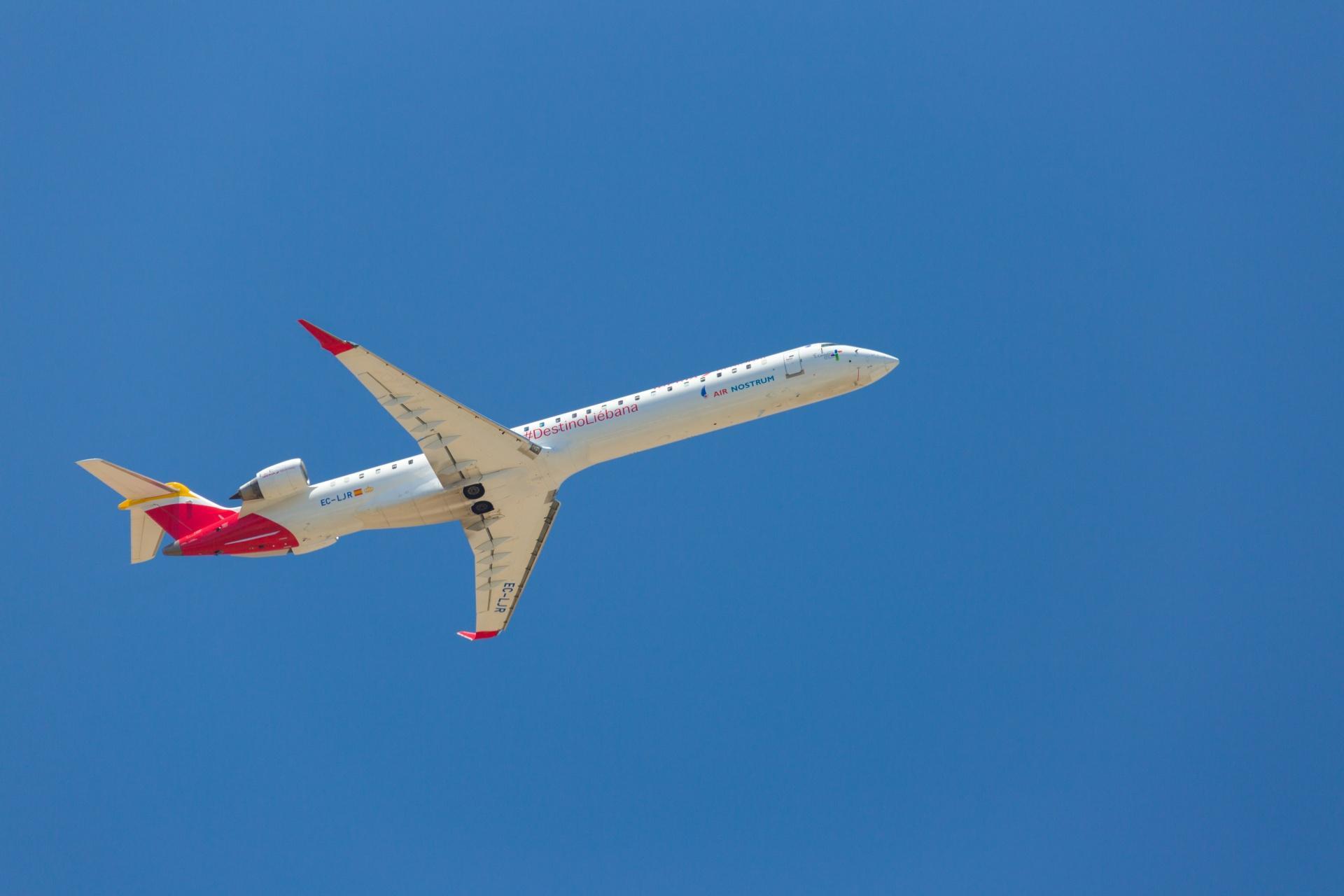
This effect is also responsible for another phenomenon known as the gyroscope. This is an instrument used in airplanes, ships and other navigational devices to maintain their stability and orientation through air and water.

What causes the Coriolis effect?
This phenomenon has its origin in the rotation of the Earth and its influence on moving objects. Imagine that we are on the earth's surface and observing the movement of an object aove the surface in a straight line. From our perspective, the object would appear to move in a straight line without any deviation. From the point of view of an observer located in outer space, the distance would mean they can observe a deviation in the object's trajectory.
This deviation means the Coriolis effect is caused by the rotation of the Earth. As we move poleward from the equator, the linear velocity of a point on the Earth's surface decreases. This means that, an object at a certain point is moving faster than the area around it and vice versa.
The Coriolis effect manifests itself as a fictitious force that acts perpendicular to the speed of an object moving in a rotating reference frame, such as the Earth. In the northern hemisphere, this force skews motion to the right, while in the southern hemisphere, it skews motion to the left.
It is important to note that the Coriolis effect is only observable in objects that move great distances or significant speeds. For example, we would not notice this effect if we threw a ball from one end of the garden to the other.

If you want to read similar articles to What Is the Cause of the Coriolis Effect?, we recommend you visit our Facts about nature category.