What Is the Thermosphere and Its Function?


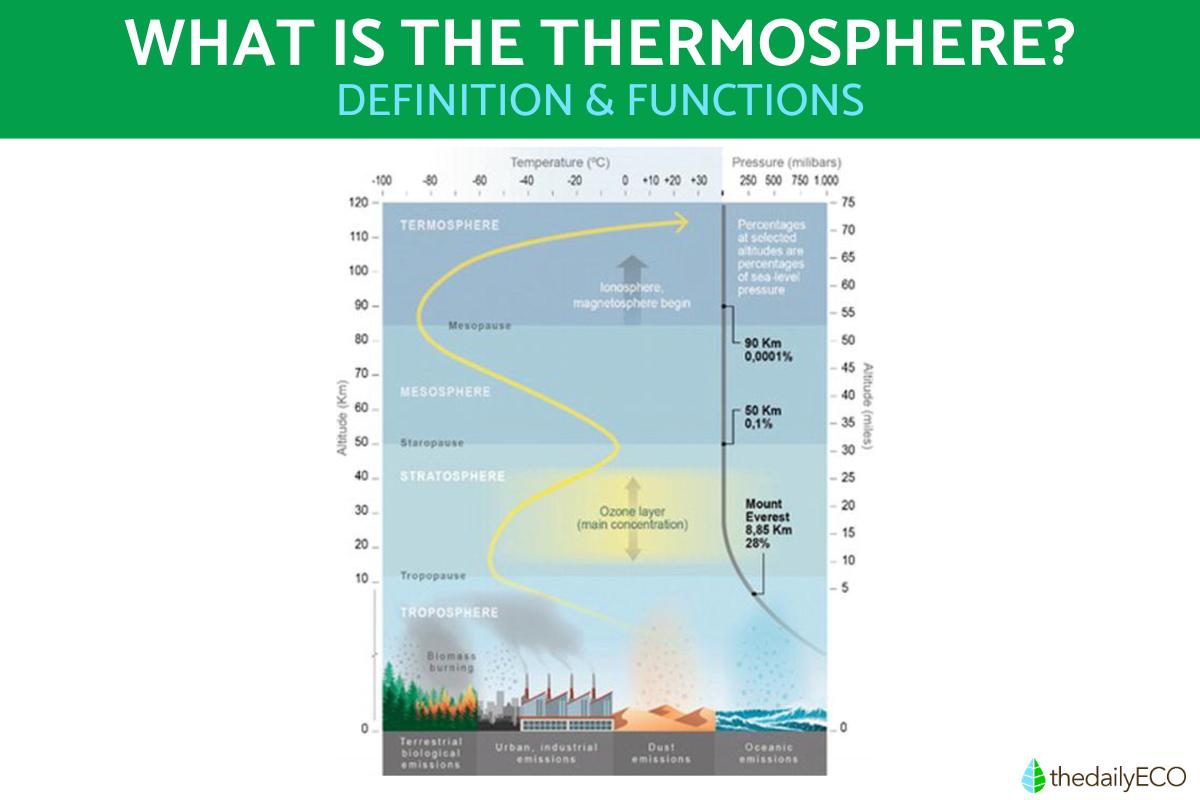
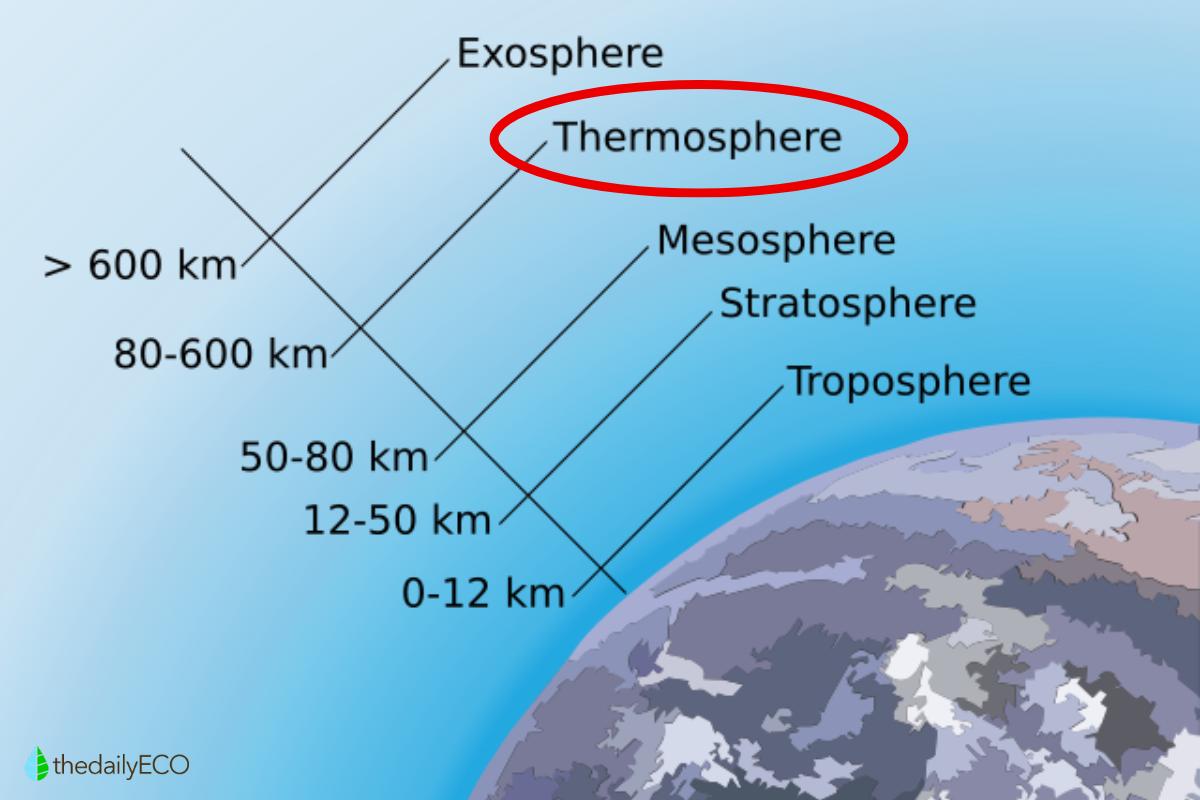
The thermosphere is one of the upper layers of the Earth's atmosphere, located between the mesosphere and the exosphere. It begins approximately 50 mi (80 km) above sea level and extends to around 435 mi (700 km). It has some key functions which allow human life on Earth to continue, such as protection against harmful solar radiation. In this article from thedailyECO, we ask what is the thermosphere and its function? In answering this question, we find out key characteristics such as the temperature of the thermosphere, as well as its composition and other important facts.
What is the thermosphere?
The thermosphere is one of the outermost layers of the Earth's atmosphere, located between the mesosphere and the exosphere. It extends from approximately 50 to 435 mi (80 km to 700 km) above sea level, although these altitudes can vary depending on factors such as solar activity.
The main characteristic of the thermosphere is the increase in temperature as altitude increases. In some parts of the thermosphere, it can reach temperatures of up to 4,500 ºF (2,500ºC) or more. This is due to the absorption of ultraviolet solar radiation and X-rays.
The composition of the thermosphere mainly includes molecular oxygen (O₂), nitrogen (N₂) and oxygen atoms (O). As you go higher, the atoms and molecules tend to become more and more dispersed due to the low density of the air in this region. Important phenomena such as the aforementioned ionization occur in the thermosphere. This is the process by which atoms and molecules become ions when receiving intense solar radiation. This generates the ionosphere which encompasses parts of the thermosphere. It is crucial for the transmission of radio waves and the formation of auroras.
It is also in the thermosphere layer that many satellites orbit. This is because air resistance is low enough to allow their trajectories. Despite the high temperatures, the heat would not affect a human in the thermosphere since the air density is so low that there are not enough particles to transfer heat to any significant degree.
Find out what is the mesosphere in our related guide.

Characteristics of the thermosphere
The thermosphere is distinguished by several notable features that differentiate it from other layers of the Earth's atmosphere. Among the main characteristics of the thermosphere are the following:
- Temperature increase with altitude: unlike layers closer to the surface such as the troposphere, temperature increases considerably with altitude in the thermosphere. This increase is due to the fact that oxygen and nitrogen molecules directly absorb ultraviolet radiation and X-rays from the sun.
- Extremely low air density: the thermosphere is one of the thinnest layers of the atmosphere in terms of particle density. As altitude increases, the density decreases rapidly to the point where molecules are very dispersed.
- Ionosphere and radio wave transmission: the ionosphere overlaps with the thermosphere. This is where solar radiation causes ionization of particles, meaning it converts atoms and molecules into electrically charged ions.
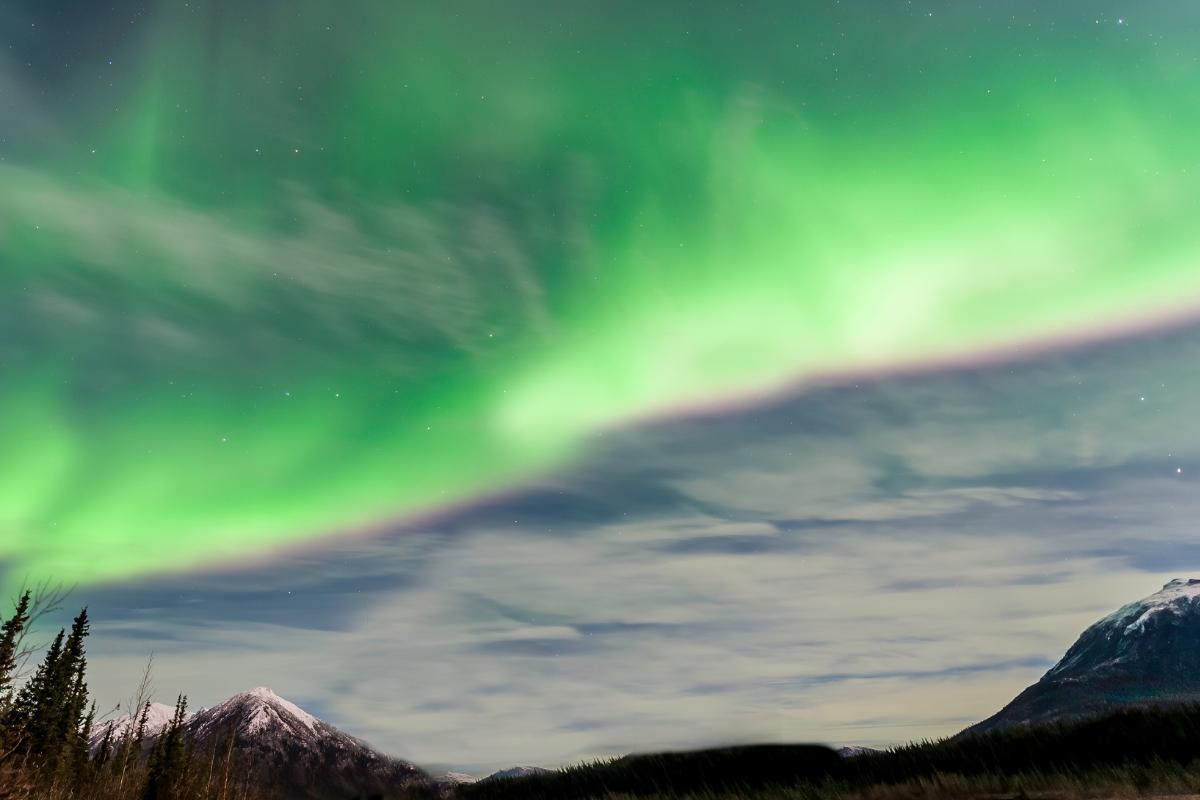
- Northern lights and southern lights: the northern lights and southern lights are phenomena that occur in the thermosphere due to the interaction between charged particles in the solar wind and gases in the atmosphere.
Learn more about how to southern lights form with our article explaining what are the Aurora Australis?

What is the temperature of the thermosphere?
The temperature in the thermosphere can vary widely, generally reaching values between 930 to 4,500 ºF (500 to 2,500ºC). In certain cases of high solar activity, it can exceed this figure. This is unlike the layers of the atmosphere closer to the surface of the Earth where the temperature is more stable. In the thermosphere this parameter depends on several factors, mainly on the activity of the sun.
Learn about the different gases and elements which can be found in the thermosphere with our article on the composition of the atmosphere.
What is the function of the thermosphere?
The thermosphere performs essential functions in protecting the Earth and sustaining certain processes that are fundamental to life. It is also very important for many of our technological systems. With this in mind, the main functions of the thermosphere are the following:
- Protection from harmful solar radiation: one of the most important functions of the thermosphere is to absorb much of the ultraviolet (UV) radiation and X-rays coming from the sun.
- Formation of the ionosphere and propagation of radio waves: the thermosphere includes much of the ionosphere, a subregion rich in electrically charged particles (ions). These are formed when the atoms and molecules of this layer interact with intense solar radiation. This ionization is essential for the propagation of radio waves and other types of telecommunications signals.
- Support for satellite orbits and the International Space Station (ISS): the thermosphere is the layer in which most communication satellites and the International Space Station (ISS) orbit, typically at altitudes between 185-250 mi (300-400 km).
- Aurora generation: the northern and southern lights occur mainly in the polar regions and form in the thermosphere. They occur when charged particles from the solar wind are attracted by the Earth's magnetic field and collide with gases in the thermosphere, such as oxygen and nitrogen.
- Regulation of thermal energy and atmospheric expansion: the thermosphere also has a role in regulating the thermal energy of the atmosphere.
Without layers of the atmosphere such as the thermosphere, our life on Earth would be completely different. Learn about some ways this can manifest with our article explaining what is the albedo effect on climate?

Why is the thermosphere important?
The thermosphere is essential for life on Earth, as well as for the functioning of modern technologies that we use in everyday life. Let's see what are the key aspects of its importance:
- Protective shield against solar radiation: the thermosphere absorbs a large amount of ultraviolet (UV) radiation and X-rays from the sun, functioning as a natural shield.
- Critical for telecommunications and navigation: the ionosphere is crucial for the transmission of AM radio signals and for long-distance communication, as well as for the functionality of navigation systems such as GPS. Thanks to the ionosphere in the thermosphere, communication devices can maintain reliable connections, allowing a constant flow of information around the world.
- Satellite and space infrastructure support: satellites in the thermosphere enable climate monitoring, prediction of extreme weather events, data transmission and telecommunications. It also allows for observation of the planet for a variety of scientific and security purposes.
- Facilitating the aurora phenomenon: auroras help to study the dynamics between the solar wind, the magnetic field and the Earth's atmosphere, allowing scientists to better understand how solar activity affects our planet.
- Regulation of thermal energy in the atmosphere: during periods of high solar activity, such as solar storms, the thermosphere acts as a ‘valve’ that dissipates the excess energy received by the atmosphere. By heating and expanding, it helps to distribute and dissipate part of this energy, limiting possible alterations in the lower layers of the atmosphere.
Now you know what is the thermosphere, discover all you need to know about another level of the atmosphere with our article asking what is the troposphere?
If you want to read similar articles to What Is the Thermosphere and Its Function?, we recommend you visit our Facts about Earth and the universe category.
- UCAR Center for Science Education. The Thermosphere.
https://scied.ucar.edu/learning-zone/atmosphere/thermosphere - Luciana Paz. (2021). The Atmosphere and its layers: What is the Thermosphere and what are its characteristics? El Popular.
https://elpopular.pe/educacion/2021/09/16/geografia-es- thermosphere-ionosphere-what-are-its-characteristics-earth-84256