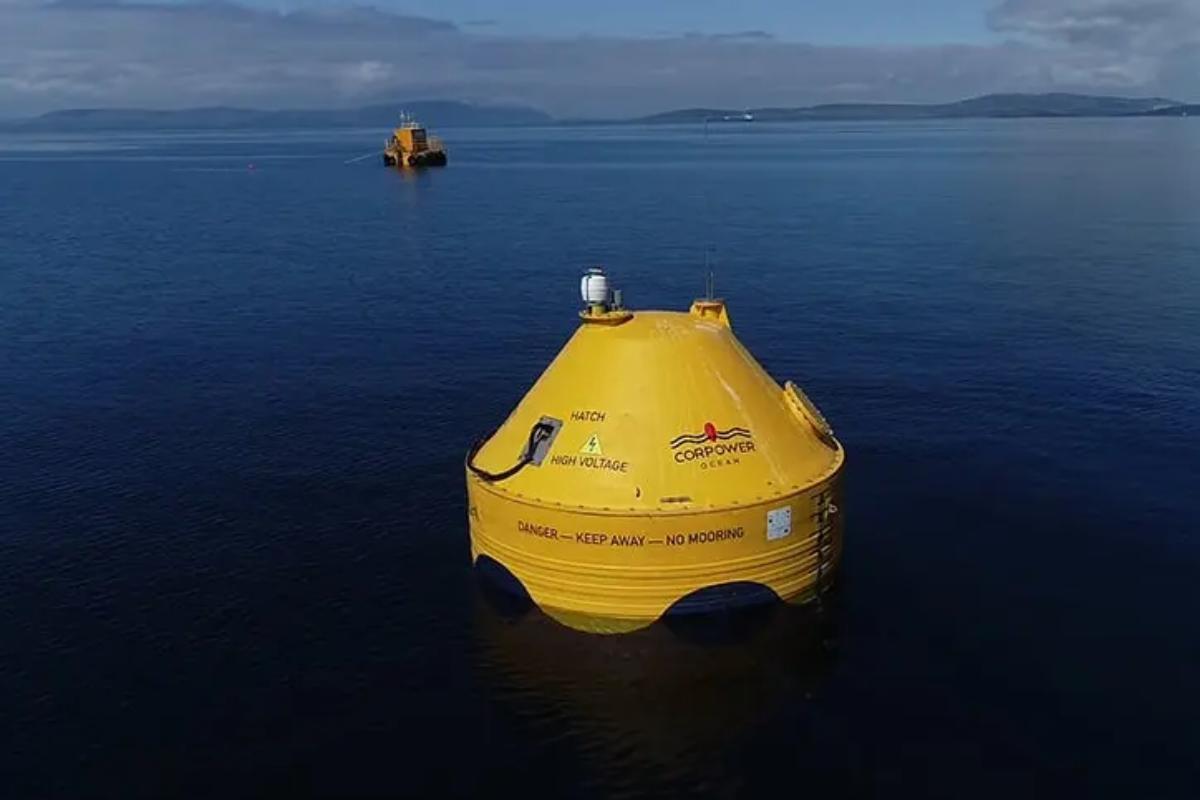
What Is Wave Power Energy?


Renewable energy sources are forms of energy which can be replaced naturally within a reasonable period of time for human use. Sources of such renewable natural energy include the sun, wind and water. This latter category is known as hydropower, harnessing the energy of various water currents to produce renewable energy. Among the types of hydropower, wave power energy stands out for its ability to harness natural wave movements as an energy source. Powered by wind, generators harness the energy of waves through various energy converters. These can be located both in the open sea or in more coastal areas.
At thedailyECO, we ask what is wave power energy? In answering this question, we examine the types of wave power and how they can be converted for electrical use. We also discuss the advantages and disadvantages of wave power to see how it compares to other renewable energy sources.
What is wave power energy?
Wave energy is a form of renewable energy derived from the motion of waves in the ocean. This energy is harnessed through technologies that capture the kinetic and potential energy generated by the movement and height of waves, converting it into electricity. Unlike other renewable energy sources, waves are constant and predictable, allowing for more stable power generation.
There is a distinction made between wave power and tidal power. Generally speaking, wave power is a result of the wind's action on the surface of a body of water. Tidal power is a result of the gravitational pull of Earth. However, gravity also influences wave currents, as do other factors such as temperature and salinity. While they are considered two distinct types of hydropower, tidal and wave power have overlap in how they generate energy.
Learn more about how we produce the world's energy resources with our article asking what are renewable and non-renewable energies?

How is wave energy produced?
The ability to derive power from wave energy is based on the conversion of wave motion into electricity. This requires systems that transform the mechanical energy of water into electrical energy. There are several technologies that allow us to harness this type of wave energy. These are the most common:
- Floating buoys: the movement of the buoys activates a system of pistons or generators located inside the buoy or on the seabed, the action of which converts the energy of the movement into electricity.
- Oscillating water columns: when a wave arrives, it raises the water level inside the chamber and compresses the air inside. This passes through a turbine that converts the energy of the air flow into electricity. When the wave recedes, the air is sucked back in, maintaining the flow and converting more energy.
- Termination devices: this type of technology uses fixed structures that intercept waves to create a pressure that moves a piston or a system of plungers, thereby generating electrical energy.
- Floating wave devices: systems of several connected sections that float on water. As they move with the waves, they generate energy through a system of hinges and pistons.
In addition to these types of natural energy sources, learn more about other methods of how electricity is made.
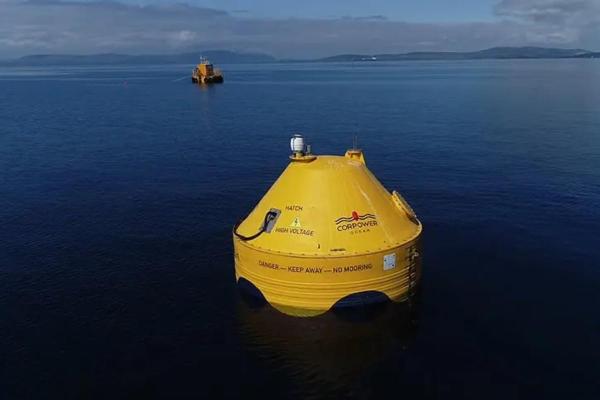

Types of wave power energy
Wave energy can be classified according to different criteria, generally based on the location of the system and the conversion technology which is used. This means we can categorize wave power energy into the following two main types:
- Onshore wave energy: onshore systems are located on or near the coastline. As they are more accessible, they are often easier to install and maintain. However, they are more exposed to changes in the coastal environment, such as storms or erosion. They may also have more potential impacts on the nearby ecosystem. Oscillating water column (OWC) devices are often used in this location.
- Offshore wave energy: offshore systems are placed away from the coastline where waves tend to be more constant and stronger. Being farther from shore, they can take better advantage of the movement of the water without interfering with the coastal landscape. Installation and maintenance are more expensive. Offshore systems include floating buoys which can be anchored to the seabed or float on the surface.
Examples of wave power energy
There are projects around the world that exemplify the different approaches and technologies of wave power energy. Some notable examples include:
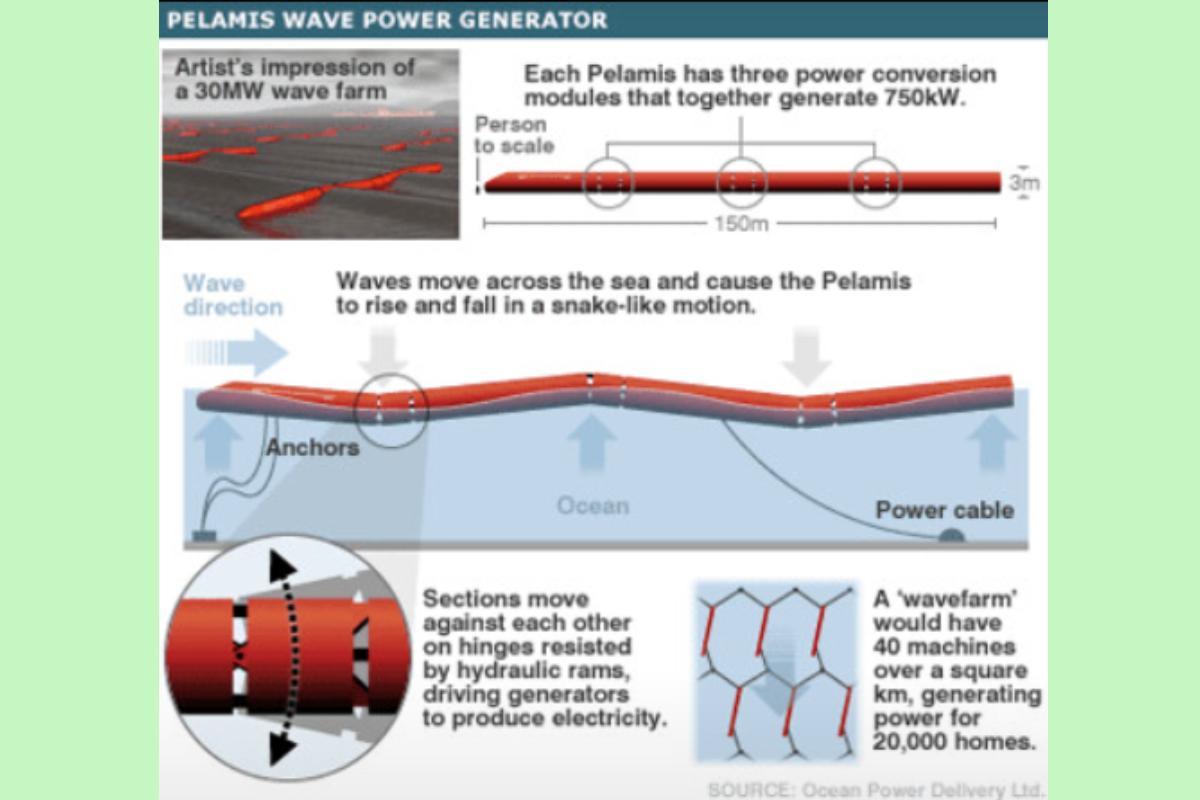
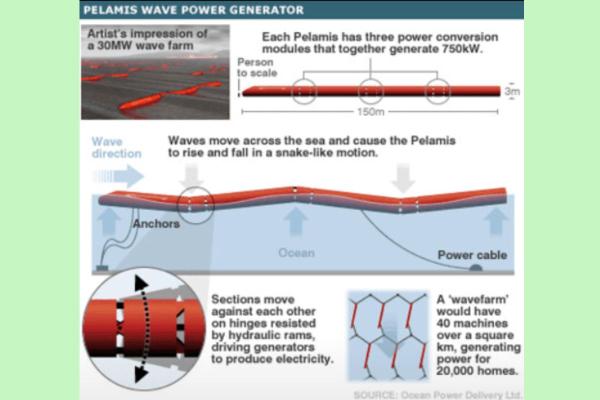
Pelamis Wave Power (Scotland)
The Pelamis system is made up of several connected segments that resemble a floating snake. As they move with the waves, the segments flex and compress hydraulic generators located at the joints, generating electricity. It is no longer in use and has been decommissioned.
Wave Hub (UK)
The Wave Hub is a project in Cornwall, UK that acts as an underwater connection platform for testing various wave energy technologies. This infrastructure allows multiple devices from different companies to connect at the same time to generate electricity and share it with the British electricity grid. While it was previously developed for wave power, it is now being developed for offshore wind energy.
Mutriku Breakwater Wave Power Plant (Spain)
The Mutriku breakwater wave power plant in the Spanish Basque Country is one of the first commercial wave energy facilities in Europe. It uses oscillating water column (OWC) technology, which takes advantage of air chambers located in the harbor breakwater. As waves rise and fall, the air in the chambers is compressed and passed through turbines that generate electricity.
Advantages and disadvantages of wave power energy
Despite being a natural energy resource and utilizing the vast amount of energy contained within the world's oceans, wave power energy is not very widely implemented. To understand why this is the case, we need to look at the advantages and disadvantages of wave power energy:
Advantages of wave power energy
- Renewable and clean source of energy: it is a clean source of energy that does not produce greenhouse gas emissions or many pollutants during the generation of electricity.
- Takes advantage of a constant and predictable resource: waves are generally more constant and predictable than wind or sunlight, as they depend on global atmospheric phenomena that act on the oceans on a regular basis.
- High energy density: waves contain a greater amount of energy per area than other renewable sources, such as wind.
- Reduces dependence on fossil fuels: by offering a renewable alternative, wave energy helps reduce the use of fossil fuels and contributes to the transition towards a more sustainable energy system.
- Minimal visual impact for submerged devices: unlike wind turbines or large solar panels, submerged wave energy devices such as floating buoys and panels on the seabed are less visible and have less of a visual impact on the coastal landscape.
Disadvantages of wave power energy
- High installation and maintenance costs: wave energy devices must withstand extreme marine conditions, such as corrosion, storms and the force of waves. This requires durable materials and designs, which significantly increases installation costs. In addition, maintenance in the marine environment is often complex and expensive.
- Environmental and marine life impact: although less invasive than other forms of energy, wave energy can negatively affect marine ecosystems.
- Interference with maritime activities: the presence of wave-powered devices can interfere with traditional maritime activities such as fishing, shipping and tourism.
- Limited to certain geographic areas: wave energy is only viable in areas with sufficient wave activity, such as coasts exposed to open oceans and seas with strong waves.
- Lack of development: this type of energy is still in the development stage and has not yet been implemented on a large scale in many parts of the world.
While this provides the pros and cons of wave power energy, our related guide on the advantages and disadvantages of hydropower provides a more general overview.
Differences between wave and tidal energy
We have already provided a brief overview of the differences between wave and tidal energy resources, but here we break them down in more detail:
- Both renewable energies take advantage of the movement of water, but they do so in different ways and depend on different phenomena. Wave power energy is based on the movement of waves caused by wind on the surface of the sea, tidal energy takes advantage of the gravitational movement of the tides.
- The availability of wave energy is relatively constant over time, but waves can vary in size and intensity depending on the weather and the season. Tidal energy is even more predictable because it depends on the regularity of tides.
- They also differ in the technology used to capture energy. Wave energy uses devices such as floating buoys, oscillating water columns and segmented platforms which convert the movement of the waves into mechanical or hydraulic energy. This is then transformed into electricity. Tidal energy harnesses the energy of the tides using tidal barrages and current turbines.
Now that you have learned about what is wave power energy, and its advantages and disadvantages, you may be interested in our article on the pros and cons of wind energy.
If you want to read similar articles to What Is Wave Power Energy?, we recommend you visit our Renewable energies category.
- Wave energy. (n.d.). Ocean Energy Europe. Available at: https://www.oceanenergy-europe.eu/ocean-energy/wave-energy/
- Hydropower explained. (2024). US Energy Information Administration. https://www.eia.gov/energyexplained/hydropower/wave-power.php
- Villasur, S. (2024). Roams, Energy. What are the differences between tidal and wave energy?
https://roams.es/energia/energia-renovable/energia-undimotriz/maremotriz/