Which Is Better Perlite or Vermiculite?


Ever wonder why some plants thrive while others struggle? The secret often lies beneath the surface, within the magic of soil additives. These special ingredients act like vitamins for your garden, influencing everything from moisture retention to nutrient availability. Whether you're a seasoned gardener or a budding green thumb, understanding these power-ups is key to unlocking lush, healthy vegetation.
In this thedailyECO's article, you'll learn about vermiculite and perlite, understand their key differences, and pick the perfect fit for your plant pals.
What is vermiculite?
Vermiculite is a mineral formed from the expansion of mica. It has a distinct appearance of golden-brown or silver flakes, resembling tiny pancakes stacked together. This layered structure makes vermiculite a champion of water retention and nutrient availability.
Distinctive characteristics of vermiculite include:
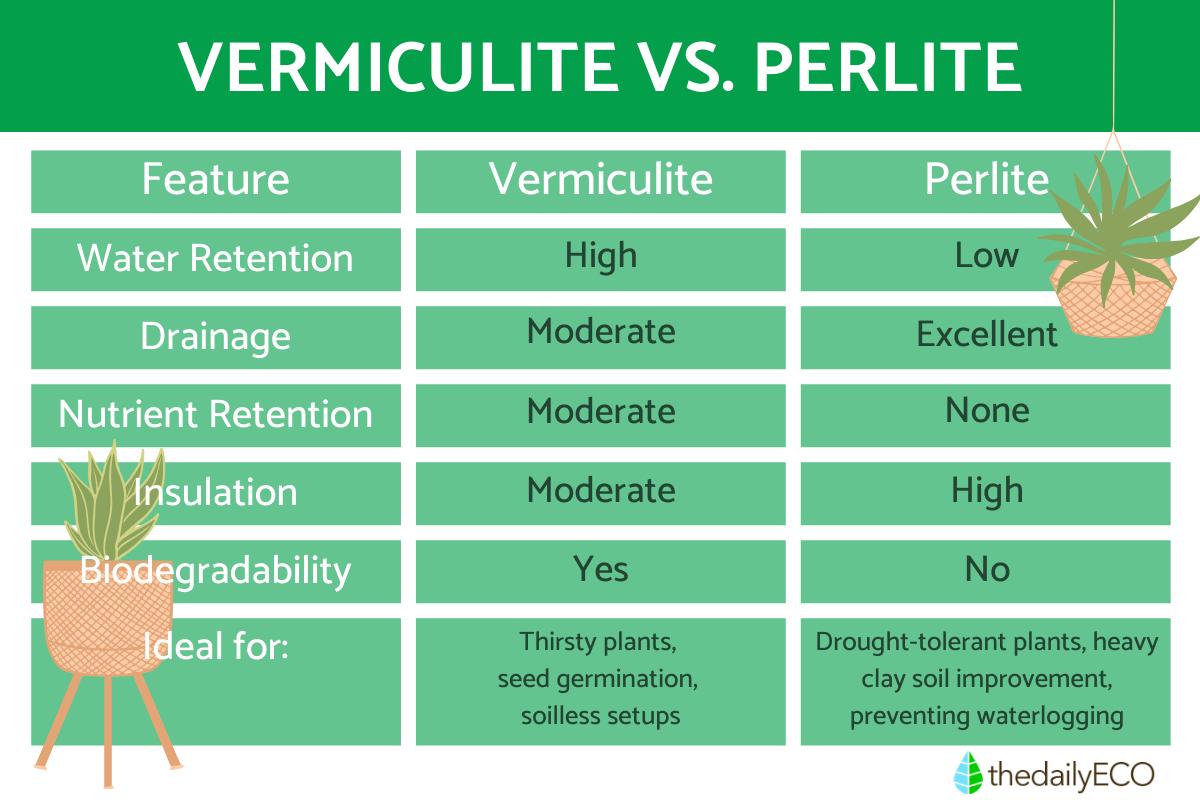
- Exceptional water retention: vermiculite can absorb up to four times its weight in water, acting like a sponge to keep your plants consistently hydrated. This makes it ideal for thirsty plants or those prone to drying out quickly.
- Nutrient retention: its porous structure also holds onto valuable nutrients, making them readily available for plant uptake.
- Neutral pH: vermiculite naturally buffers the soil, preventing it from becoming too acidic, a condition that can hinder nutrient absorption.
- Lightweight: these airy flakes won't weigh down your potting mix, promoting good drainage and aeration for healthy root development.
- Low structural stability: while beneficial for drainage, vermiculite tends to crumble easily and doesn't provide much structural support.
- Sterile: vermiculite is free from pathogens and pests, minimizing risk of disease and insect infestations.
- Biodegradable: it slowly decomposes over time, releasing nutrients back into the soil and contributing to long-term soil health.

What is perlite?
Perlite is a naturally occurring volcanic rock that's heated to high temperatures until it expands into white, popcorn-like granules. This lightweight, porous material is a gardener's secret weapon for improving drainage and aeration in potting mixes.
Key characteristics of perlite:
- Excellent drainage: P¡perlite drains rapidly, preventing waterlogging and root rot, making it ideal for plants that prefer drier conditions or are sensitive to overwatering.
- Aeration boost: its lightweight, porous nature allows air to circulate freely around plant roots, promoting healthy growth and nutrient uptake.
- Neutral pH: like vermiculite, perlite has a neutral pH, ensuring optimal nutrient availability for your plants.
- Insulation: perlite can help insulate roots from temperature fluctuations, protecting them from extreme heat or cold. In fact, it helps soil cool down faster in hot weather, benefiting heat-sensitive plants.
- Low nutrient retention: due to its open structure, perlite doesn't hold onto nutrients as well as vermiculite, potentially requiring more frequent fertilization.
- Improved soil structure: breaks up heavy clay soils, preventing compaction and allowing for proper root growth.
Explore the world of natural magic with homemade fertilizers and watch your garden explode with life.

Differences between vermiculite and perlite
Choosing the right soil amendment for your plants can be a game-changer. While both vermiculite and perlite are commonly used, their strengths and weaknesses lie in distinct areas. Understanding their key differences is crucial for optimizing your potting mix and ensuring your plants' happiness. Here's a breakdown:
Water Retention:
- Vermiculite: a water sponge, absorbing and retaining up to four times its weight, ideal for thirsty plants and seed germination.
- Perlite: a drainage champion, rapidly channeling excess water away, perfect for drought-tolerant plants and preventing waterlogging.
Nutrient Retention:
- Vermiculite: holds onto nutrients due to its porous structure, making them readily available for plants.
- Perlite: inert, meaning it doesn't retain nutrients itself, potentially requiring more frequent fertilization.
Structure:
- Vermiculite: lightweight and airy, promotes good drainage and aeration, but crumbles easily, offering minimal structural support.
- Perlite: similar in weight and texture, provides even less structural support than vermiculite but helps break up heavy clay soils.
Additional Differences:
- pH: Both vermiculite and perlite have a neutral pH, beneficial for most plants.
- Insulation: Vermiculite offers moderate insulation, while perlite helps cool down soil in hot weather.
- Sterility: Both are sterile, minimizing disease and insect risks.
- Biodegradability: Vermiculite slowly decomposes, releasing nutrients back into the soil. Perlite is inert and does not decompose.
Dive into the world of Kiryuzuna, the volcanic treasure that unlocks stunning bonsai beauty.

When to use vermiculite
Vermiculite is a versatile soil amendment that can be beneficial in various gardening and horticultural applications. Here are specific situations and scenarios when using vermiculite is recommended:
- Improving soil structure: ideal for enhancing heavy or clayey soils, improving tilth.
- Enhancing water retention: recommended for raised beds, container gardening, and situations requiring increased moisture retention.
- Seed starting and germination: valuable in seed starting mixes, fostering optimal conditions for germination and root development.
- Container gardening: beneficial for potted plants, contributing to improved water retention and aeration.
- Growing moisture-loving plants: suitable for plants that thrive in consistently moist soil, such as certain vegetables and flowering plants.
- Temperature regulation: useful for stabilizing soil temperature and providing insulation against extreme fluctuations.
- Mixing with compost or peat moss: combining with compost or peat moss creates a balanced growing medium with aeration and moisture retention.
- Improving soil in greenhouses: commonly used in greenhouse growing to maintain optimal moisture levels.
- Amending garden beds: recommended for amending garden beds, particularly those with poor soil structure.
Adjust the quantity based on plant needs and existing soil conditions, and monitor regularly for optimal results.
When to use perlite
Perlite is a versatile soil amendment suitable for various gardening and horticultural applications. Here's when you should consider using perlite:
- Improving drainage: perlite is excellent for enhancing soil drainage in gardens or containers, preventing waterlogged conditions that can harm plant roots.
- Aeration in potting mixes: ideal for creating well-aerated potting mixes, especially for plants like succulents and cacti that require fast-draining soils.
- Seed starting and root development: perlite promotes healthy root development in seedlings by providing a loose, well-aerated medium. It's often included in seed starting mixes.
- Hydroponic and soilless mixes: commonly used in hydroponic systems and soilless growing mixes to provide a lightweight, aerated substrate for plant roots.
- Alleviating soil compaction: adding perlite to compacted soils helps break up soil particles, improving aeration and root penetration.
- Amending heavy soils: suitable for lightening heavy or clayey soils, contributing to better aeration and drainage.
- Container gardening: essential for container gardening to prevent compacting of soil in pots, allowing for optimal air circulation and water drainage.
- Promoting faster growth: perlite encourages faster plant growth by preventing water stagnation, ensuring that oxygen reaches the roots more efficiently.
- Mixing with peat moss or compost: when combined with peat moss or compost, perlite creates a balanced growing medium with improved aeration and drainage.
- Growing drought-tolerant plants: well-suited for plants that prefer drier conditions, as perlite helps maintain soil moisture at an optimal level.
- Container propagation: perlite is commonly used for propagating cuttings and starting new plants in containers due to its light and well-draining properties.
When using perlite, adjust the quantity based on your specific plant needs and the existing soil conditions. Regular monitoring and observation will help ensure that the soil mix provides the desired benefits for healthy plant growth.
Think you've mastered soil mixes? Challenge yourself with the intricate balance of a closed ecosystem.
If you want to read similar articles to Which Is Better Perlite or Vermiculite?, we recommend you visit our Plant care and cultivation category.
- Uhlig, M. (2008). Cactus and other succulents . Spain: Editorial Hispano Europa, SA.
- Margarida, M. (1983). Thermal isolation . Spain: Associate Technical Editors.
- Marinas Benavides, MI (2020). Basic operations in nurseries and garden centers. MF0520 .. Spain: Training Tutor.