Hellebore Plants - Care, Watering and Propagation


The hellebore is a plant that produces elegant flowers during the winter in a range of beautiful colors. Hellebores are plants that belong to the genus Helleborus, meaning there are varies different species which bear this name. However, they all share certain characteristics which determine their care needs. In addition to the many species of hellebore, there are also various different cultivars we can find, many of which have not even been officially registered. The care for all hellebores is indirect sunlight, nutrient-rich soil, constant moisture and more. thedailyECO investigates hellebore care, watering and propagation with our complete care guide.
Hellebore characteristics
The hellebore is also known as the winter rose or Christmas rose in some cases. This is because it blooms in the winter. It is important to know it is not a type of rose, nor is it a plant that really looks like a rose. Flowering begins from late winter through spring, making a great addition to bring color to gardens. In addition, they are a refuge for various types of pollinators who are able to search for food during this cold season.
The main characteristics of hellebores are the following:
- They stand out because they have a long flowering period, blooming with colors in pink, red, white or green. Flowers with green tones are somewhat of a curiosity and are not very common
- The leaves remain all year round and are very attractive due to their arrangement in bunches, one reason why they are in such demand for garden design. Some varieties may have silvery or interestingly patterned leaves. Learn about other plants with colorful leaves in our related guide.
- They have a compact build with an average size of 30 to 45 cm (12-18").
- They are native to Europe where they are most commonly grown for gardens.
- All hellebores are toxic. They contain alkaloids that serve as protection to avoid being eaten by predators, such as rabbits or deer. Cases of poisoning in humans are not frequent because it requires ingestion, but contact dermatitis can occur. Therefore, it is recommended to handle with gloves and long sleeves. You will also need to be careful if you have pets with access to these plants.
Hellebores can also be divided into groups of those that are easy to care for and those that are not. Most of them follow the care that we will present to you later, but we list below some that are more tricky:
- Christmas black rose (Helleborus niger): needs excellent drainage in winter.
- Tibetan hellebore (Helleborus tibetanus): goes dormant in summer and emerges again in spring, but should not be watered in the interim.
- Lenten rose (Helleborus lividus): does not tolerate cold or humidity.
If you like the sound of the hellebore plant and want to have it at home, you can purchase it using this button.

Hellebore light, temperature and location
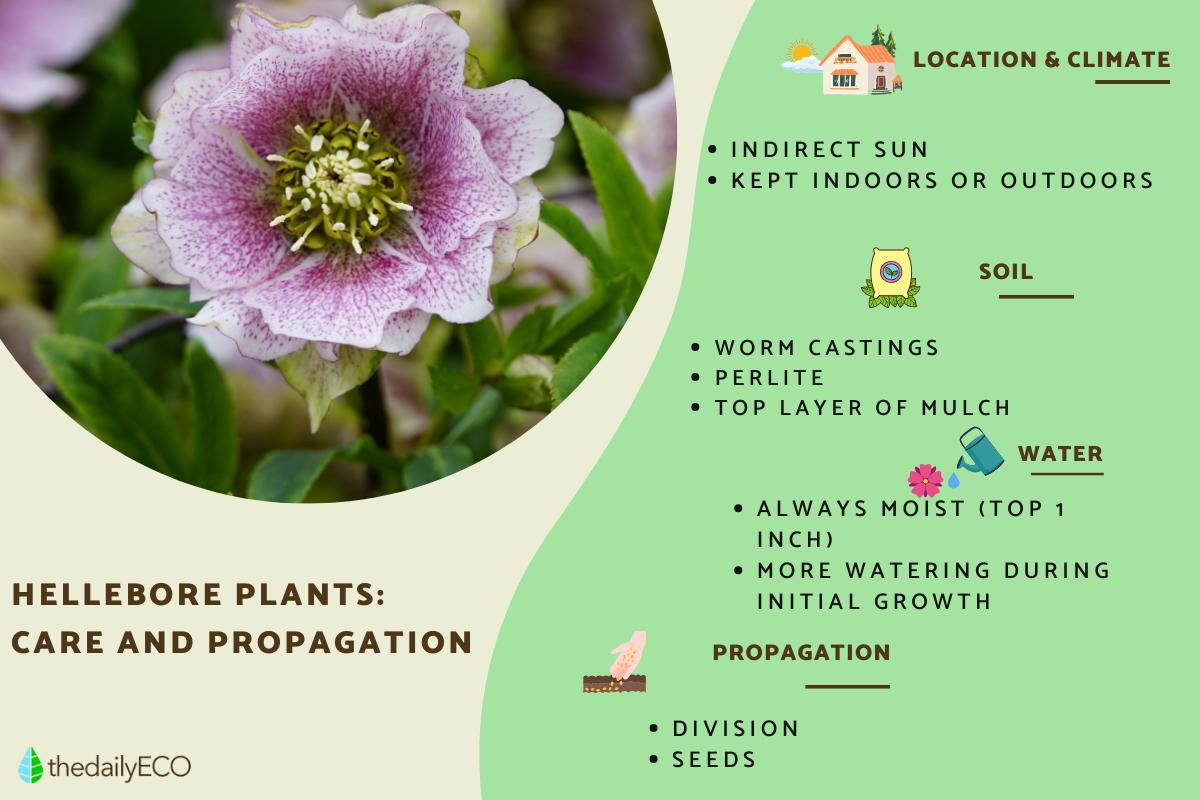
Hellebore prefer semi-shade or filtered light because direct sun burns their leaves. Place them indoors near a window, under the canopy of trees outdoors or with roofs that cover them from the sun most of the day. They can tolerate spaces with a little light, as long as the soil is not dry. They grow well in cold climates and the flowers do not suffer from the low temperatures.
They need to be planted 35 to 45 cm (12-18") apart so that they have enough room to grow. They can be kept in planters, although it is recommended to have them there only when kept indoors to flower. After flowering, it is recommended to transplant into a soil bed outside.

Substrate for hellebore plants
They enjoy nutrient-rich soil. To do this, you can prepare a mixture of equal parts worm castings or compost and peat at home. Finally, add 10% perlite to promote drainage.
- Worm castings: a type of natural organic fertilizer produced by worms and has many nutrients for plants.
- Peat: necessary for good growth and root fixation.
- Perlite: drains and prevents excess water. It also facilitates soil aeration.
A layer of compost mulch is placed on the surface to prevent the substrate from drying out too quickly. A separation must be left between the plant and the mulch so that it does not rot. This mulch is replaced annually.
No fertilizer is required. If slow growth is detected, it is probably due to a substrate that is too dry or stagnant.
Learn about how to make your own worm castings at home if you want to save money, but only if you need to use a lot of it.

Watering hellebore plants
They require constant humidity and do not tolerate very dry soil. Make sure the first inch stays moist. They also do not tolerate soil that is too wet or waterlogged, so the correct amount of watering must be provided. In the hotter seasons you can increase irrigation. When you first purchase a hellebore plant, it will need higher watering during the first stage of growth. Remember that this goes from spring to summer.
They need a container or pot with drainage that allows the free passage of water, otherwise the water will stagnate and rot the plant. Below, you can purchase nursery pots if you want to get started before planting them in a flowerbed:
Hellebore plant pruning
It is recommended to prune wilted leaves, especially before and during flowering. This will help to enhance the blooming process. This pruning also prevents the establishment and spread of the fungal disease called black leaf spot, which is caused by Coniothyrium hellebori and is specific to hellebores. Always remember to disinfect pruning sheers before and after using them.
Hellebore plant propagation
Hellebore plants can be reproduced and propagated in one of two ways:
Division
Digging up a plant that is already a good size and separating from the root to obtain two new plants. This method is also carried out in early autumn.
Seeds
The ideal time is early fall, although it can be done until spring. The essential thing is to avoid the dry summer months. The seeds are placed in a seedbed or seedbed with worm castings, lightly covering the seed with the same substrate. It should be kept slightly moist until the sprout emerges. When it reaches about 10 cm (4") in height it is ready to be transplanted. Try to do the process indoors so that the seedling is not damaged by the cold.
If you liked this hellebore care guide and you like plants withstand the cold well, you can check out our complete guide to winter outdoor plants for pots.
If you want to read similar articles to Hellebore Plants - Care, Watering and Propagation, we recommend you visit our Plant care and cultivation category.
- Royal Horticultural Society. (n.d.). Hellebore. Retrievdd from: https://www.rhs.org.uk/plants/hellebore
- Royal Horticultural Society. (n.d.). How to grow hellebores. Retrieved from: https://www.rhs.org.uk/plants/hellebore/growing-guide