What Is a Biodiversity Hotspot? - Ecological Hotpots

Also known as ecological hotspots, biodiversity hotspots are geographic areas that stand out for hosting an extraordinary diversity of endemic species that is also facing significant threats to its survival. The term hotspots was coined by ecologist Dr. Norman Myers in 1988, a term born due to the crucial role in the conservation of global biodiversity. These regions are scattered throughout the world and considered true treasures of life on Earth.
By protecting these hotspots, not only are unique species and ecosystems preserved, but vital ecosystem services are also safeguarded. This includes climate regulation, water purification and the provision of food and natural resources for local communities. Their conservation is also important for communities on a global scale. In this thedailyECO article we discover what is a biodiversity hotspot? We look what makes an ecological hotspot, as well as examples from around the world.
What are biodiversity hotspots?
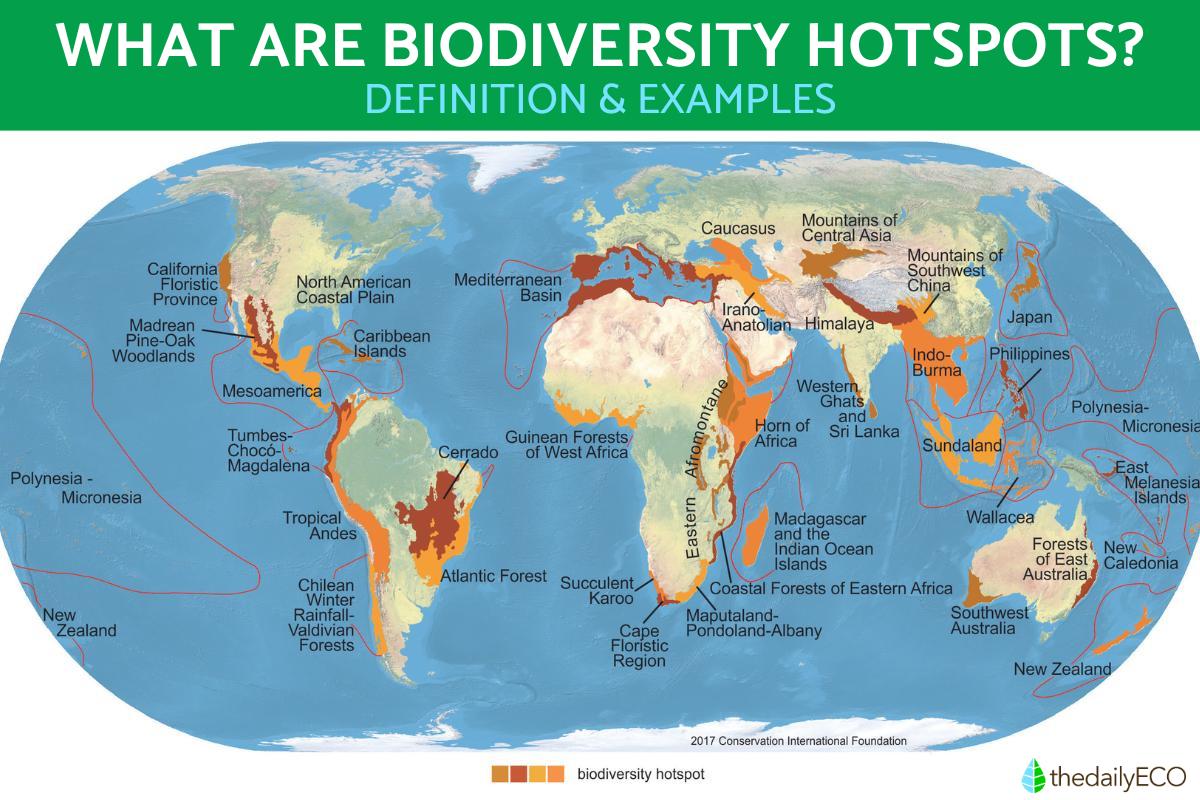
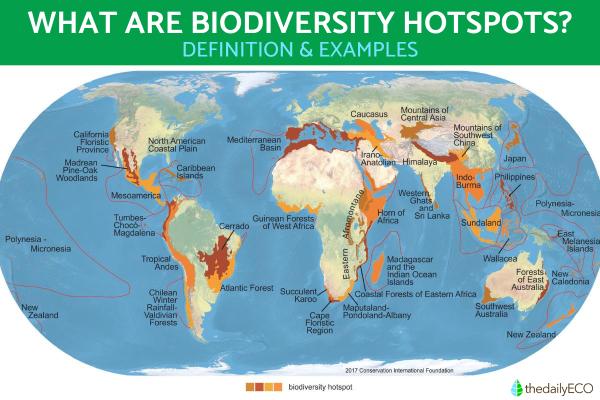
Biodiversity hotspots or ecological hotspots refer to regions that exhibit an exceptional concentration of native species, but are experiencing rapid loss of their natural habitat. To date, 36 hotspots have been identified and defined globally. Due to their strategic importance, these hotspots are considered global priorities in terms of conservation.
For a region to be recognized as a hotspot, it must meet two main criteria:
- Host a high level of biodiversity: large number of endemic species that are not found anywhere else in the world.
- Face significant threats: including habitat loss, deforestation, intensive agriculture, urbanization, overexploitation of natural resources and climate change.
Learn about how geographical locations are further categorized with our article explaining what is an ecoregion?
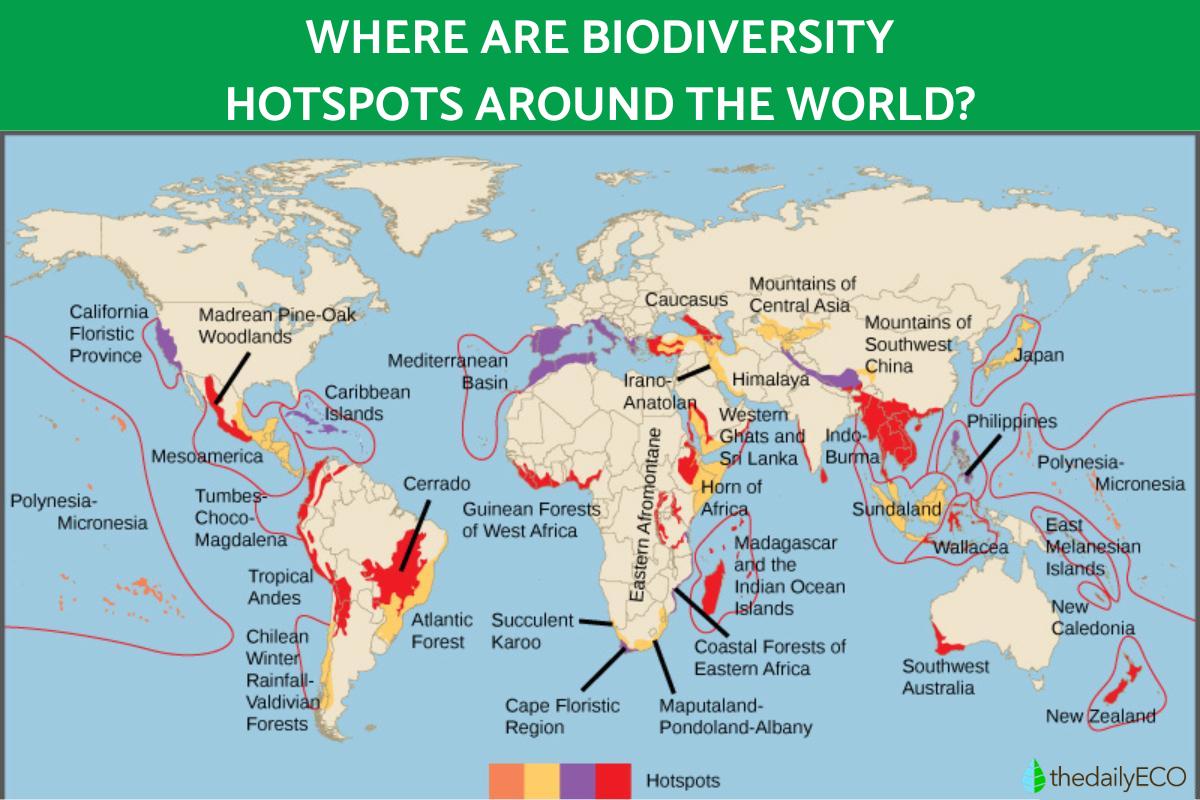
Where are biodiversity hotspots?
Biodiversity hotspots are generally located in regions that have served as refuges during glacial cycles. This is because they have been better protected from extreme environmental changes. These hotspots are characterized by areas that have experienced a loss of more than 70% of their natural habitat. Despite occupying only 2.3% of the Earth's surface, they are home to a disproportionately high number of animal and plant species, many of which are in danger of extinction.
Below we mention where the biodiversity hotspots are located around the world:
- America: Tropical Andes, Mesoamerica, Biogeographic Chocó, Antilles or Caribbean Islands, Madrean pine-oak forests, Gulf Coastal Plain, Atlantic Forest, Valdivian Forest, Floristic Province of California, El Cerrado.
- Africa, Europe and the Middle East: Madagascar, West African Guinean Forests, Mediterranean Basin and Macaronesia, Caucasus, Cape Floral Region, Iran-Anatolia, East African Coastal Forest, Succulent Karoo, Horn of Africa, Afromontane East.
- Asia and Oceania: Sundaland and Nicobar Islands, Wallacea, Philippines, Himalayas, Japan, Eastern Melanesian Islands, Western Ghats and Sri Lanka, Southwestern Australia, Central Asian Mountains, Eastern Australian temperate forests, New Caledonia, New Zealand, Indo- Burma, Southwestern Mountains of China, Polynesia and Micronesia.
Rainforests are areas which are often considered biodiversity hotspots due to the great range of biodiversity and the fact many are under threat. Discover more with our article on what are jungle ecosystems?

Examples of biodiversity hotspots
Biodiversity hotspots represent areas of great importance for the conservation of unique species and valuable ecosystems around the world. Their protection is essential to preserve biological diversity and ensure a sustainable future for future generations. There are 36 biodiversity hotspots around the world. Below, we will mention some of the most important:
- The Mediterranean basin: located around the Mediterranean Sea, it stands out for housing a large number of reptile species, with more than 40% of them being endemic. Additionally, it is recognized as one of the most important areas in the world for plant diversity.
- The Tropical Andes: this region contains about a sixth of all plant species on the planet. With approximately 30,000 species of vascular plants known to be endemic to here, it is considered the hotspot with the greatest plant diversity. We share the types of Andean plants and animals you can find in this biodiversity hotspot.
- Congo Basin: home to some of the largest tropical forests in the world, it is one of the most significant biodiversity hotspots on the planet. It is home to a great diversity of life, including emblematic species such as gorillas, elephants and bonobos.
- Great Coral Reef Region: located in Australia, it is the largest coral reef system in the world. This hotspot is home to a surprising variety of marine life, including corals, fish, sea turtles and dugongs. Learn about how marine life survives with our article explaining deep ocean currents.
- Himalayan Region: this mountainous region is home to a wide variety of flora and fauna species. Iconic animals of this area include the snow leopard, panda bear and numerous species of birds.

Importance of biodiversity hotspots
Biodiversity hotspots play an essential role in the survival of various plant and animal species, the protection of valuable ecosystems and the understanding of life on our planet. Its conservation not only has a positive impact on the health and balance of ecosystems, but also benefits human communities by providing ecosystem services and sustainable economic opportunities.
Here are some of the reasons why they are important:
- High biodiversity: hotspots are home to a wide diversity of endemic species, i.e. species found nowhere else in the world. This unique biological wealth is essential for the preservation of genetic variability and the adaptation of species to the environment.
- Key ecosystems: the ecosystems present in hotspots play a key role in regulating the climate, purifying water, preventing soil erosion and providing food and natural resources for local communities.
- Threats and risk of extinction: biodiversity hotspots are also threatened by human activities, such as deforestation, urbanization, intensive agriculture and climate change. These pressures put the survival of numerous species and ecosystems at risk.
- Scientific and educational value: these areas represent true natural laboratories, providing unique opportunities for scientific research, the discovery of new species and the study of biological processes.
Now that you know what biodiversity hotspots are, you may be interested in these articles on what is the difference between a biome and ecosystem and what is an aquatic ecosystem?
If you want to read similar articles to What Is a Biodiversity Hotspot? - Ecological Hotpots, we recommend you visit our Biodiversity category.
- Conservation International. (2024). WHY ARE BIODIVERSITY HOTSPOTS IMPORTANT? https://www.conservation.org/priorities/biodiversity-hotspots
- Pinzon, J., &Spence, J. (2013). Species distribution models and biodiversity hotspots. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/248394873_Modelos_de_distribucion_de_especies_y_hotspots_de_biodiversidad
- NatureServe and EcoDecision. (2015). Biodiversity Hotspot of the Tropical Andes. https://www.cepf.net/sites/default/files/tropical_andes_profile_final_4_2015_sp.pdf