What Is an Ecoregion? - Definition With Examples

An ecoregion is an area of the planet which is defined by both its ecology and geography in terms of natural ecosystems and size. Earth is rich in biodiversity, but different parts of Earth have very different ecological characteristics. How we understand such biodiversity requires categorization. Doing so helps us to know how different ecoregions are affected by various forces, including migration, climate, human populations and much more. Ecoregions exist comparatively with other biogeographic divisions.
At thedailyECO, we provide insight into such categorization by asking what is an ecoregion? We provide a definition of ecoregions, as well as examples which can be found across the globe. We help to illustrate what an ecoregion is thanks to photos of some of these examples.
What is an ecoregion?
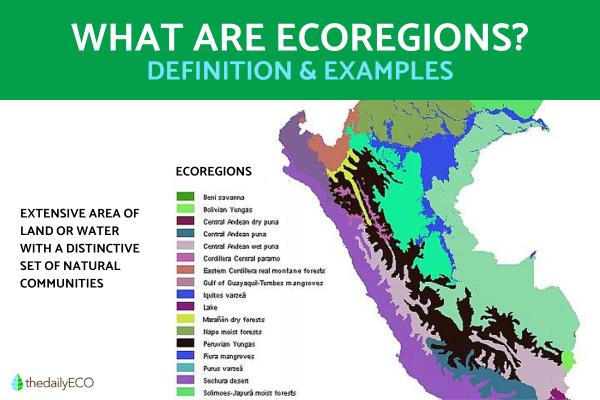
Although similar, there are several definitions of ecoregions. The World Wildlife Fund for Nature (WWF) defines an ecoregion as an extensive area of land or water that has a distinct set of natural communities. Short for regional ecosystem, ecoregions share characteristics such as environmental conditions, species, and ecological dynamics that interact in such a way as to ensure long-term maintenance.
We need to think of ecoregions in relation to other forms of categorization. One of the most confusing is when we compare it to ecosystems. The main difference between an ecosystem and an ecoregion is size. An ecosystem is the term used to describe the organisms and physical geographical environment which exist in a given space. An ecoregion is made from various ecosystems that cover a large area of land or water.
Ecoregions also exist in comparison to other collections of ecosystems. According to the WWF, they are:
- Biogeographical realm: 8 across the world.
- Bioregions: geographic clusters of ecoregions.
- Ecoregion: area of land or water with distinct natural communities.
- Ecosystem: the organisms and their interactions with their environment in a given ecological area.
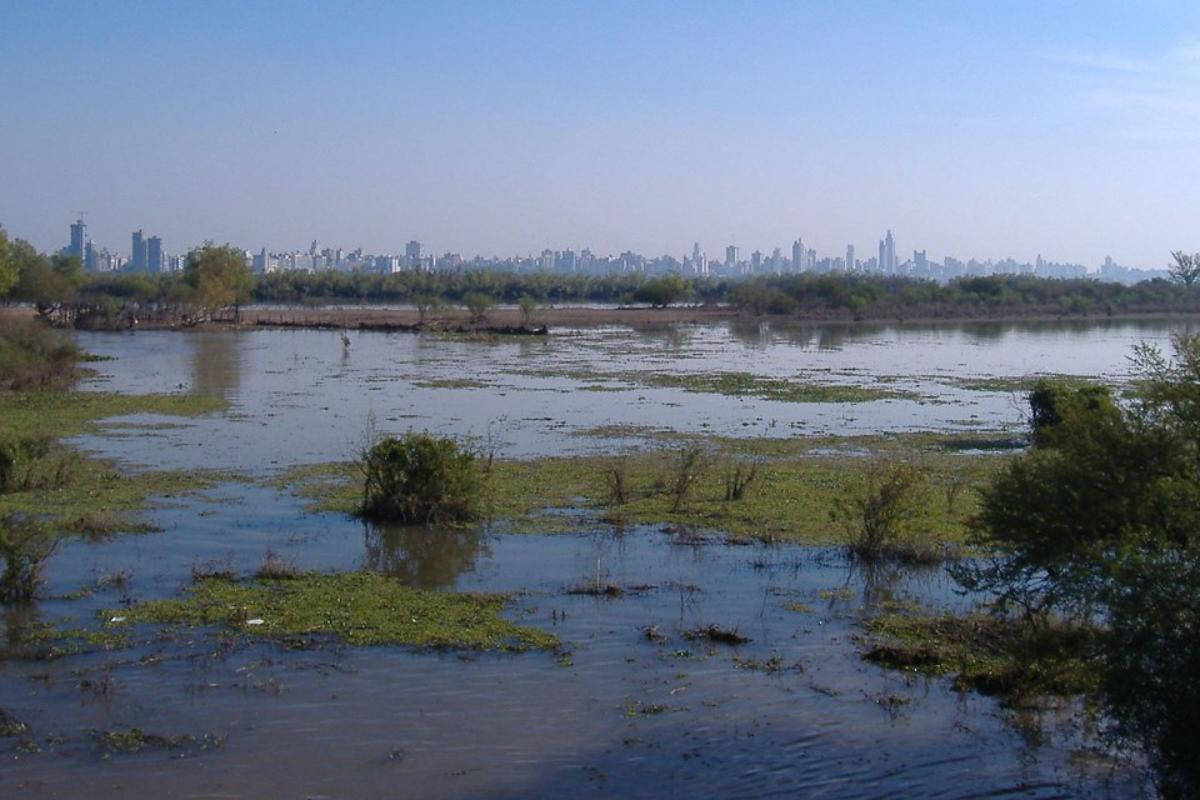
You can see an example of how an ecoregion is broken down thanks to the main photo of this article. It shows how the different ecosystems constitute a larger ecoregion. Learn more with our guide to the different types of ecosystems.
What is the difference between a biome and ecoregion?
Although they have similarities, we do need to differentiate between biomes and ecoregions. An ecoregion is a biogeographic area that is home to fauna, flora, ecology, and geomorphology with a unique and different character.
A biome refers to a biotic community characterized by being physiognomically uniform in terms of its vegetation, which is the result of climatic conditions and the type of soil that the territory has. Learn more by looking at our article on the difference between a biome and an ecosystem.
Examples of ecoregions
The three main types of ecoregion are terrestrial, freshwater and marine. We will show some examples in which we highlight various ecoregions of Peru to use as a case study. This is because the great biodiversity that characterizes this territory is home to various ecoregions. We will also look at the ecoregions of some other countries.
Examples of terrestrial ecoregions
Next, we are going to know some of the most outstanding terrestrial ecoregions:
- Beni savannah: it occupies part of Bolivia and Peru, it is characterized by its endemic biodiversity. There is a great diversity of animal and plant species within this ecoregion. The climate of this area is highly variable and has an average annual temperature between 20 °C and 27 °C, its relief is flat and its soils are poor in organic matter. This means the soils of this ecoregion can suffer from flooding or drought, which is why the flora that predominates in it is adapted to the two different types of substrate.
- Puna grassland: belongs to Peru, although it technically extends to Chile, Bolivia and even Argentina. It a high altitude ecoregion with a climate with cold temperatures that extend up to 5000 meters above sea level. Once this height is exceeded it becomes a freezing climate. The most representative fauna of this area are species that belong to the camelid family such as the vicuña, the alpaca or the llama. As for the flora, the most common to find are shrub species such as rushes which you can see depicted in the photos below.
- Páramo: extends from Colombia to the north of Peru, characterized by a mountainous relief with altitudes that can reach up to 5000 meters above sea level. It has great biological richness adapted to the extreme climatic conditions that the area presents, particularly due to strong temperature fluctuations. As a consequence, both its flora and its fauna have developed some mechanisms to face these conditions.
Example of a freshwater ecoregion
On the other hand, an example of a freshwater ecoregion is:
- Paraná Delta: it is located in the Argentinian municipality of San Fernando, in the province of Buenos Aires and is classified as a biosphere reserve due to its natural characteristics and its great biodiversity of flora and fauna. It is a territory formed by the dragging of sediments from different tributaries such as the Bermejo River and has a temperate climate.
Examples of marine ecoregions
- Mesoamerican Barrier Reef System (MBRS): it is the second longest reef on the planet, extending for 1000 km of coasts of the countries of Belize, Mexico, Guatemala and Honduras. Populations of sea turtles manatees and whale sharks coexist in this ecoregion. There are also more than 500 different species of fish, some 350 species of mollusks, some crustaceans and approximately 70 species of coral. It is not only the habitat of a wide variety of flora and fauna species, it also works by protecting the coasts from hurricanes, erosion and strong waves.
- El Mar Frío: an ecoregion in Peru with very cold waters that come from the Humboldt current. Plankton predominates in these seas, giving a green hue to the water and serves as food for the life of all those plants and animals that are inhabiting them. Learn more about how water colors change due to organic life with our article on what is a red tide?
- The tropical sea in Peru: located on the north coast of Peru where temperatures between 19 °C and 23 °C occur. Its waters are warm which contributes to the formation of clouds that will later give rise to rain. As you can see in the photo, the vegetation found in this area is very abundant. For example, species of flora characteristic of warm waters such as mangroves cam be found there. In terms of animal life, you can find beautiful shark species, as well as crocodiles, lobsters, crabs and turtles.
Learn more about different ecoregions with our article on the different Andean plants and animals.



If you want to read similar articles to What Is an Ecoregion? - Definition With Examples, we recommend you visit our Ecosystems category.








