What Is Integral Ecology?


Integral ecology is an emergent approach to ecological study that transcends the limitations of traditional perspectives. It does so by addressing environmental and social challenges from a holistic vision. This means approaching the study of natural systems from a perspective that considers its interconnectedness, considers various perspectives and promotes ecological harmony. By recognizing the interconnection between humans, nature and society, this approach promotes integrated solutions that consider ecological, social, economic and cultural aspects.
There are numerous areas where integral ecology can benefit study. We learn more about such benefits at thedailyECO by asking what is integral ecology? In answering this question, we also look at its importance for ecosystems and practical examples of its use.
What is integral ecology?
Integral ecology is a holistic vision that addresses the interconnection between humans, nature and society. It is based on the understanding that all aspects of the world are interrelated. It stresses that environmental problems cannot be addressed in isolation. Rather, they require a comprehensive perspective that considers all ecological, social, economic and cultural aspects.
At its core, integral ecology recognizes that humans are part of a larger ecosystem. Our actions have a direct impact on the environment and other species. In this way, integral ecology promotes the idea of living in harmony with nature, respecting its diversity and recognizing the intrinsic value of all living beings.
This perspective goes beyond simply protecting the environment or conserving natural resources. It is also concerned with addressing the underlying causes of environmental problems. Such problems include social inequality, poverty and rampant consumerism. In this sense, integral ecology seeks to promote sustainable development that meets our present needs, doing so without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their needs.
Furthermore, integral ecology recognizes the interdependence between different aspects of human life. Considering our physical, emotional, spiritual and social health is fundamental to this approach. Integral ecology is not limited to the environmental field, but also covers issues related to social justice, gender equality, education and culture.
Learn more about integrated ecological approaches with our article on what is the blue economy?

Examples of integral ecology
The full extent of integral ecology is both too great to cover here and yet to be determined. This is because it is an ongoing process which will change, adapt and evolve just as our ecosystems do the same. However, we can achieve a better understanding of what integral ecology is with the following examples:
Agroecology
This is an agricultural approach based on the principles of integral ecology. Instead of relying on intensive agricultural practices that deplete natural resources and harm the environment, agroecology promotes sustainable agricultural systems that work in harmony with nature.
Agroecology uses techniques such as crop rotation, polyculture cultivation and integrated pest management:
- Crop rotation: growing different in the same land during different seasons. This affords many benefits such as preventing soil erosion and optimizing nutrient use.
- Polyculture cultivation: growing multiple crops in the same area at the same time. This optimizes resources and integrating the right crops can provide mutual benefit to individual produce. You can learn about an important type of polyculture with our article on the benefits of agroforestry.
- Integrated pest management (IPM): instead of relying solely on potentially hazardous chemicals to manage pests, integration of biological control, natural pesticides and even cultural practices can prevent pests without toxifying the environment. Learn more about pest management with our article on what is green biotechnology?
These approaches are not only beneficial for the environment, but are also economically viable and socially fair for farmers and local communities.
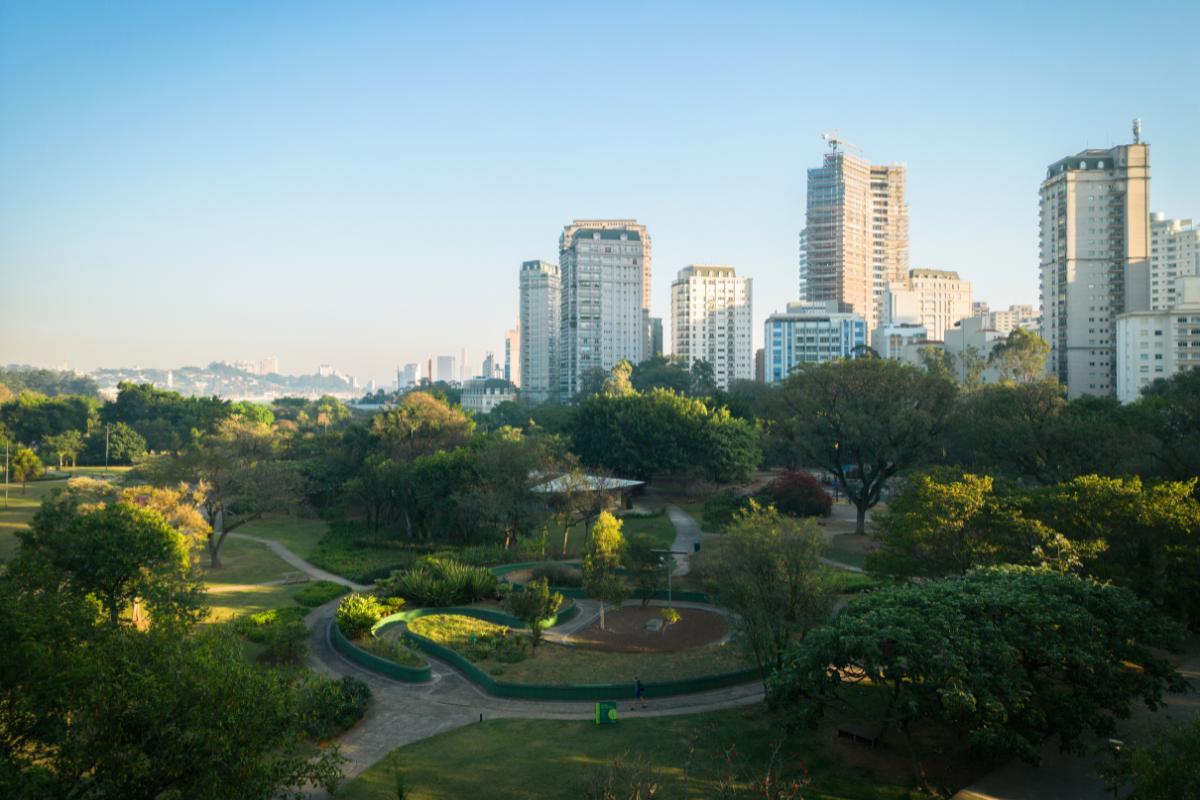
Sustainable urban planning
In urban environments, integral ecology can be applied in the planning and design of sustainable cities. This planning includes the following considerations:
- Creation of accessible green spaces
- Promotion of public transport and active mobility (such as walking and cycling)
- Efficient management of natural resources
- Promotion of cultural and social diversity
A concrete example would be the transformation of degraded urban areas into public parks and gardens. This not only provides environmental benefits, such as carbon capture and improved air quality, but also fosters social cohesion and community well-being.
Learn about an aspect of such integrated sustainable urban planning with our article on the benefits of urban forestry.
Ecosystem conservation
Ecosystem conservation is fundamental to integral ecology, as it recognizes the intrinsic value of biodiversity and the importance of protecting natural habitats. It involves not only the creation of protected areas, such as national parks and nature reserves, but also the adoption of integrated conservation approaches that involve local communities in the sustainable management of natural resources.
An example of this type of ecosystem conservation can be found in conservation projects that combine the protection of biodiversity with the economic and social development of local communities. Specific examples include ecotourism and sustainable agriculture.
Learn more about one of these approaches with our article on what is solidarity tourism?

Importance of integral ecology
The importance of integral ecology lies in its ability to address environmental and social challenges in a holistic and sustainable manner. The following aspects stand out the most about the importance of integral ecology:
- Holistic approach: integral ecology recognizes the interconnection between humans, nature and society-Doing so allows environmental problems to be addressed from a broader and more complete perspective. Not only the ecological, but also the social, economic and cultural aspects of a problem are considered, leading to more effective and lasting solutions.
- Sustainability: integral ecology promotes a sustainable development approach that seeks to meet present needs without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own. By considering the long-term impact of our actions on the environment and human communities, the adoption of more responsible and respectful practices with the natural environment is encouraged.
- Resilience: by addressing environmental and social problems comprehensively, the resilience of ecosystems and human communities is strengthened in the face of adverse impacts. Types of environmental impacts include climate change, land degradation and natural disasters. This is achieved by promoting healthy natural systems and more cohesive communities prepared to face the challenges that may arise.
- Equity and social justice: integral ecology recognizes the interdependence between environmental and human society. This leads to greater emphasis on social justice and equity. By considering the needs and concerns of all people, especially those most vulnerable or marginalized, more inclusive and fair solutions can be designed that promote the well-being of all of society.
- Promotion of human well-being: by living in harmony with nature and respecting the limits of the planet, integral ecology contributes to human well-being in all its aspects. These include those which are physical, emotional, spiritual and social. In doing so, there is a higher quality of life for people and communities, as well as a greater sense of connection and belonging with the natural world that surrounds us.
Integral ecology is a responsible approach to our natural ecosystems which respects both human and non-human communities. Such an approach is to the benefit of everyone, especially because it can best ensure the survival of these ecosystems.
If you want to read similar articles to What Is Integral Ecology?, we recommend you visit our Ecology (other) category.