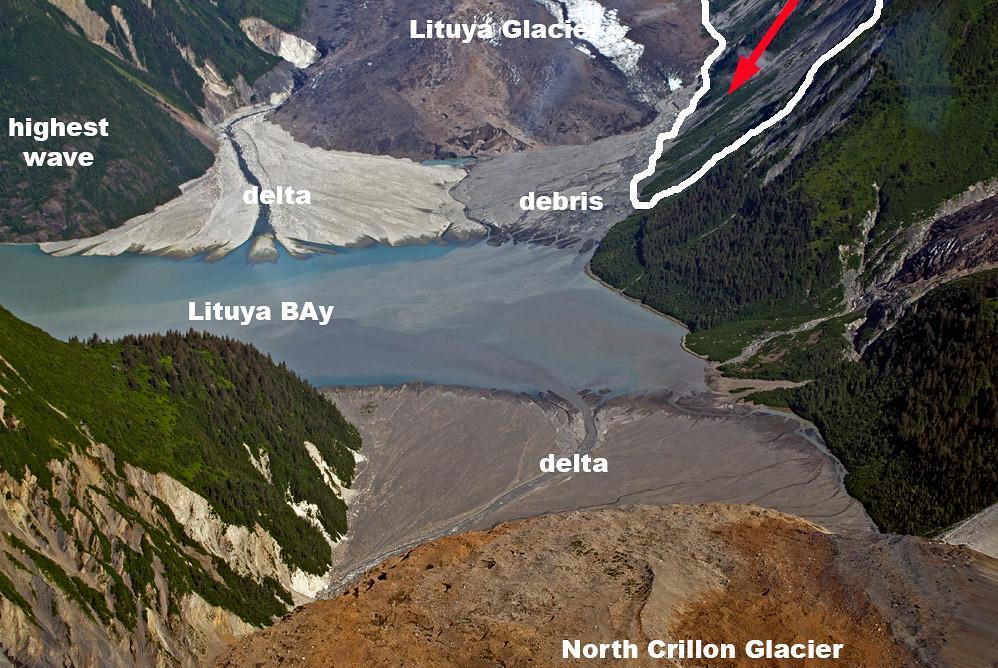
What Is the Largest Tsunami in History?


Tsunamis, often referred to as "seismic sea waves," are natural disasters that can cause widespread devastation along coastlines. Mostly triggered by underwater movements like earthquakes or eruptions, these massive waves begin as ripples in the open ocean, transforming into towering walls of water as they reach shallow areas. The impact is catastrophic, leading to flooding, infrastructure damage, tragic loss of life, and long-term economic and environmental consequences.
The following article by thedailyECO presents a closer look at history's 5 most devastating tsunamis ever recorded.
Indian Ocean Tsunami (2004)
The 2004 Indian Ocean Tsunami, also known as the Boxing Day Tsunami due to its timing on December 26th, stands as one of the deadliest natural disasters in recorded history.
A colossal earthquake measuring 9.1 on the Richter scale struck off the coast of Sumatra, Indonesia. This earthquake stands as the most powerful ever recorded in Asia and the 21st century, ranking among the top three strongest globally since the dawn of modern seismology.
This undersea earthquake triggered a series of devastating tsunami waves that surged across the Indian Ocean, impacting coastal communities in Indonesia, Thailand, Sri Lanka, India, and the Maldives. These massive waves, reaching heights of over 98 feet (30 meters) in some areas, swept ashore with incredible force, leaving a trail of unimaginable destruction.
Tsunamis undergo a dramatic transformation during their journey. In deep waters, they're barely noticeable humps speeding at incredible velocities. But as they reach shallow coastal areas, their speed drastically slows while their height surges into the destructive waves we know.
The human cost of the tsunami was staggering. Over 230,000 lives were tragically lost, with countless others injured and displaced. Entire villages were wiped away, infrastructure crumbled, and livelihoods were destroyed. The economic impact was immense, with billions of dollars in losses incurred across the affected regions.
Intrigued by the destructive power of tsunamis? Dive deeper into their formation in our next article.

Tohoku Tsunami (2011)
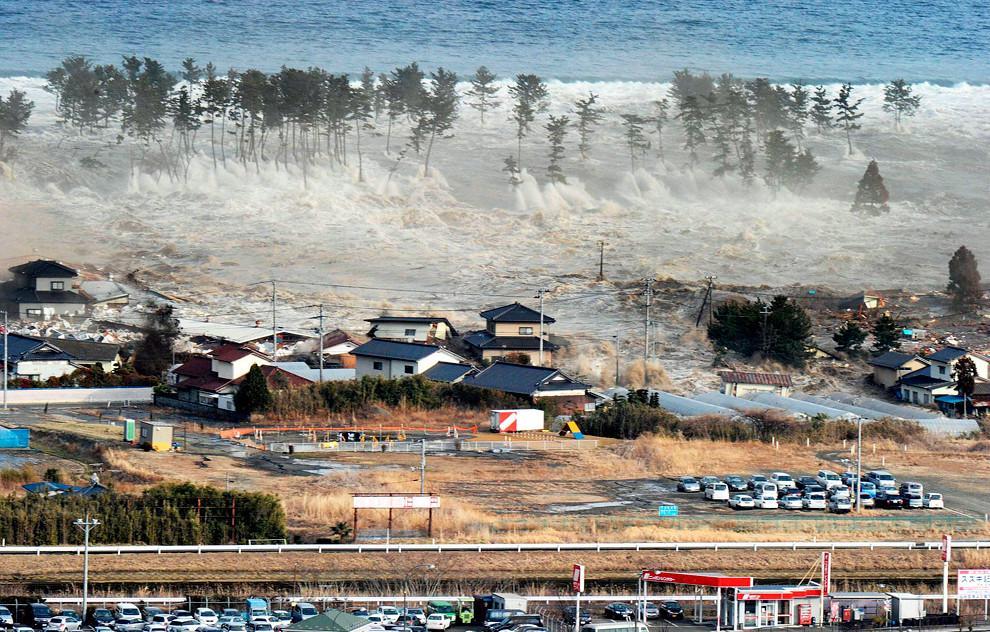
On March 11, 2011, a massive 9.0 magnitude earthquake struck off the east coast of Japan, triggering a devastating tsunami in the Tohoku region. Shaking Japan to its core, this earthquake registered as the most powerful ever recorded in the nation's history, ranking a staggering fourth strongest globally since the dawn of modern seismology.
A massive undersea movement, triggering a 20-26 ft (6-8 meter) upthrust along a 110-mile (180-kilometer) stretch of seabed, unleashed a devastating tsunami on Japan's east coast. The tsunami's destructive power wasn't confined to Japan. It traveled across the Pacific Ocean, reaching the entire Pacific coast of North and South America, from Alaska to Chile.
Entire towns were submerged, buildings collapsed, and infrastructure was destroyed. The human toll was immense, with over 15,000 lives lost and many more injured or displaced. A major factor in the devastating death toll was the unanticipated surge of the tsunami. Sea walls in many cities, designed to withstand much smaller waves, were tragically inadequate.
The tsunami triggered a cascading disaster at the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant, leading to meltdowns in three reactors. This resulted in the release of radioactive materials into the surrounding environment and the establishment of evacuation zones that displaced hundreds of thousands of residents.
The economic devastation caused by the Tohoku disaster was staggering. The World Bank's final assessment placed the total economic cost at US$235 billion, making it the most expensive natural disaster ever recorded.

Valdivia Tsunami (1960)
The 1960 Valdivia earthquake, with a staggering magnitude of 9.5, remains one of the most powerful seismic events ever recorded. This megathrust earthquake struck near Lumaco, Chile, approximately 570 kilometers (350 miles) south of Santiago. The epicenter's location placed Valdivia in the direct path of its destructive power.
The tsunami's origins trace directly to the earthquake's characteristics. Subduction of the Nazca Plate beneath the South American Plate within the South Pacific subduction zone released immense energy, causing substantial vertical displacement of the seafloor. This displacement set off tsunami waves that spread across the Pacific Ocean.
The destructive force of the Valdivia tsunami was staggering. Reports cite waves exceeding 82 feet (25 meters) along the Chilean coast. The earthquake's sheer magnitude generated tsunami waves that traveled vast distances, impacting distant regions like Hawaii, Japan, and the west coast of the United States.
Chilean coastal communities suffered significant loss of human life and extensive material damage. The combined impact of the earthquake and tsunami led to the complete destruction of numerous coastal towns. The exact number of lives lost and the financial cost of this widespread disaster remain unclear. Estimates suggest fatalities may range from 1,000 to 6,000, and economic losses could be anywhere between US$400 million and $800 million (or roughly $4 billion to $7.9 billion in today's dollars).
Uncover the deadliest earthquakes on record by reading our next article to learn more.

Krakatoa Tsunami (1883)
Unlike previous tsunamis, the Krakatoa tsunami was caused by a volcanic eruption rather than an earthquake. In 1883, the eruption of Krakatoa, an Indonesian volcano, unfolded over several months, reaching its peak in late August. A monstrous explosion ripped through the island, collapsing over 70% of Krakatoa and its surrounding archipelago into a massive caldera.
This eruption, considered one of the loudest ever recorded, unleashed unimaginable violence. The explosion unleashed a sound so deafening it was heard a staggering 3,110 kilometers (1,930 miles) away in Perth, Western Australia, and an incredible 4,800 kilometers (3,000 miles) away near Rodrigues, Mauritius. The sheer force of the eruption generated an acoustic pressure wave that circled the globe not once, but more than three times!
Massive underwater landslides were triggered by the sheer power of the event, displacing a colossal volume of water. This displaced water surged outwards, forming a devastating tsunami that slammed into nearby coastal communities.
The resulting tsunami waves, reaching heights exceeding 98 feet (30 meters) in some areas, swept ashore with incredible force, leaving a trail of utter destruction. The human cost was immense, with over 36,000 lives tragically lost.
The Indonesian town of Merak bore the brunt of the tsunami's fury, struck by a wave reaching a staggering 46 meters (150 feet) in height.
The colossal amount of ash and debris spewed into the atmosphere by Krakatoa triggered a volcanic winter. This phenomenon caused a noticeable dip in global temperatures, with average Northern Hemisphere summer temperatures plummeting by 0.4°C (0.72°F) in the year following the eruption.
Ever wondered what ignites a volcano? Our next article delves into the science behind volcanic eruptions.

Lisbon Tsunami (1755)
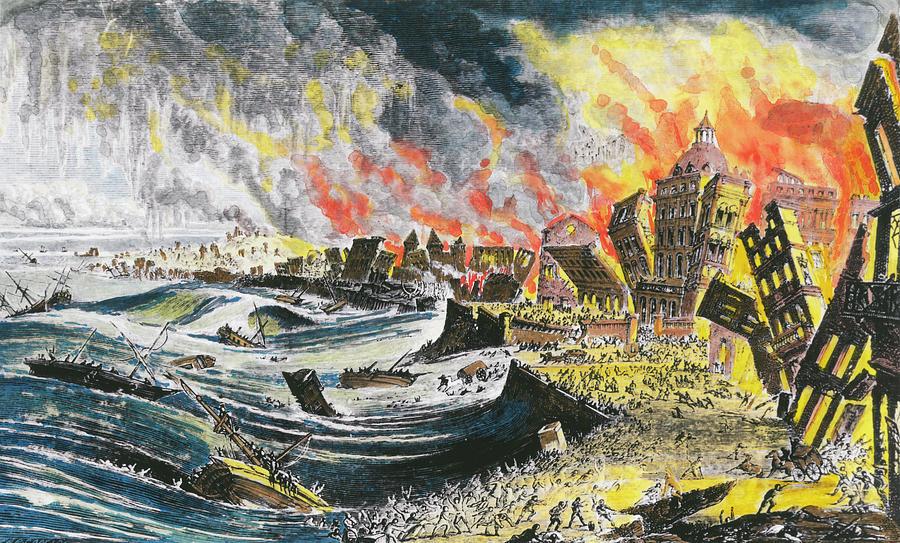
On November 1, 1755, a massive earthquake, estimated between 8.5 and 9.0 on the Richter scale, struck Lisbon, Portugal, leaving a lasting impact on the city and European consciousness. A staggering 12,000 lives were lost in Lisbon alone, marking the earthquake as one of history's deadliest.
The earthquake triggered terrifying tsunamis along the Atlantic coastline, reaching heights of up to 98 feet (30 meters) in some areas. Lisbon and other coastal towns in Portugal, Spain, and North Africa were hit hard. The earthquake unleashed a devastating tsunami and triggered widespread fires, leaving Lisbon and surrounding areas in ruins.
Lasting between three and a half to six minutes, the tremor ripped open the city center with fissures as wide as 5 meters (16 ft). Terrified survivors fled to the docks, only to witness the horrifying sight of the receding sea, exposing a muddy seabed littered with wreckage. Roughly 40 minutes later, their worst fears materialized. A monstrous tsunami surged into the harbor, engulfing the downtown area and rushing up the Tagus River with incredible speed.
Candles lit for All Saints' Day celebrations were overturned by the tremors, igniting a firestorm that raged unchecked for hours. The inferno, fueled by the city's dense buildings, trapped and suffocated countless victims within a 30-meter radius of the flames.
The Lisbon earthquake rippled far beyond the physical devastation. It ignited political tensions within Portugal and significantly weakened its colonial empire.
The event sparked intense philosophical debates among Enlightenment thinkers, particularly regarding the question of reconciling God's existence with evil.
Furthermore, the earthquake marked a turning point in scientific understanding. As the first event meticulously studied for its widespread effects, it laid the foundation for modern seismology and earthquake engineering.
Want to understand earthquakes better? Our next article explores the fascinating science behind these earth-shaking events and their various classifications.

If you want to read similar articles to What Is the Largest Tsunami in History?, we recommend you visit our Facts about nature category.