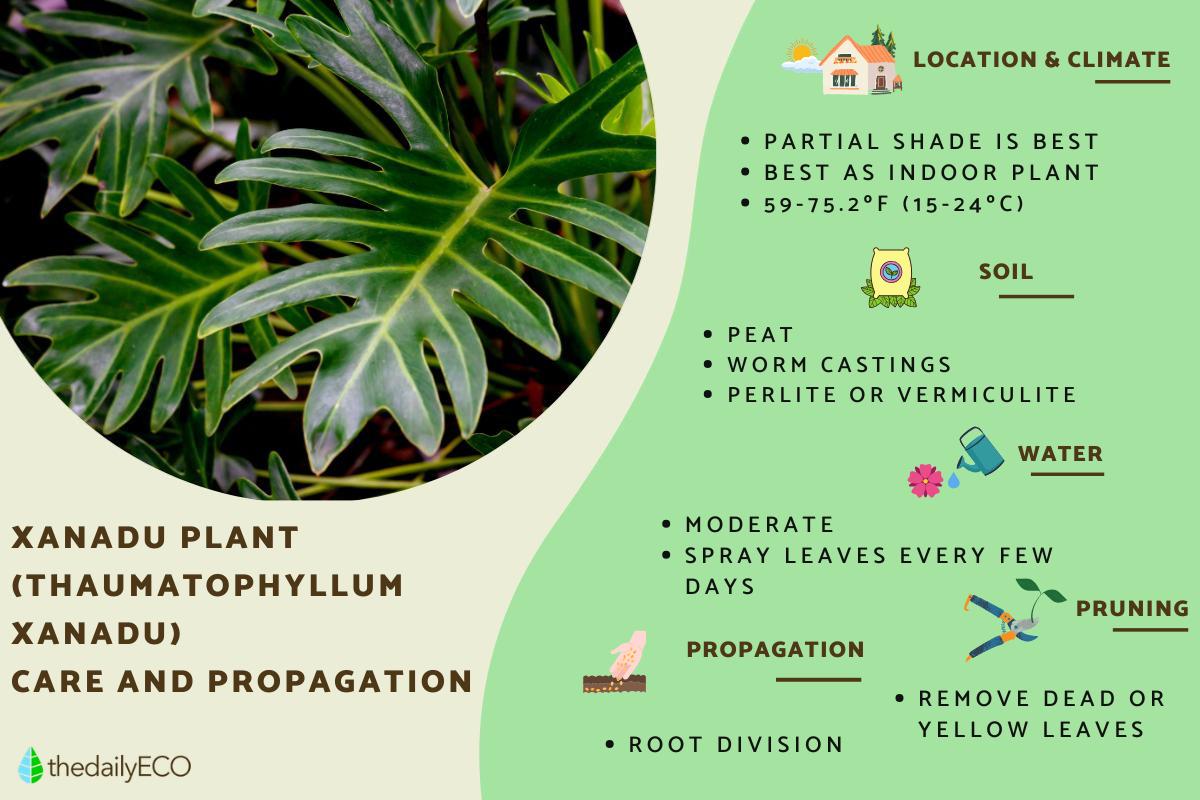
Xanadu Plant Care and Propagation

Although commonly known as philodendron xanadu, the xanadu plant (Thaumatophyllum xanadu) is no longer considered a type of philodendron. This is because it has been reclassified as being of the genus Thaumatophyllum, as have other plants in this genus. We can see the confusion since there are various morphological similarities, especially in terms of leaf shape and growth patterns. However, phylogenetic studies have shown significant genetic differences. Despite these differences, caring for a xanadu plant is not dissimilar to caring for philodendron. You can understand what this entails with thedailyECO as we explain xanadu plant care and propagation.
Characteristics of the xanadu plant
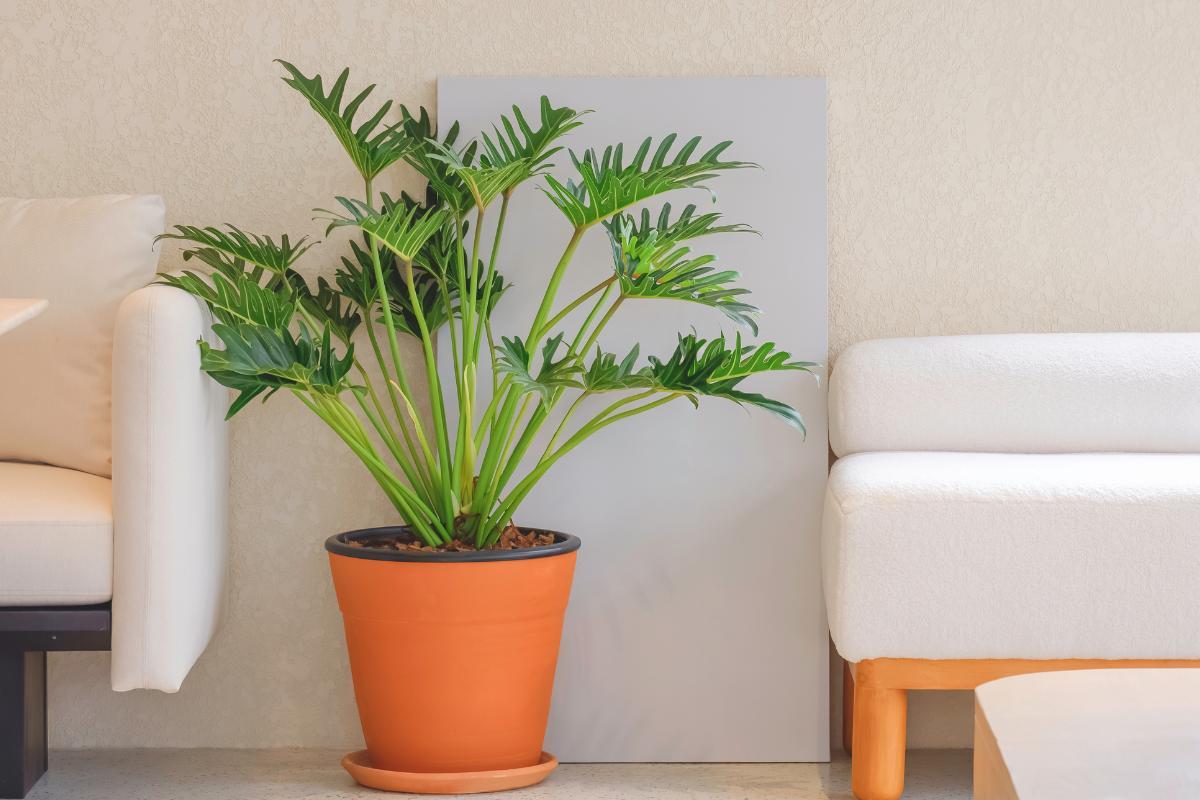
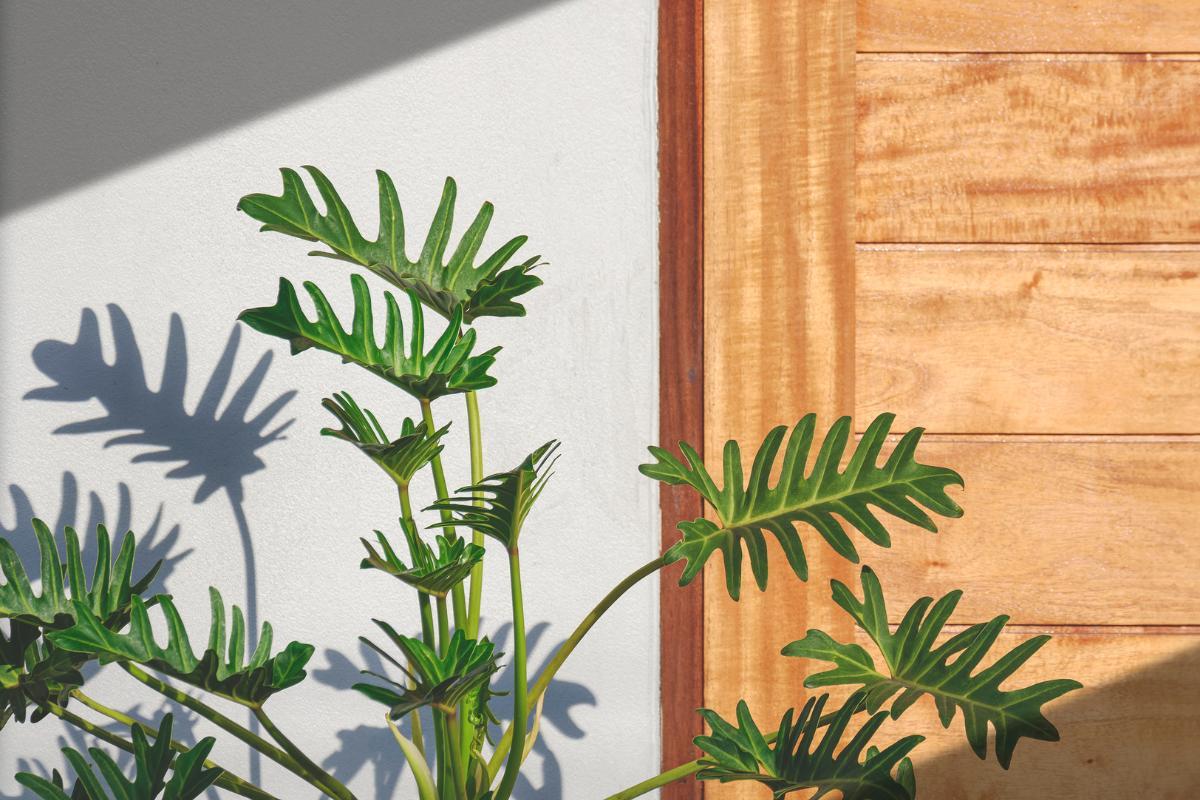
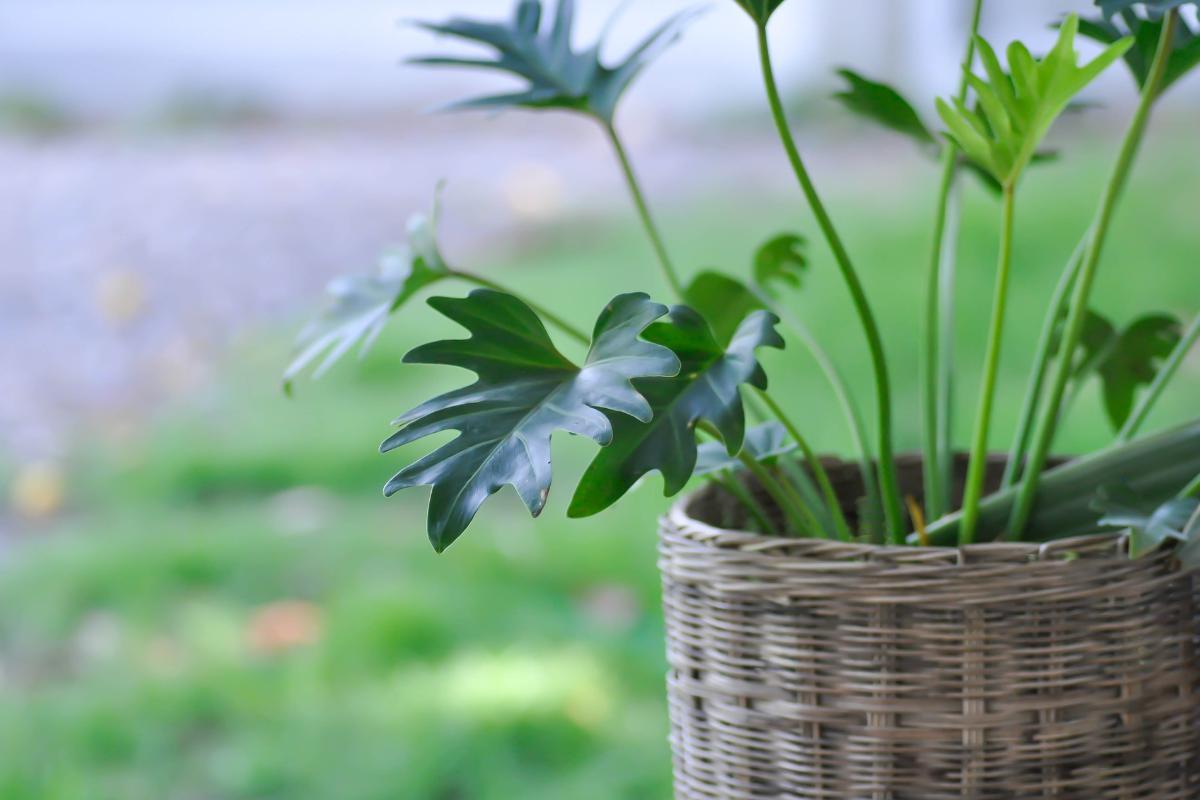
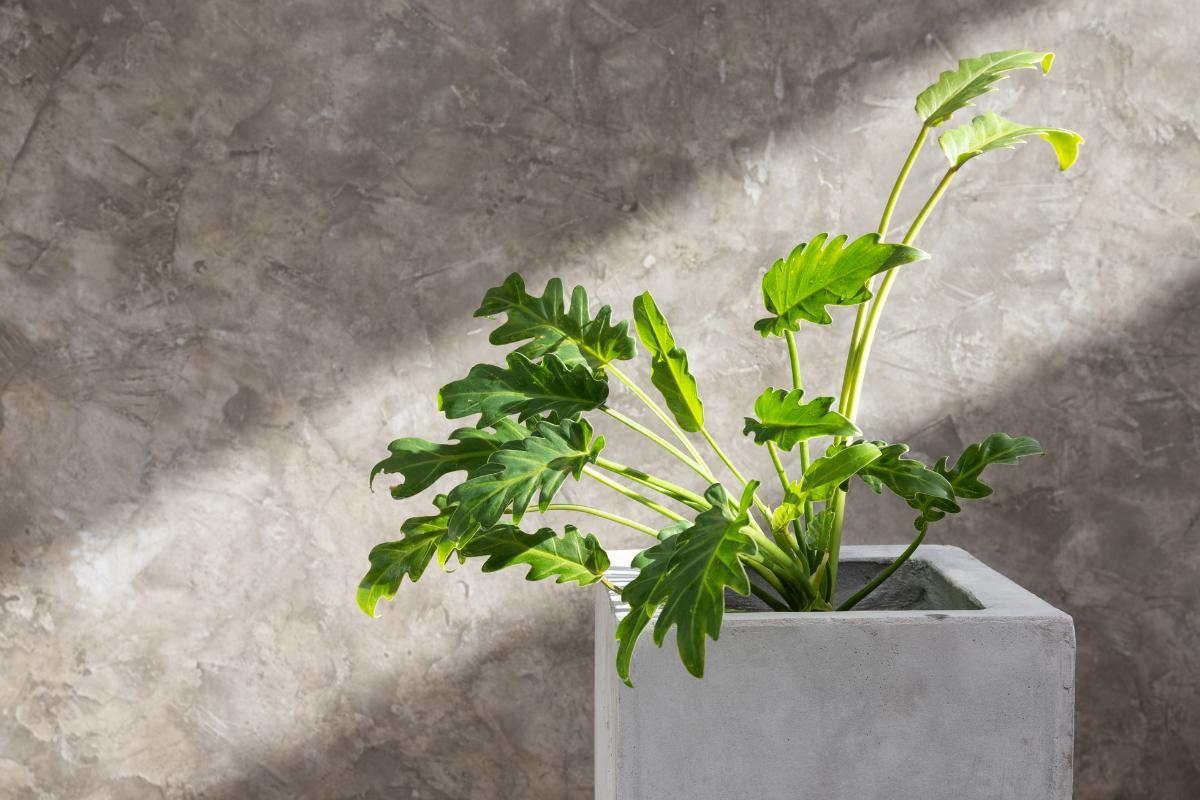
The xanadu plant is highly sought after for its spectacular, large and lobed leaves which are up to 18" (45 cm) long. They are a vibrant and deep green color. These distinctive leaves grow from a long stem which forms dome-shaped plants 3.2 ft (1 m) both high and wide. They grow in width over time, meaning the oldest plants tend to be the leafiest.
Xanadu plants can produce a red flower-like structure in summer called a spathe, although this is not very common. It is normally cultivated for the beauty of its leaves. These are perennial and last all year round.
As we have explained, the xanadu plant is no long considered part of the Philodendron genus, but you can discover the different types of philodendron plants with our related guide.

Light, temperature and location for xanadu plants
We know a little about the characteristics of the xanadu plant, but we need to know more so we can determine the right place to put them in our home or garden:
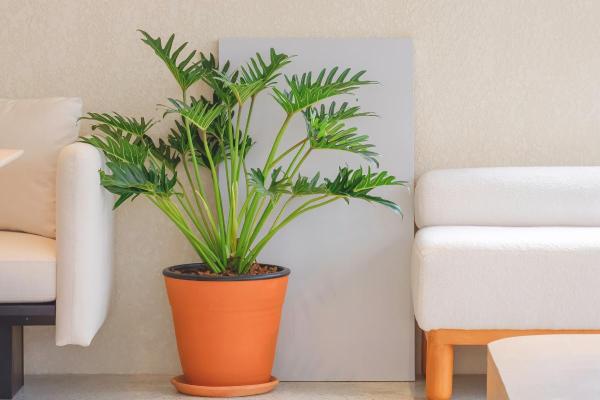
- Since they are tropical plants that grow under the canopy of rainforest trees, their light requirement is low. They should not be kept in full sun or the leaves will turn brown. They will tolerate partial shade the best. While most philodendrons tolerate low light, the Xanadu is more light hungry than most of these plants. Although they tolerate shade well, they should receive some light for best growth.
- An indicator that they need more light are stems that are too long and reach for the sun. This plant must be kept compact, so very long stems are not a good sign.
- Due to their light requirements, they are best kept as types of indoor plants that will help you to create some green spaces inside your home. They also feel very comfortable in bathrooms, where the humidity, light and temperature are similar to those of their natural environment.
- They are large and voluminous plants, ideal for large living rooms. They can be kept in garden beds under the shade of trees. Because they can grow to be very wide, you may want to consider placing it in a large space. If you do not, it will look contained and will not give its full potential.
- They require a tropical temperature of around 59-75.2ºF (15-24ºC), so it is not recommended for temperate areas.
- They develop aerial roots. If placed near a tree or wall, it can cling to them for support.

Xanadu plant soil and fertilizer
Now we move on to consider the best substrate for the xanadu plant:
- The soil for this plant should be rich in nutrients and have good drainage. You can use a mixture based on peat and worm castings, adding a handful of perlite and vermiculite to encourage water escape.
- To produce large, healthy and shiny leaves, it is advisable to add a liquid fertilizer every week during the growing season.
- No fertilization is necessary in winter.
- Every two years it can be transplanted to a larger pot, so that growth does not stagnate.
Watering xanadu plants
Now we know where to place them, we can look at how much to water a xanadu plant:
- They require moderate watering in warm seasons from spring to early autumn. You should make sure that the first layer of substrate is always moist, but be careful not to flood the pot. In winter, reduce watering and allow the top layer of the substrate to dry out.
- It needs a humid environment, so it is advisable to spray the leaves with water regularly or place the pot in a dish with water at the bottom. It is recommended to spray with water lightly and not to do it daily.
- The leaves are prone to dust accumulation, so you can use a damp cloth to clean them at least once a month. This will help the plant to photosynthesize and transpire better, directly benefiting growth.
Discover the potential benefit of rice water for plants with our related article.

Pruning xanadu plants
Pruning philodendron xanadu plants is not strictly necessary, but can be done to maintain its compact and healthy shape. It is advisable to remove yellowed, dry or damaged leaves at any time of the year to avoid the accumulation of pests and diseases. To control its size or shape, perform light pruning at the beginning of spring, before its active growth stage, using clean and sharp tools.
Xanadu plant propagation
The easiest way to propagate a xanadu plant is by dividing the roots. To do this, dig up a plant that already has several stems with leaves. You will divide it from the root into two and place each one in a different substrate. Always use gloves and long sleeves when handling it because it is toxic.
This xanadu propagation process should be done when the temperature is above 66.2ºF (19ºC), so that the roots are not affected and the temperature does not interfere with development.

Philodendron xanadu diseases and pests
It is a plant that is not prone to many diseases, with the notable exception of root rot. This happens due to overwatering. The first symptoms will appear as yellow leaves. To avoid this, it is important to provide a good mix of substrate with elements that provide structure and drainage. The container or pot must also have holes. It should also be watered in moderation so as not to stagnate the water.
The red spider mite is perhaps the most common xanadu plant pest. This is a type of mite that develops cobwebs and that extracts the sap from plants. It tends to proliferate in very dry conditions, so make sure to always water your plant well and provide adequate humidity.
Another common pest is scale insects which stick to the underside of leaves or stems. These also extract sap. To eliminate them, it is recommended to place natural predators such as ladybugs. Find out why a plant's leaves are turning black with our related guide.
Now that you know how to care for xanadu plants, you can discover the other best partial-shade plants with our related guide.
If you want to read similar articles to Xanadu Plant Care and Propagation, we recommend you visit our Plant care and cultivation category.
- RHS House Plant: Practical Advice for All House Plants, Cacti and Succulents. (2024). United Kingdom: Dorling Kindersley Limited.
- Koster, M., Sibley, E. (2017). Urban Botanics: An Indoor Plant Guide for Modern Gardeners. United Kingdom: Quarto Publishing Group USA.