Creeping Fig Plant Care and Propagation


Also known as creeping fig or climbing fig, Ficus pumila is an evergreen type of fig that is often used in homes and gardens. Its common names are related to the fact they are a type of vine, meaning it can be used to adorn walls, trellises and other spaces. Since it can climb, this means creeping figs can cover large areas. Although it is often associated with this type of planting, creeping figs can also be kept as indoor plants in planters or hanging baskets. Whether being kept in a planter or being used on walls, it is considered an easy-to-care-for plant. This does mean there are certain things we need to consider when providing Ficus pumila care.
thedailyECO explains the details with our guide to creeping fig plant care and propagation.
Creeping fig light, temperature and location
Where you situate your creeping fig plant is very important in terms of its care. Light is a particularly important factor, but ambient temperature and other factors also need to be considered. These include:
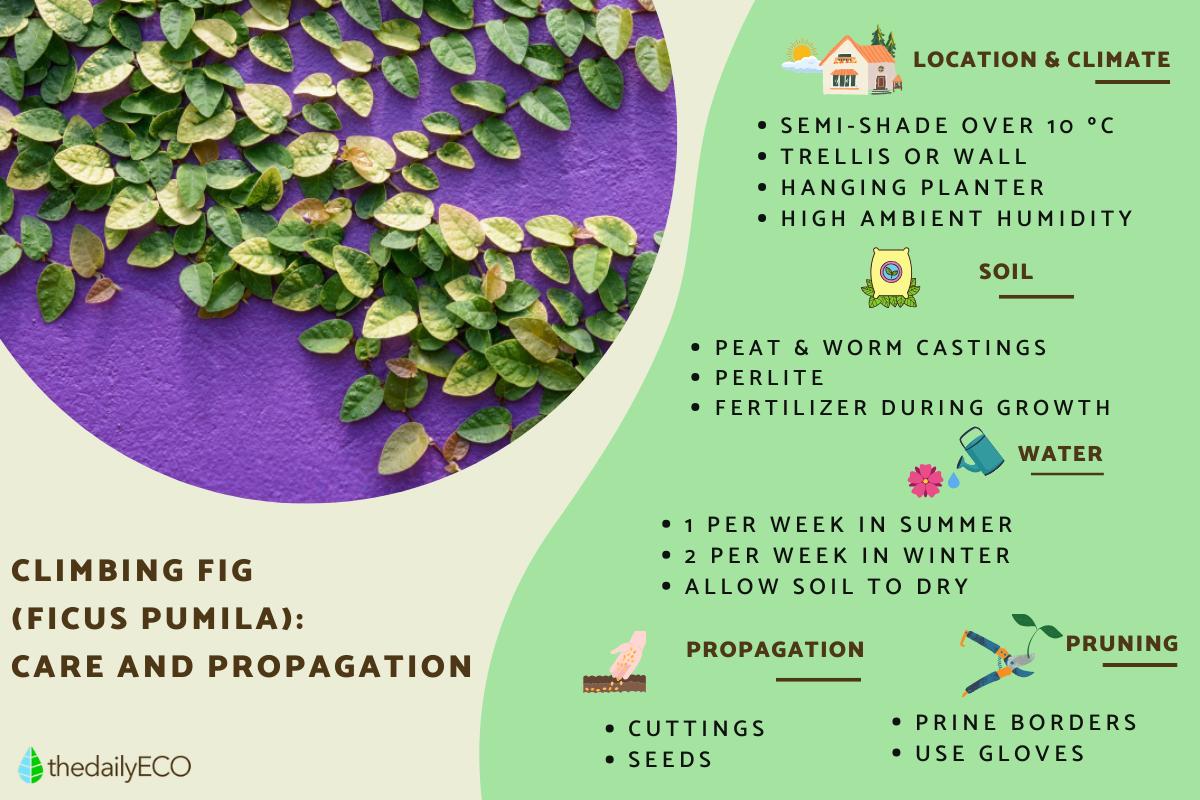
- Light: a creeping fig can do well in different light conditions. It can be kept in full sun or in partial shade. However, direct sun can cause yellow leaves due to excess light, so we should move it if this occurs. Ideally, it is recommended to place the plant in semi-shade because this should result in the plant having leaves which are a rich dark color. Learn about other types of partial-shade plants you might want to keep at home.
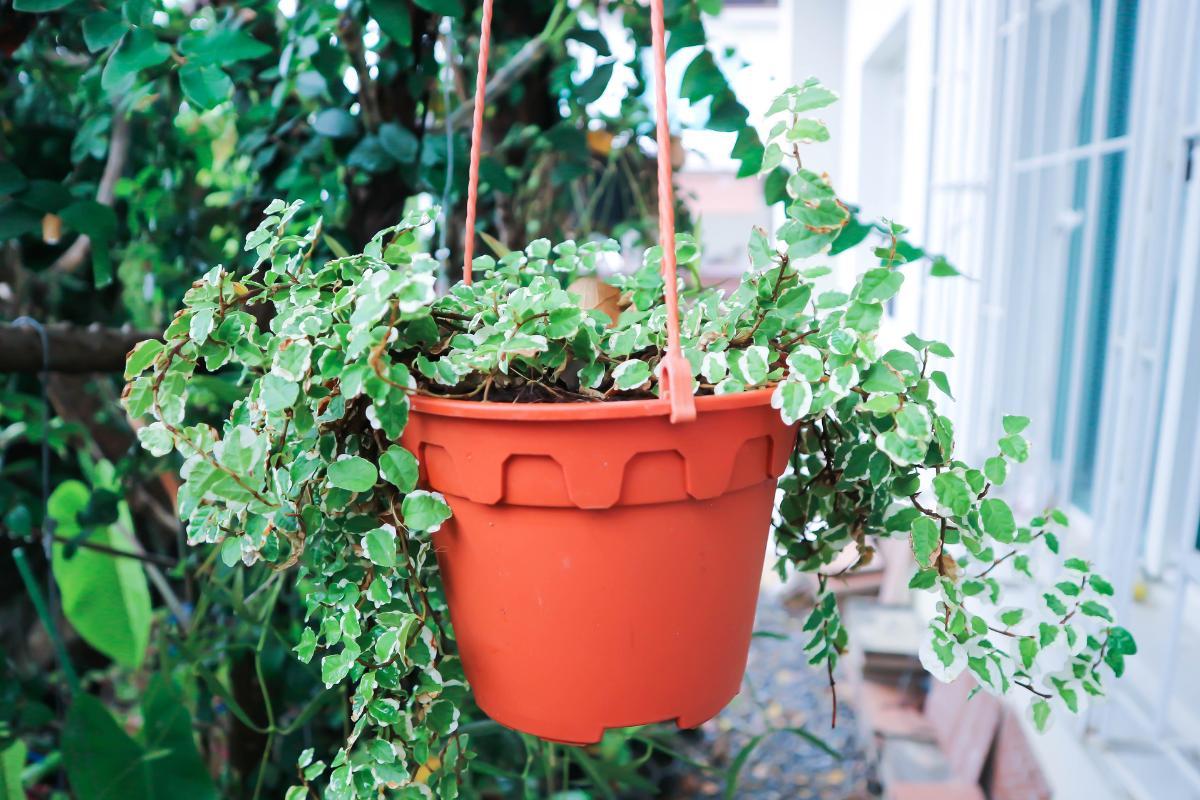
- Varieties: within this species there are many varieties, with the most popular being the Ficus pumila ‘Variegata’. This type is identified by having a white margin, giving an interesting look to the plant. It is necessary to give this type of creeping fig a lot of light, otherwise the white margins will begin to fade.
- Walls: when used on vertical surfaces, it still manages to cover walls densely without leaving visible space. It is a perennial plant that keeps its leaves all year round. This helps to keep your garden design consistent throughout this time using vertical landscaping.
- Planting: when F. pumila is used as a climber, a support is needed to guide growth. This can be in the form of a as a thick stick, a fence, a trellis or directly on a wall. This helps the plant to guide itself, but it can also be left to run over the ground as a creeper. It is also often used in hanging baskets or over balconies. Hanging vines require specific pots to ensure they are able to thrive.
- Temperature: it is a plant native to tropical areas, so it adapts well to warm places. It must be kept protected from frost as this will cause the leaves to become damaged without being able to recover the plant. The temperature must always be higher than 10 ºC/50 ºF.
- Placement: it is not recommended to keep creeping figs indoors where there are stoves or heaters because they have a high demand for ambient humidity. These devices eliminate it from the environment and can cause the plant to dry out.
If you want to grow a climbing fig at home, you can use the link below to purchase a potted version of this plant:

Climbing fig plant soil and fertilizer
The substrate for F. pumila should be rich in organic matter. You can find nutrient-rich soil for sale, but it is best done at home by mixing 3/4 parts peat with one part worm castings to provide nutrients. To this is we should add a handful of either lava rock for plants, medium grain pumice or vermiculite. This will give structure to the soil and allow good drainage. All parts should be integrated well and then we can place the roots of the plant inside.
The growth stages of climbing figs occurs during spring and summer. At this time, it is recommended to apply a nitrogen-rich fertilizer once a month to boost growth.
If the climbing fig plant is kept in a pot, it is recommended to transplant once every 3 years to give it more space. If you do not consider transplanting necessary, add a mulch of compost or worm castings covering 3 centimeters of the surface to replenish nutrients.
Learn how to make worm castings at home with our related guide.

Watering climbing figs
The climbing fig plant needs to be moderately watered during the growth stage. During the hot season, you have to water the plant twice a week and once a week during the winter. Make sure the substrate dries out a little between waterings.
Ficus pumila plant greatly appreciates environmental humidity, so you should spray the leaves with water when it is hot. If kept as an indoor plant, another suggestion is to have a humidifier in the room where the plant is located. This will help to ensure the ambient air has enough moisture. We also recommend that you learn about hygrometers which measure humidity for plants. This helps to regulate the environment for the plants.

Pruning Ficus pumila
Pruning this species is recommended if vertical or horizontal growth is not desired. Climbing figs it tend to grow quickly on surfaces. It is also recommended to trim the edges of the plant to keep it within your preferred margins. This regular maintenance prevents the plant from growing uncontrollably, something helpful since it has a tendency toward aggressive growth and can invade unwanted spaces. Always remember to disinfect the shears before and after pruning.
You have to be careful when pruning climbing figs. Wear long sleeves and gardening gloves because the sap of Ficus pumila is toxic. It oozes like white milk and can cause skin irritations. Consuming it internally can also have consequences, so you must be especially careful not to leave it within the reach of children and pets who are unaware of the dangers of nibbling on the plant.
Climbing fig propagation
The simplest propagation is done by cuttings using semi-woody stems. To propagate Ficus pumila use the following steps:
- You should look for a healthy mother plant, and cut the stem with well-washed and disinfected pruning shears to prevent the spread of fungi.
- The cutting is placed in a pot with soil that is kept moist.
- If you have a heating mat or lamp for plants, use it with your cuttings to speed up the growing process of the roots. This propagation process should be done in spring or summer.
Another method of climbing fig reproduction consists of guiding the stem of the plant over soil where it will take root. It can be cut later or left in place to create a dense ground cover. It can also be reproduced by seed, but you have to get them from specialized gardening stores and it is a longer and more complicated process.
If you want to learn about other plants you want to care for at home, you can look at our plant care guides how to care for Kalanchoe farinacea and how to care for paddle plants.
If you want to read similar articles to Creeping Fig Plant Care and Propagation, we recommend you visit our Plant care and cultivation category.
- Royal Horticultural Society. (n.d.) Ficus pumila 'Sonny' (v). Retrieved from: https://www.rhs.org.uk/plants/86173/ficus-pumila-sonny-(v)/details
- Harrison, M. (2006). Groundcovers for the South. United States: Pineapple Press.