The Differences Between Atoms and Molecules

The origin of life has intrigued humans since the beginning of consciousness. It is no surprise that understanding these origins has been influential in various scientific disciplines. Desire to understand and the ability to do so have not always been equal and our understanding of the fundamental building blocks of life is both relatively recent and still incomplete. Part of the reason we have furthered our knowledge as far as we have is the advancement of technology, especially that which involves microscopy. This is the field of study addressing microscopic entities. This is where atoms and molecules come in.
You may be aware that atoms and molecules are fundamental building blocks of life. However, you may not be aware of their characteristics and function. This is why thedailyECO explains the differences between atoms and molecules. By making an atom and molecule comparison, we can better understand how matter is formed.
Difference between atoms and molecules
Although they are both microscopic entities, atoms and molecules are not the same. They share certain characteristics such as the fact they are the component parts of both living and non-living matter. It is these similarities which can lead to some confusion, especially since one is made from the other. For this reason, a helpful way to explain is that molecules are made from atoms.
The atom is the smallest known unit in the universe. We may think of the cells in our body as being infinitesimally small, but even plant and animal cells are made up of atoms. Molecules are entities which are made up of two or more atoms. Independent atoms can exist, but not molecules without atoms. However, atoms do not exist individually on their own, whereas molecules can do so.
If this still makes it difficult to understand the differences between molecules and atoms, we can help elucidate by looking at the definition of atoms and molecules individually.
Learn more about how atoms and molecules create life with our comparison between animal and plant cells.
What is an atom?
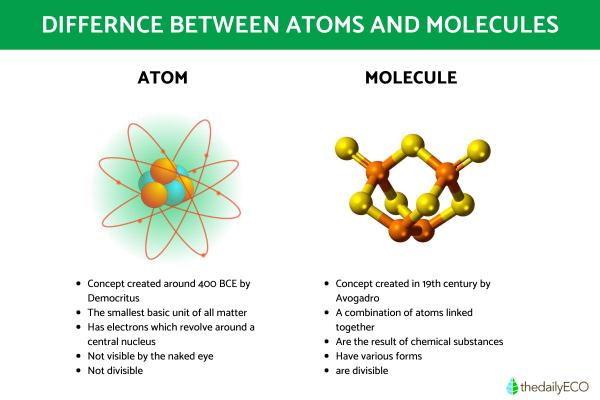
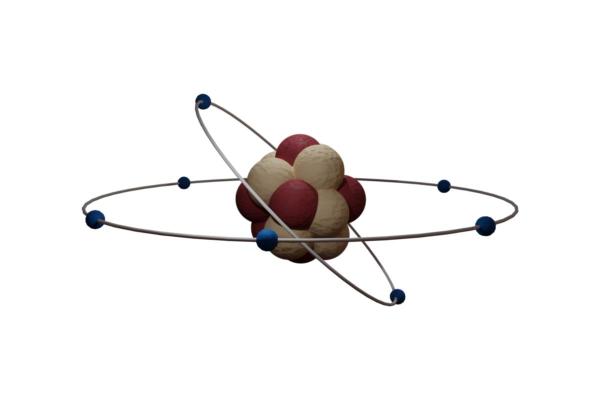
The atom is the smallest basic unit that makes up matter. Each atom has electrons that revolve around a central nucleus, which is made up of neutrons and protons. Each of these parts of an atom exist thanks to a balance in electrical charge:
- Electrons have negative charge
- Protons have a positive charge.
- Neutrons have a neutral charge
Not all atoms are the same. Chemical elements are not made of atoms, but are different types of atom. Each one has different numbers of protons, something we refer to as their atomic number. Since no element has the same number of protons, each element has their own unique atomic number, something we can see charted on the periodic table of elements. These are also distinguished by their atomic mass, i.e. the total number of protons and neutrons.
Our knowledge of atoms comes from the development of atomic theory, a field of study which has its origins in ancient Greece. Specifically, it is believed the Greek sage Democritus created the concept around 400 BCE. This kernel of an idea was that there must be an indivisible unit which makes up all matter. It wasn't until twenty centuries later that scientists were able to find proof of this concept.
Now we know what atoms are, we can take a look at some of their specific characteristics:
- They are not visible to the naked eye: instead, optical tools such as the electron microscope are required.
- They are indivisible: that is, they cannot be divided (with the exception of nuclear fission).
Examples of atoms
Some examples of atoms that we find in our day to day are the following:
- Sodium atoms
- Potassium atoms
- Helium atoms
- Hydrogen atoms
What is a molecule?
The concept of a molecule was created by the Italian chemist Avogadro who lived between 1776 and 1856. He did so as a response to a problem in the calculation of volumes in gases. He determined that some gases must exist as diatomic molecules, i.e. they have two atoms. From this approach it was understood that atoms can be united.
From this basis, we can define a molecule as the combination of more than one atom that are linked together. These molecules are generated as a result of chemical substances. They not only occur with gases, but with all kinds of elements such as liquids or solids.
The union in the molecule can be of the same or different elements. Some may be of few bonded atoms and others very large. Unlike atoms, molecules can have various shapes and sizes.
These are some characteristics of molecules:
- They are made up of more than one atom
- They are divisible into smaller parts
- They create interactions between them
- They can have a wide variety of shapes
Molecules can create interactions with other molecules thanks to ionic or covalent bonds. Ionic bonds occur when an electrical balance is sought from a charge difference between atoms. From here an electron is transferred to another forming a bond. On the other hand, covalent bonds are formed when an electron is shared between both atoms. These bonds prevent the molecules from having any charge and make them electrically neutral.
Variations in shape of molecules is due to the fact they are made up of two or more atoms. These shapes generally range from helical, pyramidal, round or linear, among others.
Examples of molecules
After having read the definition of what a molecule is and some of its characteristics, here we bring you examples of it.
- Salt (NaCl): found naturally in seas, soils and organisms, but it is also used for human consumption in food.
- Water (H2O): the basic molecule of life.
- DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid): is the molecule in which the genetic material of living beings is housed.
- Polyethylene ((C2H4)n): it is the common plastic that we know and it is the simplest polymer.
- Proteins: also called biomolecules. They are made up of the elements oxygen, phosphorus, sulfur, nitrogen, carbon and hydrogen.
We look at how molecules influence life with our article on the differences between DNA and RNA.
If you want to read similar articles to The Differences Between Atoms and Molecules, we recommend you visit our Biology category.
- Trejo, M. (1986). The structure of the atom. Mexico: Cultural Publications.






