The Difference Between Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic Cells

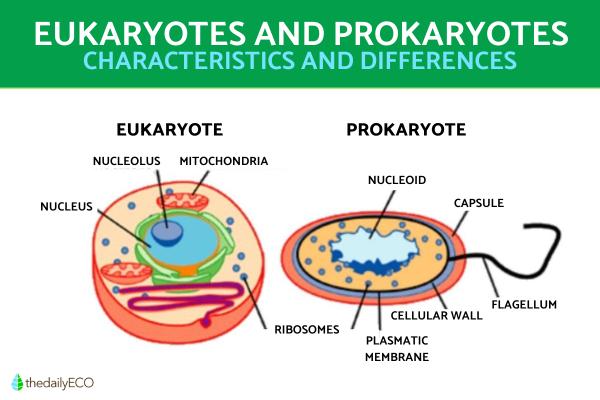
When we look at the diversity of nature, we may marvel at how these incredible organisms that inhabit are planet differ from each other. This wonderment is made all the greater when we consider the fact all the cells of living beings evolved from the same common cell ancestor. We know this thanks to the science of cells, otherwise known as cell biology. They have allowed us to understand the characteristics of the fundamental units of life. With microscopic investigations, we have been able to understand different types of cells. All cells fall into one of two cell types, either prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
At thedailyECO, we explain the differences between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. We do so by providing explanations of their characteristics and functions, as well as diagrams of what they look like.
Differences between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cell
The main differences between eukaryotes and prokaryotes are determined by their size, as well as the presence or absence of certain organelles and cell structures. For this reason, we are going to look a the main differences between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells:
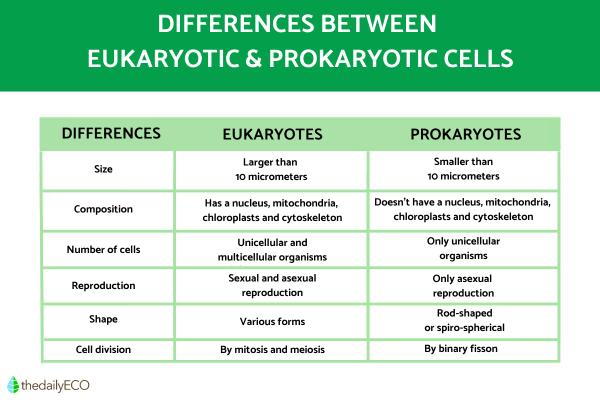
- Size: generally speaking, we can establish that eukaryotic cells are larger (more than 10 micrometers) and have greater complexity compared to prokaryotes. The latter's size does not exceed 10 micrometers and they have a simpler structure.
- Composition: the cell nucleus is where the cell's DNA is bounded. This nucleus is present only and exclusively in eukaryotic cells, as are the cytoskeleton and other cell organelles, such as mitochondria, chloroplasts and vacuoles.
- Number of cells in organism: prokaryotes are characteristic of independent unicellular organisms, while some eukaryotic cells are unicellular and live freely, others constitute complex multicellular organisms.
- Reproduction: another aspect to differentiate between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells is reproduction. Prokaryotic cells always carry out asexual reproduction, while eukaryotes can carry out both asexual and sexual reproduction processes.
- Shape: while eukaryotic cells can have a wide variety of shapes, prokaryotic cells are usually rod-shaped or spiral-spherical. In addition, the latter can form colonies.
- Cell division: eukaryotes carry out cell division through mitosis and meiosis. On the other hand, prokaryotic cells perform it directly, by binary fission.
One of the key differences between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells is their ability to be multicellular. While eukaryotic cells can be unicellular, they are also able to make up multicellular organisms. Prokaryotic cells can only be unicellular.
Similarities between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cell
Now we have explained the differences between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells, it is important to remember they also have much in common. The following similarities between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells are based on both form and function:
- Significance: both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells are the basic and fundamental units of life on Earth. Thanks to these basic building blocks of life, each and every one of the different unicellular and multicellular organisms have been able to evolve and colonize the different habitats of the planet.
- Structures: both types of cells are characterized by being structures delimited by membranes that preserve their DNA or genetic information inside. They also contain different enzymatic machinery that allows them to develop their vital functions, i.e. feeding, growth and reproduction.
- Development: in order to survive and evolve, eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells constantly convert energy from one form to another. They also maintain a continuous relationship with their exterior in order to respond to the different sources of chemical-biological information they receive from the environment.
As we have explained, different organisms have differences in their cellular structure. Learn more about these differences with our comparison between plant and animal cells.
What is a eukaryotic cell?
The meaning of eukaryote comes from the Greek, where eu means ‘true’ and karyon means ‘nucleus’. In this way, the main characteristic that defines eukaryotic cells is the presence of a true nucleus inside their cellular structure, which delimits and maintains the cell's DNA in an organized way.
In addition to the nucleus, among the characteristics of eukaryotic cells we find that they have a wide and complex system of cellular organelles. The following organelles of eukaryotic cells stand out:
- Mitochondria: capable of generating energy that the cell uses to feed itself and grow.
- Chloroplasts: present in photosynthetic organisms.
- Cytoskeleton: responsible for cell movement.
- Endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus: in which countless substances and chemical components of the cell membrane and other structures are manufactured, transported and modified.
Regarding their organization and way of life, these complex eukaryotic cells are capable of living freely as unicellular organisms (such as amoebas of the Protista kingdom or yeast, Fungi kingdom), as well as being able to form groups and create multicellular organisms of astonishing complexity. Multicellular organisms include all of the Plantae kingdom and the Animalia kingdom, and some of the Fungi kingdom.
You can learn more about the structural parts of cells with our article on what are organelles?
What is a prokaryotic cell?
Prokaryotes are the most diverse type of cell, as well as the simplest and oldest. We know this by looking at the evolutionary history of living organisms. Its derives from the Greek pro which means ‘before’, referring to its existence prior to the appearance of the other type of existing cells, the aforementioned eukaryotes.
The different prokaryotic cells that have flooded practically all the habitats on Earth with cellular life belong to the kingdom Monera and are bacteria (Eubacteria) and archaea (Archea). You can find out more about these organisms with our article on the Kingdom Monera.
If we make use of a high-resolution electron microscope, we can observe how the interior of prokaryotic cells is practically reduced to a matrix without a well-organized internal structure. The cytoplasm appears in a single compartment (aqueous gel in which the accumulate chemical molecules) which contains cellular DNA. Likewise, we could see how a resistant protective layer surrounds said compartment. This is the cell wall.
Other of the main characteristics of prokaryotic cells are their variable morphology (spherical, spiral, rod, etc.), as well as their rapid division through asexual reproduction. They also have the ability to exchange generic material with other organisms through certain structures present in their cell wall, membrane and cell.
Learn more about the importance of chloroplasts with our article on types of chlorophyll and their functions.
If you want to read similar articles to The Difference Between Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic Cells, we recommend you visit our Biology category.
- Becker, W., Kleinsmith, L., & Hardin, J. (2007) The world of the cell. Pearson Publisher, pp: 1-19.
- Alberts, B. et al., (2011) Introduction to Cell Biology. Editorial Medica Panamericana, 3rd edition, pp: 1-23.






