Ecosystems
Dive into ecosystems with expert insights on biodiversity, habitat dynamics, and human impact. Explore compelling, science-driven narratives today!
71 articles

New
New
The Gran Chaco forest is the second-largest forested region in the Americas, second only to the Amazon rainforest. Located in South America, the Gran Chaco spans southern Bolivia, western Paraguay, northern Argentina, and a small part of Brazil. This massive ecosystem covers over 647,000 square miles,...

Have you ever wondered why some places on Earth are covered in dense forests while others are barren deserts? Or why certain animals and plants can only be found in specific locations? The answer lies in the fascinating world of terrestrial ecosystem. Terrestrial ecosystems are all around us, from the trees...

Desert pavements are arid topographical regions which are characterized by a surface covered in rocks, pebbles or gravel with little or no sand. While we might most associated deserts with sand, desert pavements represent a very large portion of this planet's desert areas. Of great importance to their respective...

The terms "flora" and "fauna" represent the living organisms that inhabit our planet. These classifications help scientists and nature enthusiasts alike understand the diversity of life across Earth's many ecosystems. Simply put, flora refers to all plant life while fauna encompasses all animal life. This...

A wadi is a dry channel in that only transports water intermittently, usually after intense rainfall in arid and semi-arid regions. Essentially, it is a dry river bed because it was created by water which once passed through the channel. These channels are characteristic of deserts and other similar areas...

Volcanic islands start underwater, where Earth's internal forces push magma up through the seafloor. Out of the millions of volcanoes on the ocean bottom, few grow tall enough to break through the water's surface. These islands take different paths to formation, some pop up where tectonic plates meet...

An oasis is a fertile area with water that is located in the middle of a desert or a similarly arid region. Its formation is dependent on underground water sources, rivers, fossil waters or human intervention through wells and irrigation systems. Oases have been fundamental for the survival of communities in...

Forests are more than just collections of trees, they are complex and dynamic ecosystems characterized by intricate interactions between living organisms and their environment. These vital habitats, covering vast portions of the Earth's land surface, play a crucial role in regulating climate, supporting...

The Hadal Zone, the deepest part of the ocean, remains one of Earth’s most mysterious and unexplored regions. This dark and high-pressure environment is home to fascinating flora, resilient fauna, and a unique ecosystem that thrives against all odds. From bioluminescent creatures to microbial life surviving on...

In a world where urbanization, agriculture, and infrastructure development continue to encroach upon natural habitats, wildlife corridors have emerged as a critical strategy for conservation. These pathways, which connect fragmented ecosystems, play a vital role in ensuring the survival of countless species...

Sand dunes are accumulations of sand formed by the action of the wind. Their formation is associated with the transport of grains of sand which are deposited in large amounts when they encounter certain obstacles. There are different types of dunes, often defined by their shape and direction in which they...

Also known as flooded forests, freshwater swamp forests are characterized by periodic flood by bodies of water such as rivers or lakes. While this flooding can be seasonal, it can be more frequent in certain areas. Their duration and the depth of the flooding can also vary according to region and the...

Also known as tropical dry forests, dry forests are a relative description. While rainforests have periods throughout the year when there is more rainfall, high rainfall occurs throughout the year. In a dry forest, there are distinct wet and dry seasons with periods of little to no rain. As with rainforests,...

A sclerophyllous forest is an ecosystem characterized by the presence of vegetation adapted to Mediterranean climate conditions. This is largely defined by its dry summers with hot temperatures and wet winters which are relatively mild. The flora and fauna of these ecosystems have specific adaptations to...

A chaparral is a biome characterized by dense and shrubby vegetation which have a Mediterranean climate. The latter means they have dry summers and went winters. This type of biome is most associated with the United States, but there are chaparrals outside of the US such as in the Mediterranean basic, Chile,...

We know that different ecosystems can vary greatly in terms of biodiversity and geographical features. However, we can define ecosystems by certain characteristics. For example, a marine ecosystem is defined by saltwater and a desert ecosystem is defined by a lack of precipitation. One of the most defining...

Fynbos is the term for a type of vegetation characteristic of the southwestern region of South Africa, known for its extraordinary biodiversity and adaptations to its Mediterranean climate. This ecosystem is part of the Cape Floral Kingdom. It is one of the world's six floral kingdoms and is home to a rich...
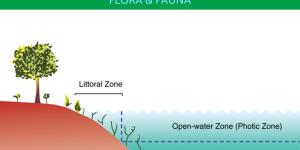
Bodies of water such as oceans and lakes have different characteristics depending on the part in question. When the body of water is sufficiently large, it can be divided into various parts known as zones. These zones have varying characteristics, influenced by various factors. One of the most important is...

The pelagic zone is a part of the open ocean which is divided into different layers. It begins horizontally at the end of the neritic zone, but extends vertically from the surface to the depths of the ocean. The different layers of the pelagic zone have different characteristics, impacting the types...

Lotic ecosystems are freshwater ecosystems which have dynamic currents of water, as opposed to those bodies of water which are relatively stagnant. Aquatic ecosystems are defined by various factors, such as size or temperature with the level of salinity being a major determinant. Movement is a categorization...

Have you ever stood at the edge of a river, gazing out towards the vast ocean, and wondered what happens where the freshwater meets the salty sea? The answer lies in a fascinating and crucial coastal ecosystem: the estuary. These dynamic zones, where rivers and oceans collide, are a blend of freshwater...

Tundras are geographical areas which are characterized by short growing seasons, harsh conditions and other limitations for the development of life. While these geographical areas constitute a biome, each tundra biome can have various ecosystems within it. They are all subject to certain types of landscape,...

The coastline is a transition area between land and sea that encompasses a diversity of coastal ecosystems. These ecosystems are of great importance for both natural and human life. Coastlines vary greatly in term of geographical formation, ranging from sandy beaches to coral reefs. These dynamic environments...

Lentic ecosystems are aquatic ecosystems associated with lakes and other slow-moving bodies of water. As they are a type of ecosystem, they are used to refer to how plant and animal life interacts with their environment as a community. In this case, it is a lentic environment. The types of life which...

Our planet thrives with life, a vibrant tapestry woven across diverse environments. From the sun-drenched stratosphere to the crushing depths of the ocean, a multitude of habitats provide the stage for this extraordinary biodiversity. While habitats seem infinitely varied, we can broadly classify them...

Swamps often get a bad rap – murky, mysterious, and maybe even a little monstrous. But look beyond the surface, and you'll discover a fascinating and vital ecosystem teeming with life. These unique wetlands are characterized by their waterlogged soils and the presence of standing water, creating a dynamic...
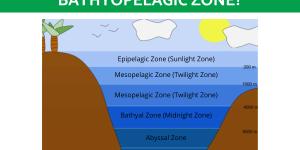
Our planet's oceans hold a hidden world, a vast realm shrouded in perpetual darkness. This region, known as the bathypelagic zone, plunges from 1,000 to 4,000 meters below the surface. Sunlight never reaches these depths, yet the bathypelagic zone teems with life. Extraordinary creatures, adapted to the...

Stacks are prominent rock formations present in various geographical environments, providing prominent elements in the configuration of the natural landscape. While there are geological stacks present inland, we may me more familiar with sea stacks than land stacks since they are more revered for their...

Have you ever gazed out at a dramatic coastline and wondered about those landforms jutting into the sea or the deep indentations carving inland? These captivating features, capes and gulfs, represent opposite yet fascinating interactions between land and water.
This article from thedailyECO dives into the...

A bay in geography is a natural coastal inlet of a large body of water such as a sea, ocean or lake that has a considerable area, but is generally smaller than that of a gulf. Such a coastal relief can be the result of various geological processes such as coastal erosion, glacial movement, volcanic activity...

Our planet is a watery world, with aquatic biomes covering a vast majority of its surface. These biomes are classified based on factors like salinity (salt content) and water movement. Understanding aquatic ecosystems isn't just for curious minds. It's crucial for ensuring the health of our planet and...

Like many geographical features, it can be difficult to differentiate between a gulf vs. bay. They are very similar coastal areas, surrounded both by bodies of water and land on either side. There are some notable differences which can lead us to describe one or the other. These differences can be found...

A cape is a geographical feature that is formed by an extension of land that projects into the interior of the ocean. Such capes have served for years as navigation reference points and as strategic points for the placement of lighthouses. Similarly, they are home to a rich biodiversity of plant and...

Fjords are responsible for some of the most beautiful and picturesque sights in the world. Found near the sea, they are coastal features which can vary greatly in form and appearance. They always have steep and rocky slopes, geographical features which are related to fjord formation. They are the result...

We often confuse the terms jungle and forest, but this is because they are closely related. A jungle is a type of dense forest, usually found in tropical or subtropical regions. This is why we often associate jungles with tropical rainforests since they are one of the densest types of jungle forest. A...

An alluvial plain is a flat landform that is created by the accumulation of sediments. These are sediments carried by river courses, especially common in lower areas where the speed of the current decreases. An alluvial plain may be completely or partially covered by water during periods of flooding. Among...

A river delta is a geographical feature that forms at the mouth of river systems, given its distinctive landform properties thanks to a dynamic sedimentation processes. Deltaic systems give rise to the formation of intricate channels and sandbanks. This creates regions rich in biodiversity, thanks to the...

The upper layer of a forest or jungle formed by branches and leaves where the treetops intertwine is known as the tree canopy. More than simply a referential term, tree canopies are unique ecosystems in which only certain types of life can thrive. In addition to providing habitat to the various plant and...

An atoll is a coral island that is characterized by having a ring shape, enclosing an interior lagoon that is connected to the ocean. Atolls are formed by the accumulation of corals at the base of the island that provide an ideal environment for their growth. After a long period of time, the island sinks...

Peatlands are a type of wetland which contain peat, a substance made from accumulated partially decomposed organic matter. When this peat reaches a certain standard, it can be used for fuel. Peatlands can be found in approximately 180 countries, in different climatic zones. Peat in its moist state serves...

A biome is a large-scale ecosystem that is characterized by its unique climate, vegetation, and wildlife. Biomes are classified based on their temperature, precipitation, latitude, altitude, plant structure, leaf types, spatial distribution of plants, and ecological succession. From the lush rainforests...

Riverbanks are ecosystems that line the shores of rivers, creating a seamless transition between the aquatic and terrestrial worlds. These dynamic zones are teeming with life, hosting a rich variety of flora and fauna uniquely adapted to the distinct conditions they offer. As well as providing shelter and...

Nestled at the meeting point of land and sea, mangroves make up a complex and fascinating coastal ecosystems. These habitats are known for their rich biodiversity, exceptional adaptations and ecological importance. Mangroves have evolved special strategies to thrive in diverse habitats, including their remarkable...

The differences between seas and oceans is not simply due to terminology. The two terms are often used interchangeably, both referencing large marine bodies of saltwater. Despite certain similarities in the two concepts, seas and oceans are not the same. One of the key differences between seas and oceans...

The different types of deserts include sand, rock, salt, polar, cold and many more. Some of us may not be aware there are so many different types of deserts. This is partly due to the often misunderstood definition of what is a desert. A desert is an ecosystem characterized by low rainfall and limited...

Artificial forests, also referred to as cultivated or planted forests, are created by human intervention and serve specific purposes such as timber production, biodiversity conservation, or carbon sequestration. Unlike natural forests that evolve and develop spontaneously, artificial forests are meticulously...

The polar environment is one of the most fascinating and challenging regions on Earth. It's a place of extremes, where the temperature can drop to -50°C or lower, and the sun doesn't rise or set for months at a time. Despite the harsh conditions, the polar regions are home to a unique and diverse range...

Also known as laurisilva, laurel forests are subtropical forests known for high humidity and broadleaf tree species. While their name comes from the trees which constitute the Lauraceae family of plants, not all laurel forests will contain laurel trees. However, the trees which inhabit laurel forests...

Beneath the captivating surface of our oceans lies a world of astonishing beauty and ecological significance. Among the remarkable ecosystems that flourish in this aquatic realm, seagrass beds stand as a true testament to the wonders of nature. However, these lush underwater meadows often go unnoticed,...

Gallery forests, also known as riparian forests, are unique and vital ecosystems that occur along the banks of rivers and streams in arid or semi-arid regions. These forests are characterized by their linear shape, often appearing as a ribbon of trees winding through the surrounding landscape. Gallery...
