What Are Plastids in Plant Cells?


Plastids are organelles found in certain cells which play a crucial role in the survival of the organism. They are most associated with plants, but they can also be found in algae and some other eukaryotes. One of the key characteristics of plastids is that they are bound by a membrane, allowing for various process to take place. What these processes are depends on the type of plastid which include chloroplasts, chromoplasts, gerontoplasts and leucoplasts. Their functions depend on organelle type and include carrying out photosynthesis, storing nutrients, producing pigments, synthesizing essential compounds and others. thedailyECO reveals them in more detail by asking what are plastids in plant cells?
What are plastids in plant cells?
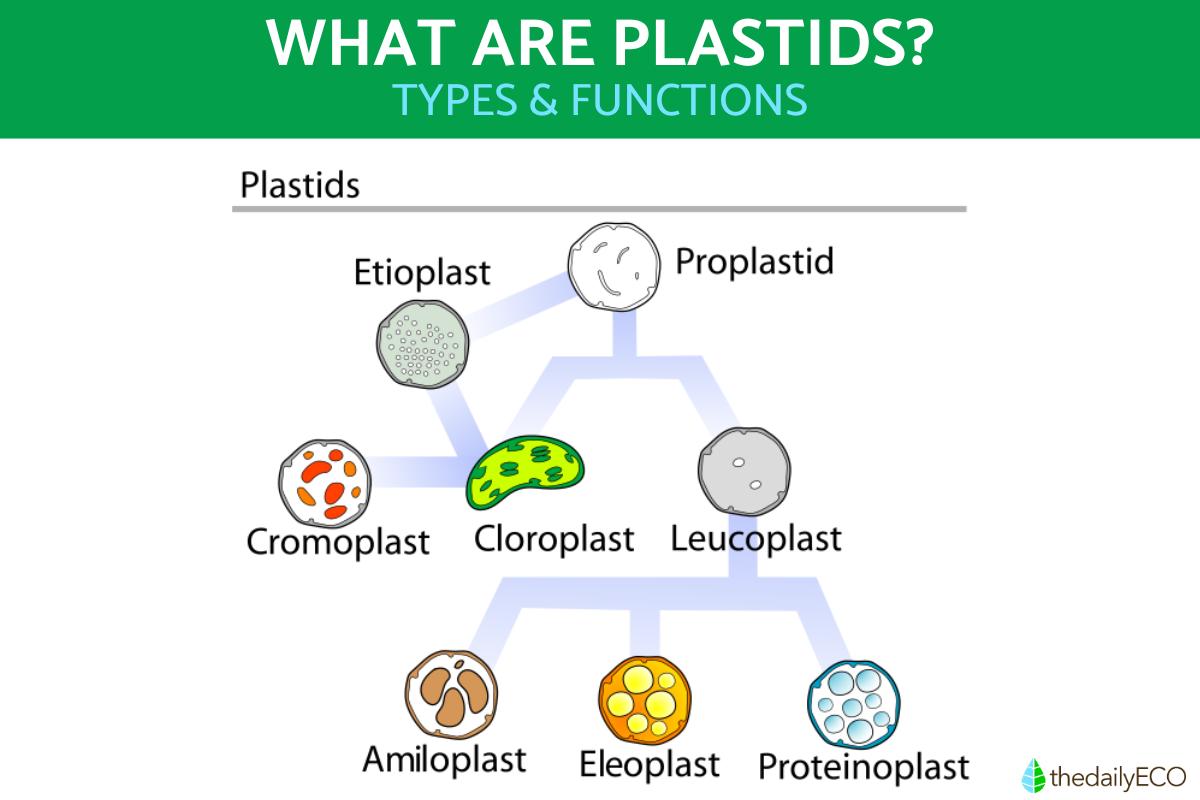
Plastids are organelles found in the cells of plants, algae and other eukaryotes. They play a crucial role in the survival of these organisms, especially in plants. All plastids begin as protoplastids, immature versions of plastids which cannot fill the functions of mature plastids. They are only functional once they develop and differentiate into several types depending on the metabolic needs of the plant.
Plastids are essential for vital processes in plants such as photosynthesis. For this process to occur, chloroplasts convert sunlight into chemical energy using the chlorophyll pigment contained within them. Chromoplasts possess other plant pigments which are responsible for providing color to different parts of the plant, while leucoplasts are primarily dedicated to food storage.
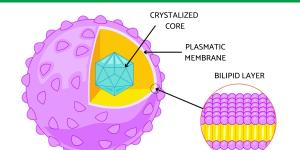
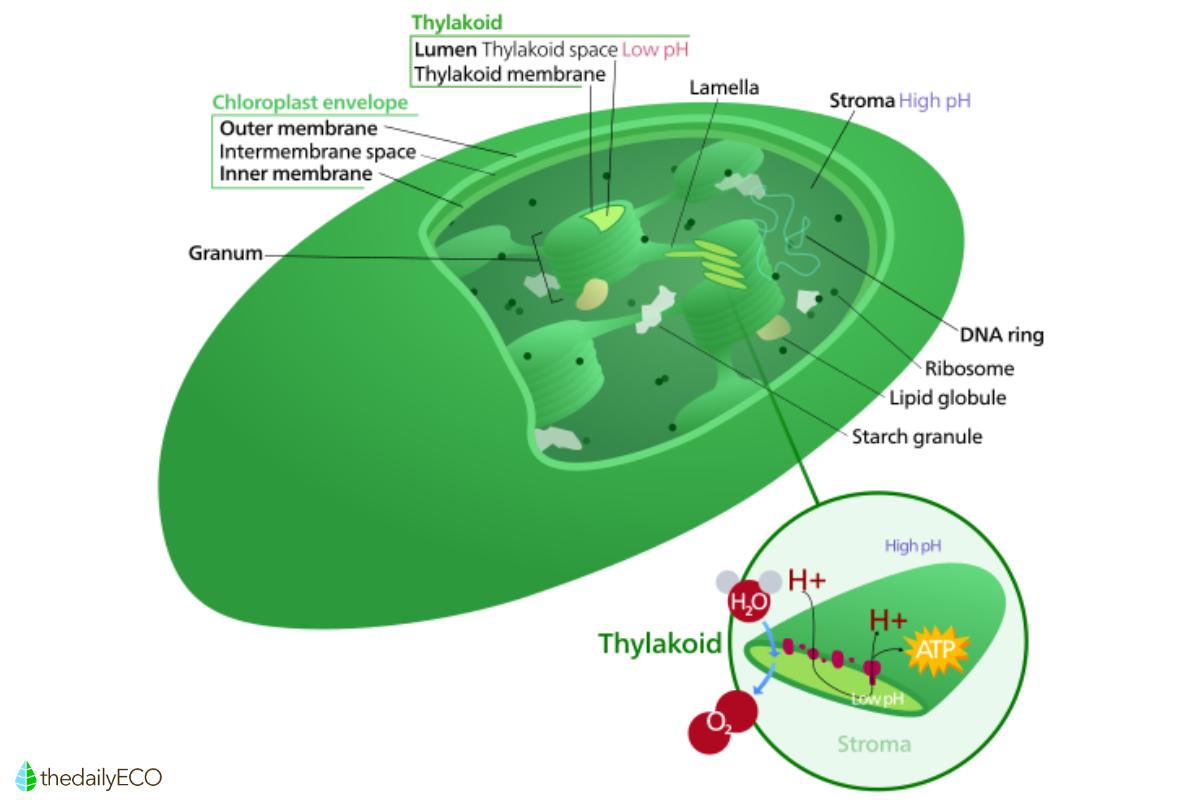
The structure of plastids includes two membranes separated by an intermembrane space and internal compartments. These differ according to the type of plastid, such as the thylakoids found in chloroplasts. These organelles contain circular DNA and molecular machinery for its replication and division. The process allows them to grow independently under the control of nuclear genes. Plastids arose through a process of endosymbiosis where a photosynthetic bacterium was engulfed by a eukaryotic cell, becoming an endosymbiont.
Discover the differences between DNA and RNA in our related guide.
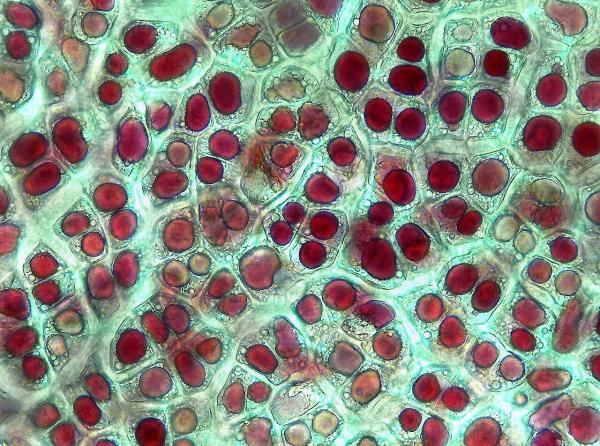
Types of plastids
To know more about what are plastids in plants, we need to understand the different types which can be found in their cells. The types of plastids in plant cells include:
Chloroplasts
Chloroplasts are the best-known plastids and are responsible for photosynthesis, an essential process for life on Earth. They contain chlorophyll, a compound which gives them their green color, and are mainly located in the mesophyll of leaves. They can be discoid, oval or spherical in shape and are surrounded by a double membrane. The stroma houses grana, stacks of thylakoids where photosynthesis takes place. Chloroplasts are essential for capturing solar energy and converting CO₂ and water into glucose.
Learn more as we ask what is a chloroplast and its function?
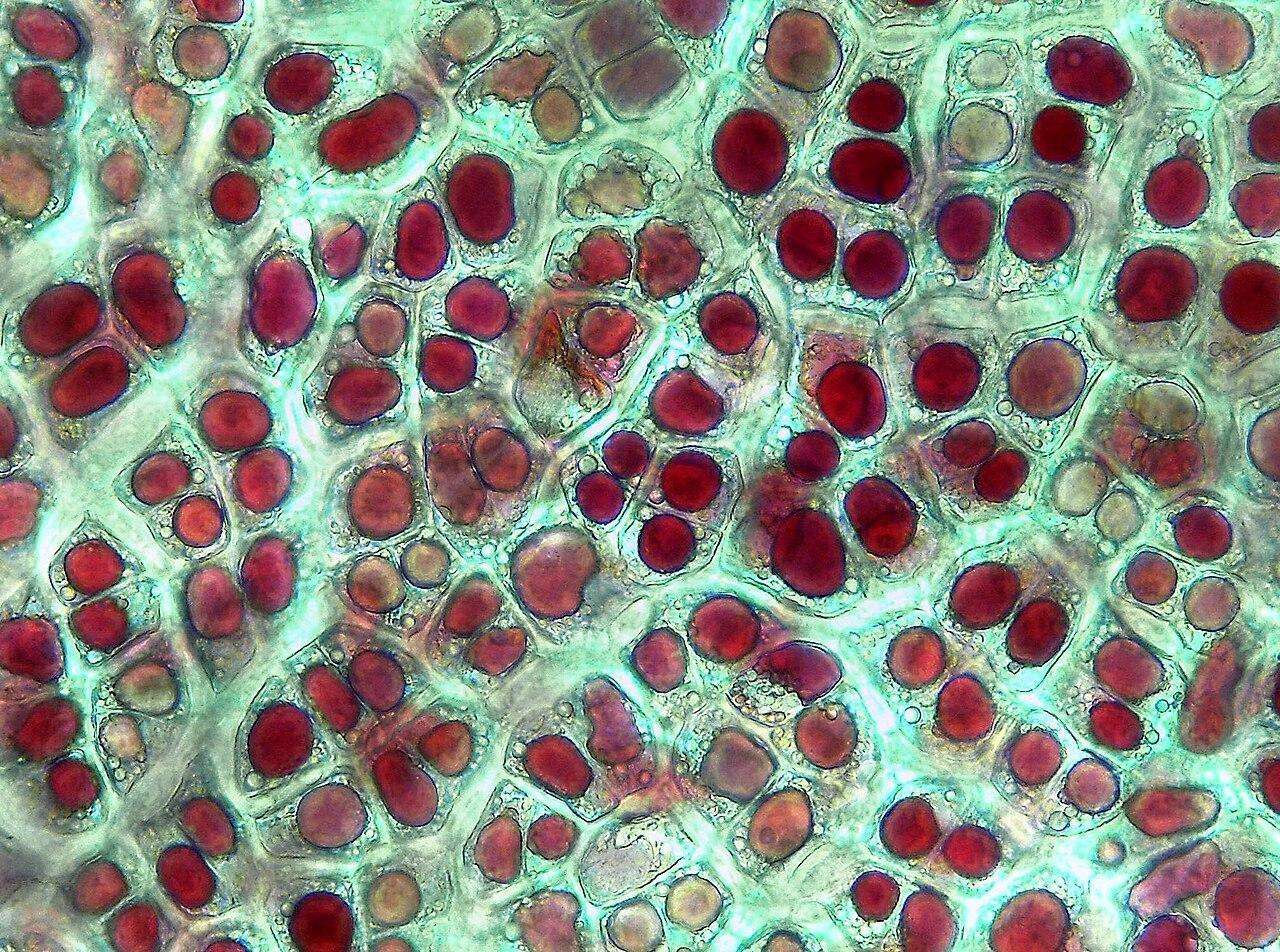
Chromoplasts
Chromoplasts are also highly pigmented plastids , but they lack chlorophyll. Instead, they are involved in the synthesis and storage of pigments such as carotenoids that give vibrant colors to flowers and fruits. These plastids are metabolically active and are found in plant parts such as flowers and fruit that attract different types of pollinators. Chromoplasts can have different morphologies, being globular, membranous or tubular, with each shape adapted to store carotenoids in different ways.
We explain their function in more detail by asking what are chromoplasts?
Gerontoplasts
As leaves age and stop performing photosynthesis, chloroplasts transform into gerontoplasts. These aged plastids regulate the dismantling of photosynthetic components and are crucial for recycling nutrients vital for plant survival such as nitrogen. Gerontoplasts exhibit significant structural changes, such as the degradation of starch granules and chlorophyll. They also provide an increase in the size of lipid storage structures.
Leucoplasts
Leucoplasts are nonpigmented plastids that are specialized for the storage of starch, lipids and proteins. They are classified into amyloplasts (starch storage), elaioplasts (lipid storage) and proteinoplasts (protein storage). These organelles are found in non-photosynthetic tissues such as roots and tubers. They are essential for nutrient storage and the synthesis of important metabolites.
We discover more about this last type of plastid as we ask what is a leucoplast?

Function of plastids
Although we have explained some of what each type of plastid does in the cell separately, we provide a more general overview as we discover what are the functions of plastids:
- They carry out photosynthesis: chloroplasts capture sunlight and convert it into chemical energy in the form of glucose, a process which is essential for plant life.
- They store nutrients: leucoplasts are responsible for storing important compounds such as starch and lipids which serve as energy reserves for periods of growth.
- They produce and store pigments: chromoplasts synthesize and store pigments that give color to various parts of the plant, such as flowers and fruits. These are very useful in helping to attract pollinators such as insects or birds.
- They synthesize essential compounds: plastids actively participate in the production of amino acids, fatty acids and hormones, compounds which are crucial for the development and function of the plant.
- They facilitate plant defense: plastids help generate secondary metabolites that protect plants against environmental stressors, such as various pathogens and adverse conditions.
- They facilitate intercellular communication: they produce signaling molecules that influence processes such as growth, development and response to external stimuli.
- They have their own DNA and ribosomes: this allows them to replicate and be used in phylogenetic studies to understand the evolution of plants. You may be interested in our article on our article on the structure and function of ribosomes to learn more.
- Their functional diversity shows that they are essential for cellular functioning: this ensures the survival and optimal development of plants in different ecosystems.
Now you know what plastids in plant cells are, you may want to know more generally about plant function with our article on the differences between animal and plant cells.
If you want to read similar articles to What Are Plastids in Plant Cells?, we recommend you visit our Biology category.
- Choi, H., Yi, T., & Ha, S. H. (2021). Diversity of Plastid Types and Their Interconversions. Frontiers in plant science, 12, 692024. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2021.692024
- Megías, M., Molist, P., & Pombal, M. A. (2023). Atlas of Plant and Animal Histology.
http://mmegias.webs.uvigo.es/index.html