What Is a Drupe in Botany? - With Examples


When we classify fruits, we may think of them in terms of consumption. For example, an aubergine is technically a type of fruit, but we eat it like a vegetable. Different fruits can be eaten in different ways, but botanical classification is not necessarily the same as culinary. In botany, fruits are classified according to whether they develop from multiple flowers, their structure and other features. One of these types of fruit is known as a drupe. While it is a term used less often outside of botany, many of the types of drupe fruits will be very well known to you.
At thedailyECO, we find out what is a drupe in botany? We look at the characteristics common to all drupes, as well as the examples we can find in nature and in the kitchen.
What is a drupe in botany?
In botany, a drupe is a simple fruit with a fibrous or leathery exocarp, a fleshy mesocarp and a woody endocarp. This endocarp is the part of the fruit commonly known as a pit or a stone. For this reason, drupes are also known as stone fruits. In simple and colloquial terms, these are mostly fleshy fruits with a maximum of two pits in their center, although the majority only have one. These fruits may be composed of one or more carpels.
You can discover more about the differences between exocarps and endocarps with our article on the different parts of fruits.
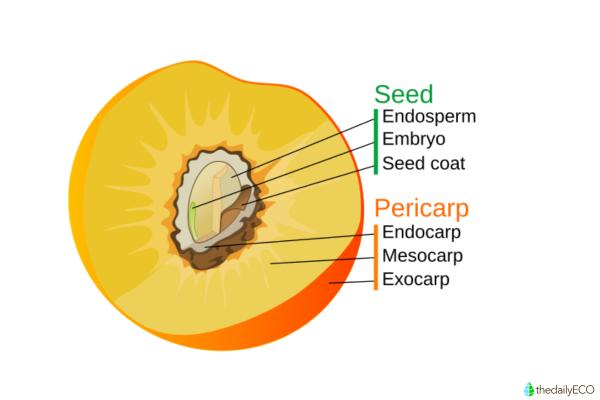
Characteristics of drupes
As we have stated, it is common to refer to drupes as stone fruits. Despite their previously defined characteristics, it is not always easy to differentiate drupes from berries. It is important to distinguish the drupe from other types of fruits such as hesperidia, pomes or berries, the latter being the most common of the simple fleshy fruits. Aside from those already mentioned, these are some of the characteristics of the drupe:
- Origin: although they usually develop from a single carpel, there are drupes that come from inferior ovaries or syncarpous ovaries.
- Amount of pits: in cases where there may be more than one carpel, each carpel may develop its own endocarp and therefore the fruit may contain one stone for each carpel.
- Variety: while examples of fleshy drupes may be better known, it is a very varied family in which we find both fleshy and dry fruits.
- Seeds: it is characterized by the fact that its seeds are extraordinarily well protected by the very hard stone, which is often confused with the seed itself.
Each fruit originally derives from the flower of angiosperms. Learn more about these origins by looking at the different parts of a petal and their functions.
Examples of drupes in botany
There are many trees and plants with drupes as their fruit, many of which are quite distinct from one another. This can be seen in the fact that both a peach and a coconut are types of stone fruit, despite seeming very different from a lay perspective. In botanical terms, we can see they both have the defining characteristics of drupes. In this way, we can say a coconut is misnamed, since it is a drupe and not a nut.
Here are some more examples of drupes in botany:
- Peach
- Olive
- Coconut
- Apricots
- Almond
- Plums
- Avocados
- Cherries
- Nectarines
We look at some of these types of drupes in more detail below:
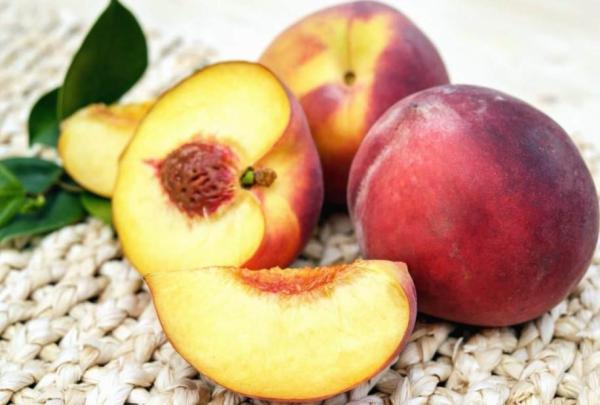
Peach
The peach tree (Prunus persica) is probably the most representative tree when it comes to types of drupe species. Drupes are generally called called stone fruits precisely because of the peach fruit. Its pit is very hard like, something you'll know if you have accidentally bitten into one.
This is a fruit tree native to China and produces a sweet and juicy fruit that is now consumed virtually all over the world. It is a deciduous species that grows to approximately 33 ft (10 m) in height, although in fruit orchards it is pruned lower to make harvesting easier.
Peaches are known for their cholesterol-fighting properties, but they also have a host of other benefits for the human body. They are also rich in vitamin A and flavonoids, which help prevent some heart diseases and ailments.
Learn more about the plant this drupe fruit comes from with our article on fruit trees that have pink flowers.

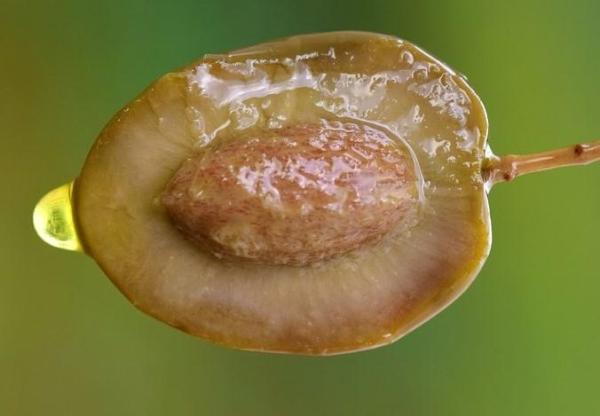
Olive
The olive tree (Olea europaea) has been cultivated for its drupe fruits since the time of the ancient Egyptians. It originates in Asia Minor and has traditionally been cultivated in the Mediterranean region, which is ideal both for its climate and the hardiness of the plant.
It is an evergreen tree with a lifespan of hundreds or even thousands of years, although it only produces useful fruit for the first few hundred years. This is especially when the tree young. They reach heights of between 6.5 to 33 ft (2 to 10 m9). As with many of these species, they are kept shorter on farms and agricultural sites to facilitate harvesting.
Despite the great resilience of olive trees, it is important that they receive sufficient minerals and water before flowering. Otherwise the flowering process can be seriously affected. Although this does not affect the tree's health, it means the fruits will not be able to grow properly. Olives are consumed in countless ways on their own, in addition to being the ingredient from which the prized olive oil is extracted. This is essential in Mediterranean cooking.
Learn more about the longevity of olive trees with our article asking what is the oldest tree in the world?

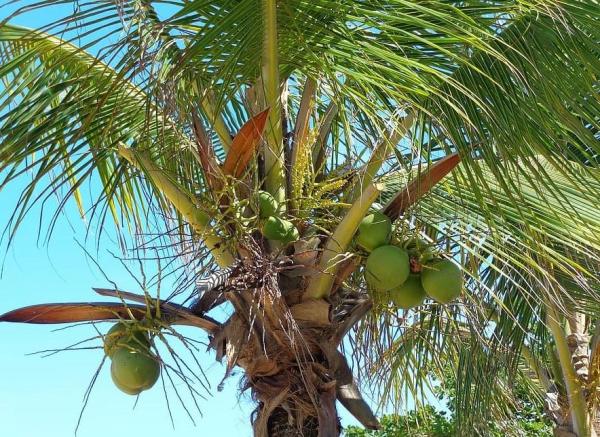
Coconut tree
The coconut tree (Cocos nucifera) is a type of palm tree which can reach impressive heights of up to 98 ft (30 m). It is a species native to sandy beaches in tropical areas, such as on the coasts of the Indian and Pacific Oceans. It is also well known on various Caribbean coastlines and its flavor is synonymous with Caribbean cooking.
Besides its striking appearance, the most remarkable feature of this palm tree is its drupe, commonly known as the coconut. Not an actual nut, it is the largest seed in existence. Coconuts are not fleshy fruits, although their white endosperm is edible. So is the water the drupe contains, known as coconut water or milk.
Thanks to such elaborate protection, coconuts can travel enormous distances by floating across the sea. They then reach the beaches and germinate there without the slightest problem.

Almond
As with all members of the genus Prunus, the almond tree (Prunus dulcis) has fruits known as drupes. This is a deciduous tree native to Central Asia. Its fruit is prized not only for the seed contained within its drupe, but also for its spectacular blossoms. The white or pink flowers appear long before the leaves themselves, so all the tree's branches are covered in this soft hue, giving it a unique appearance.
The almond fruit is not commonly eaten, but the seed inside the pit is. It is a widely known and widely used nut in many cuisines, with numerous properties. In cooking, it is used both as a seasoning or in sauces. It is also used to make almond milk, an alternative to cow's milk.
Discover more about some of the most famous trees that bear drupes with our article on the different types of cherry trees.

If you want to read similar articles to What Is a Drupe in Botany? - With Examples, we recommend you visit our Biology category.










