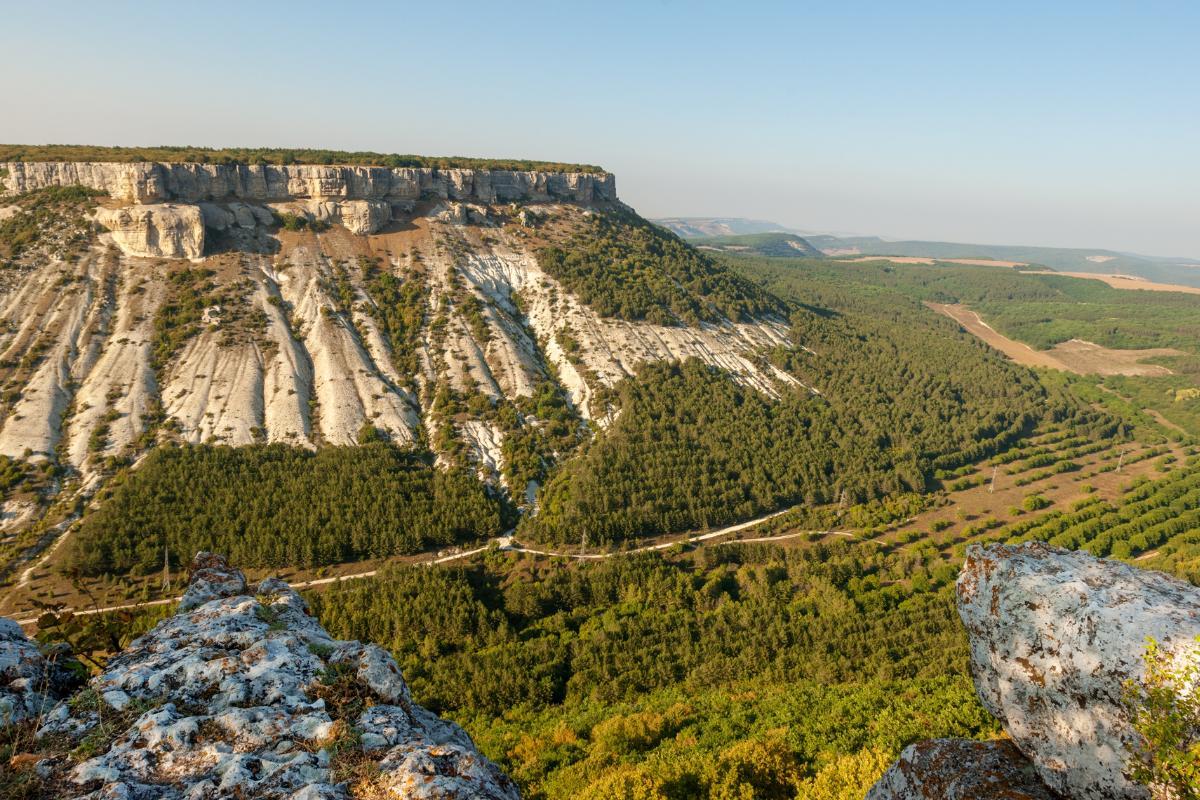
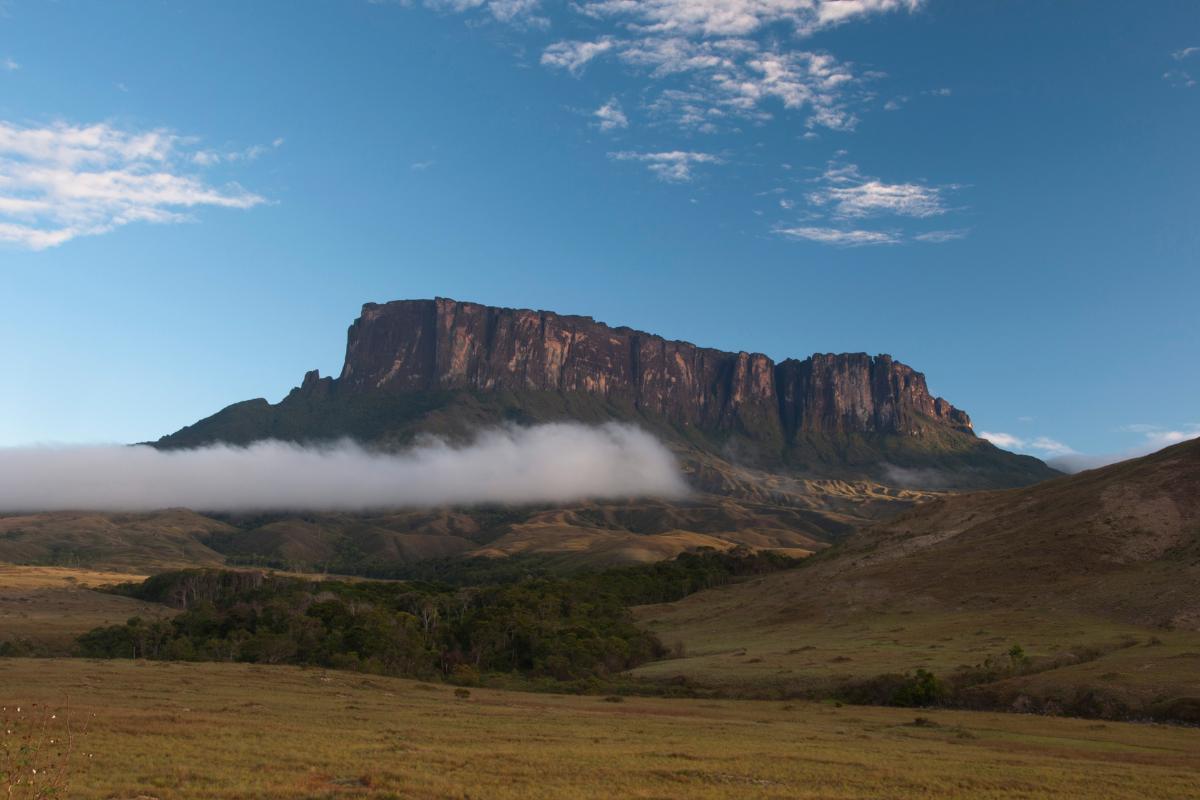
What Is a Plateau in Geography?
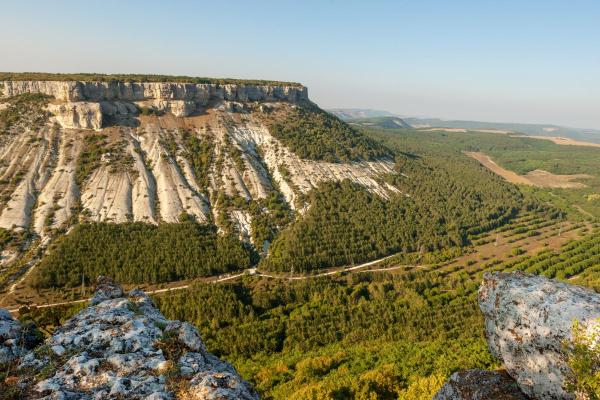


In geography, a plateau is a large geological structure which has a flat or gently undulating structure at least 500 meter above sea level. This highland landform is also known as a tableland or high plain. This is because they are a flat surface at heigh which mimics the basic structure of a table, i.e. a raised flat surface. Formation of plateaus can be a result of various geological processes, such as volcanic activity, tectonic movement or erosion. Some of the most famous vistas on Earth can be seen from plateaus. At thedailyECO, we ask what is a plateau in geography? In addition to provide information on how a plateau is formed, we see how they compare to plains and mountains.
What is a plateau in geography?
A plateau is a large, flat or gently rolling surface located at a considerable altitude above sea level. This altitude is generally over 500 meters above sea level. Its origin can be due to various geological processes such as tectonic uplift, the erosion of ancient mountains or the emergence of underwater platforms. In many cases, plateaus are ancient mountains that have been eroded by the continuous action of wind, rain and other erosive agents over many thousands or millions of years.
Depending on the region of the world, plateaus may have certain variations. These tend to vary according to factors such as size or extension. Some of the variations of plateaus include the following:
- Altiplano: this is a high and extensive plateau found between major regions of the Andes, composing one of the largest plateaus in the world.
- Butte: refers to an isolated and steep-sided hills found in the United States and Canada. They have flat tops, are located in arid areas and are smaller than most other plateaus.
- Chapada: located in the Center-West and Northeast of Brazil, it is a high rock formation (higher than 600 meters) with a very flat top and steep escarpments.
Discover how plateaus relate to other main types of relief with our related article.
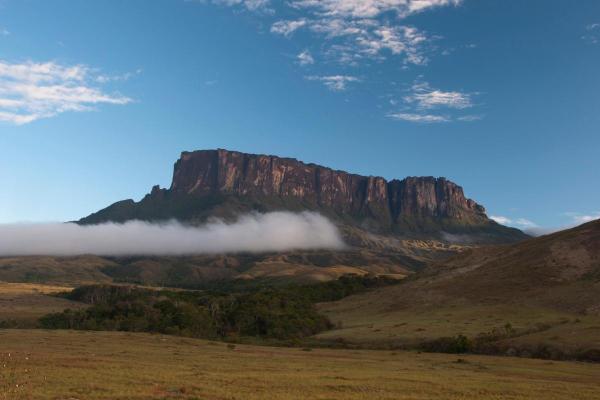

How does a plateau form?
Plateaus can form through various geological processes. Their origin varies depending on the geographical region and environmental conditions. In this way, there is no one process by which plateaus form. We look at the different processes of plateau formation below:
Volcanic formation
Plateaus generated by volcanic activity are formed by volcanic materials creating these formations. This could be the upwelling of magma from the Earth's mantle or the extrusion of lava through cracks in the crust. In the former, the magma rises and causes the terrain to rise. Tis forms large and flat surfaces at high altitudes. In the latter, the lava spreads horizontally across the surface, cooling and accumulating in successive layers to build a plateau.
Tectonic formation
Tectonic plateaus are formed by the movement of tectonic plates. This movement generates the uplift of large blocks of the Earth's crust. They are usually of considerable size and at uniform altitudes.
Formation by erosion
Some plateaus are formed by the erosion of mountains or elevated landforms. Wind, water and even glaciers found in colder regions of the planet slowly erode the terrain. This leaves flat surfaces between mountain ranges. This plateau formation process can give rise to dissected plateaus, which are highly eroded landforms cut by rivers and broken by narrow valleys.
Discover more about how glaciers affect landforms with our article on what is a U-shaped glacial valley?
Examples of plateaus around the world
Some of the most beautiful views on Earth are from plateaus. They include the following:
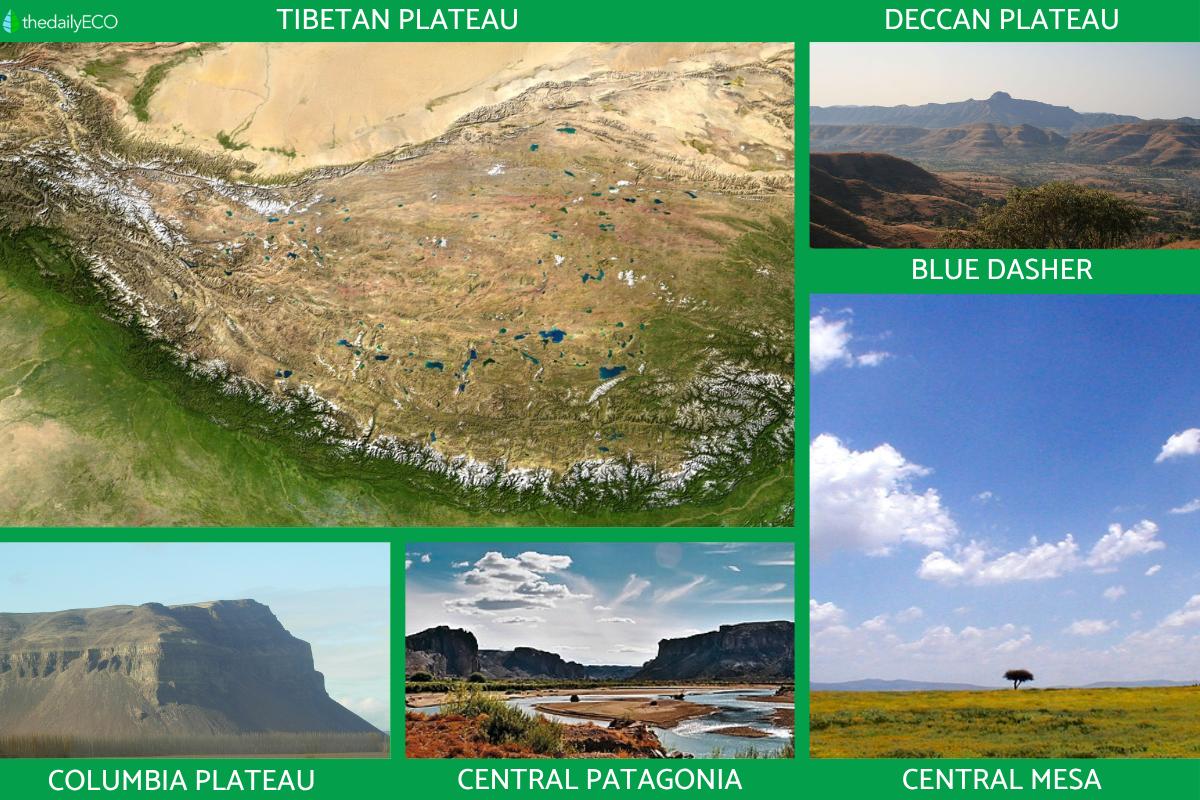
- Tibetan Plateau: also known as the Qingzang Plateau, it is colloquially said to be the ‘the roof of the world’. The Tibetan Plateau is the highest and largest plateau in the world. It is located at the intersection of Central, South and East Asia, with an average elevation of 4,500 meters.
- Deccan Plateau: the Deccan Plateau is a large plateau that extends across most of south-central India. Its altitude varies between 80 and 750 meters above sea level and covers an area of 800,000 km².
- Columbia Plateau: a broad Pacific plateau in the Northwest of the United States, it is crossed by the Columbia River and located between the Cascade Range and the Rocky Mountains.
- Plateaus and lowlands of the extra-Andean Central Patagonia: located in the extra-Andean Patagonia region, from the Colorado River to Tierra del Fuego in Argentina. It presents a landscape of endless plateaus crowned by sandy gravels and basalts. Extends for hundreds of kilometers, this relief was created by river currents produced during the melting of Andean glaciers.
- Central Mesa (Mexican Plateau or Central Mexican Plateau): lies between the Sierra Madre Occidental and Sierra Madre Oriental mountains of Mexico, encompassing territory in the states of San Luis Potosí, Guanajuato, Aguascalientes, Zacatecas, Jalisco and Querétaro. Most of the territory consists of a vast plateau with a few isolated mountain ranges, most notably the Sierra de Guanajuato and the Sierra Cuatralba.
Explore how we classify landforms and geological structures with our guide to what are natural regions?
Difference between plateau vs. plain vs. mountain
Below we present the main differences between plateau, plain and mountain:
- Altitude: plateaus are moderately high, generally around 500 meters above sea level. Plains are low-lying landforms of very low altitude, less than 200 meters above sea level. Mountains have very high altitudes and steep slopes, rising more than 1,000 meters above sea leve.
- Origin: plateaus can be generated by tectonic movements, volcanic activity or erosion processes. Plains usually form as a result of sedimentation caused by the erosion of higher elevations and the evaporation of lakes. In comparison, mountains arise from a process called crustal deformation. This occurs when two sections of the lithosphere collide, causing the slabs to pile up on top of each other, gradually elevating and deforming the Earth's crust. Discover more about the differences between mountains and plateaus with our article on how mountains are created.
- Surface: plateaus have a flat or gently rolling surface, regardless of their altitude. Plains are also flat, but are found at lower altitudes. Mountains have irregular surfaces, with peaks, valleys, slopes and ravines.
We discover more about these features of mountains with our article asking what is a ravine in geography?
If you want to read similar articles to What Is a Plateau in Geography?, we recommend you visit our Environment (other) category.
- Simeoni, A. (2008). Plateaus and Lowlands of Extra-Andean Central Patagonia. Relief Inversion.
https://repositorio.segemar.gov.ar/handle/308849217/1368