What Is the Climate in the Desert Like?


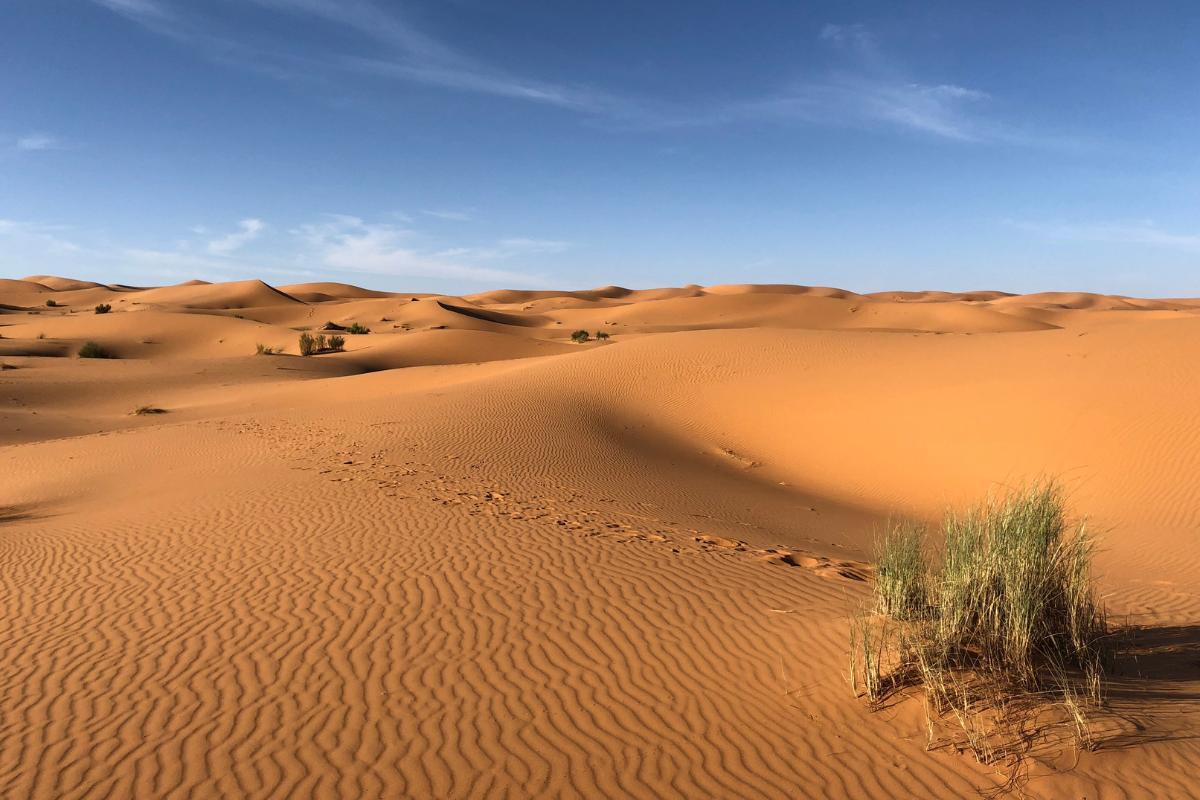
The climate of a certain area is its long-term weather patterns which are established over time, as opposed to weather which changes regularly. Desert climate is the long-term weather patterns of desert areas, geographical ranges which are defined by having little precipitation and subsequent harsh living conditions. In this way a desert is a landscape which is partly defined by its climate. The desert climate has distinctive characteristics such as low atmospheric humidity, extreme temperature variations throughout the day and arid landscapes dominated by infertile soils and scarce vegetation.
At thedailyECO, we explain more by asking what is the desert climate like? We look at how the climate influences the plants and animals of the desert which include succulent plants, xeric shrubs, camels, desert foxes and even kangaroos.
What is a desert climate?
The desert climate is characterized by a lack of precipitation and extreme temperatures, both high and low. These temperatures change dramatically during the day and night. This is because a lack of water vapor means it cannot trap heat that is kept in other more humid environments. It also means there is little cloud cover to also trap the heat that is generated by the sun during the day. When night falls, the temperature drops dramatically.
Desert environments are known for their rocky landscapes due to a scarcity of vegetation. This is also due to the high levels of sun and low levels of moisture. Despite the extreme conditions, life has developed impressive adaptations to survive in these hostile environments. Plants such as cacti and xeric shrubs have deep roots and tissues that allow them to conserve water. Animals have also evolved to resist a lack of water. This is the case with types of camelids which can use fat storage as food and water sources.
In addition to its impact on flora and fauna, the desert climate also influences human activities and the daily lives of the people who inhabit these regions. The scarcity of drinking water and the need to develop efficient irrigation techniques are major challenges for communities living in these areas. In these locations, agriculture and livestock can be difficult to maintain due to lack of rainfall and soil quality.
These desert environments have many similarities, but are not completely homogenous. Learn more with our guide to the different types of deserts around the world.

Location of desert climate
This climate is typically found in regions near the tropics. In these regions, evaporation far exceeds precipitation and results in an arid and dry landscape. Desert climates can be found in various geographical locations across several continents.
In North America, deserts range across the southwestern United States, including parts of California, Arizona, Nevada and New Mexico. In South America, they can be found in northern Chile, western Peru and parts of Argentina. In Africa, large areas of the Sahara, as well as parts of Namibia and Botswana, have a desert climate. In Asia, the Gobi Desert and parts of Saudi Arabia and Iran also exhibit this type of climate.
Learn about a weather phenomenon influenced by desert climate with our article on what causes sandstorms?
Characteristics of the desert climate
To better understand what the desert climate is like, we should investigate their characteristics. Some of the mean features of desert climates are:
- Low humidity: one of the most prominent features of the desert climate is low atmospheric humidity.
- Low rainfall: deserts receive very little rain throughout the year. In some cases, it can rain less than 250 millimeters a year. In many deserts, precipitation is even scarcer.
- Extreme temperature variations: during the day, temperatures can be scorching, easily exceeding 40ºC (104ºF) or more. This is due to intense direct solar radiation. At night, temperatures can drop dramatically, sometimes below freezing,. As explained above, this is partly due to the lack of clouds for heat retention.
- Daily thermal amplitude: the difference between day and night temperatures, known as daily thermal amplitude, can be significant in deserts.
- Intense solar radiation: solar radiation in deserts is high due to the lack of clouds and the clean, dry atmosphere. Learn about a phenomenon caused by solar radiation with our article on what is the albedo effect?
- Strong winds: in many deserts, winds can be strong and constant.
- Diverse landscapes: although deserts are commonly thought of as vast expanses of sand, they can also include rocky, saline or stony landscapes. Depending on factors such as geology and topography, deserts can have a variety of landforms and physical characteristics.
To learn more about the characteristics of different ecosystems by looking at our article on what are biotic factors?
Flora of the desert climate
The plants that live in the desert climate are those which have evolved to survive in extremely arid conditions with fluctuating temperatures. Despite the challenges presented by deserts, some plants have evolved remarkable adaptations to be able to survive in these harsh environments. Some of the adaptations of the flora that inhabit desert climates include:
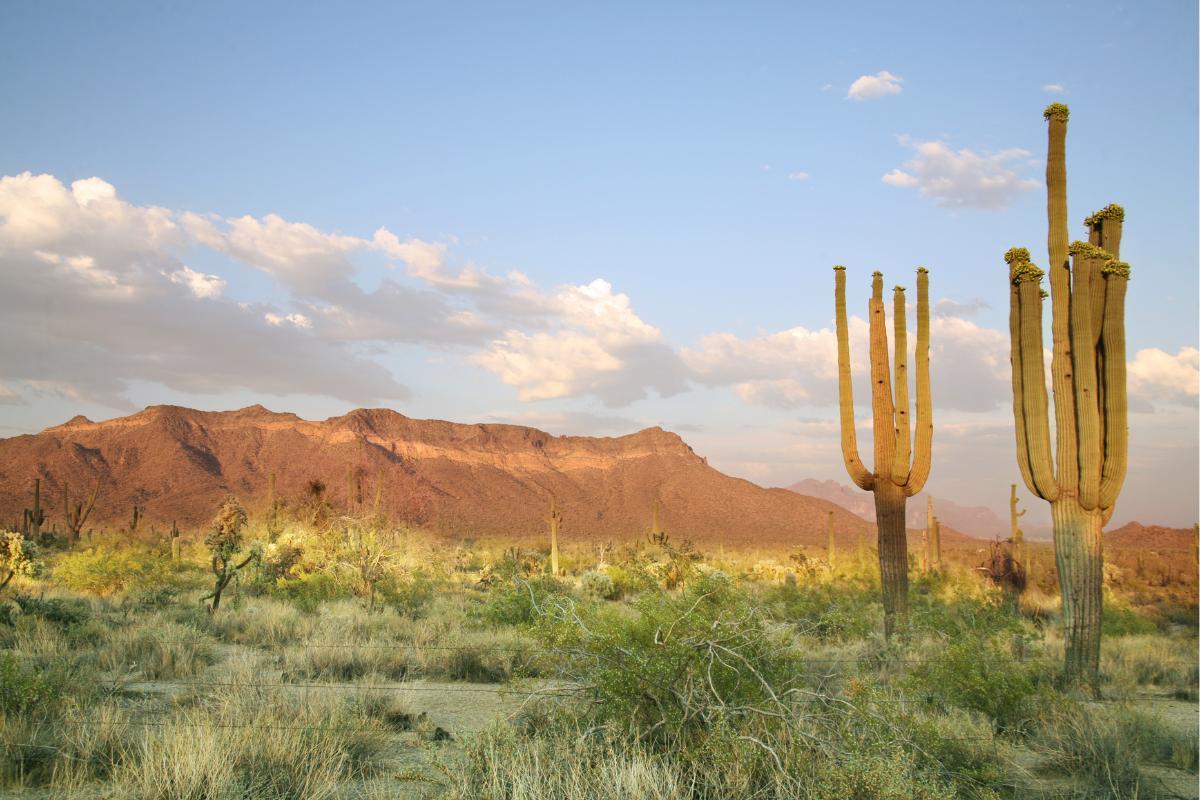
- Succulent plants: many desert plants are succulent, meaning they have the ability to store water in their tissues. Cacti are an emblematic example of this type of plant, with their ability to store large amounts of water in their fleshy stems and leaves. Discover the difference between cacti and succulents in our related guide.
- Deep roots: to access groundwater, many desert plants have developed deep roots that can extend down considerably in search of moisture. Thanks to their roots they can survive during prolonged periods of drought.
- Reduced or absent leaf: to reduce water loss through transpiration, many desert plants have small leaves or even lack them completely. Instead, they may have green stems that carry out photosynthesis, as in the case of cacti.
- Protective hairs and waxes: some desert plants develop a layer of hairs or waxes on their surfaces to reduce water loss through evaporation and protect themselves from intense solar radiation. They can also protect them from consumption by animals.
- Short growth cycles: to make the most of favorable conditions, some desert plants have short growth cycles. This allows them to germinate, grow, flower and produce seeds quickly after rains.
- Adaptations to salinity: in coastal or saline deserts, some plants have developed adaptations to tolerate high levels of salinity in the soil. These plants are called halophytes. They can filter salt from water or accumulate it in their tissues without suffering damage. Learn more about the biological adaptations of living beings in our related guide.
- Protective strategies: in addition to physical adaptations, some desert plants use protective strategies such as thorns or toxins to defend against herbivores and reduce water loss through transpiration.
Some examples of plants from the desert climate are agave, aloe, acacia, biznaga, yucca, candelabra cactus, Joshua tree, organ cactus and many others. Learn about some of these plants which lack protection in our article on types of cactus without spines.

Desert climate fauna
The fauna of the desert climate is made up of a variety of animal species adapted to survive in extreme conditions of aridity, high temperatures and scarcity of resources. These adaptations include physical, behavioral and physiological characteristics that allow desert animals to make the most of available resources and avoid dehydration.
Some of the adaptations and examples of animals found in deserts include:
- Nocturnal species: many desert animals are nocturnal, meaning they are most active at night when temperatures are cooler. An example is the desert fox or fennec fox (Vulpes zerda) which hunts for food mainly at night.
- Ability to conserve water: desert animals have developed various adaptations to conserve water in their bodies. Some have specialized tissues for storing water, such as camels which use fat reserves as a means of sourcing energy and water.
- Reduced activity: during the hottest periods of the day, many desert animals reduce their activity and seek shelter in underground burrows or under the shade of rocks to avoid heat stress and dehydration.
- Skin and fur adaptations: some desert animals have thick or scaly skin to protect themselves from the sun and reduce water loss through evaporation. Others have light or reflective fur that helps reflect solar radiation.
- Specialized diet: the scarcity of resources due to desert climates has led many species to develop specialized diets that allow them to make the most of available food. Some feed on succulent plants, like desert herbivores. Others are carnivores or feed on carrion.
- Mobility: many desert animals are nomadic or migratory, allowing them to move in search of food and water depending on seasonal availability.
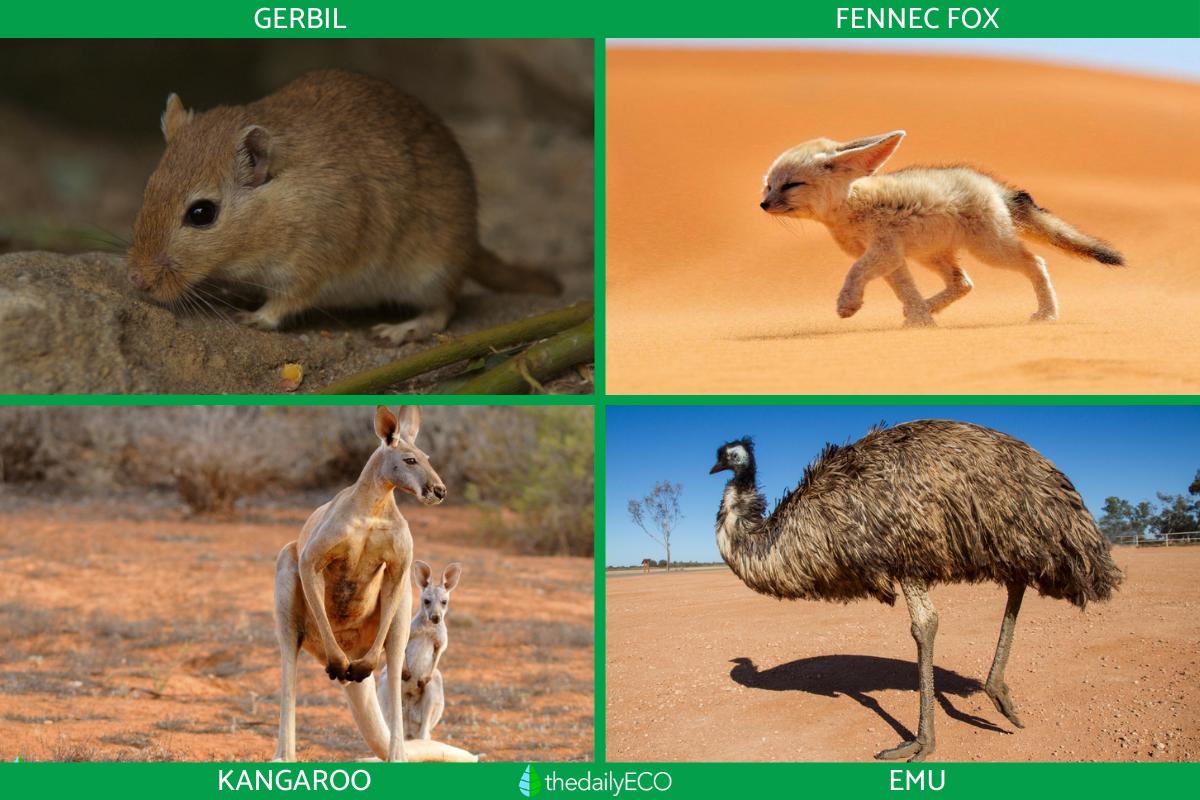
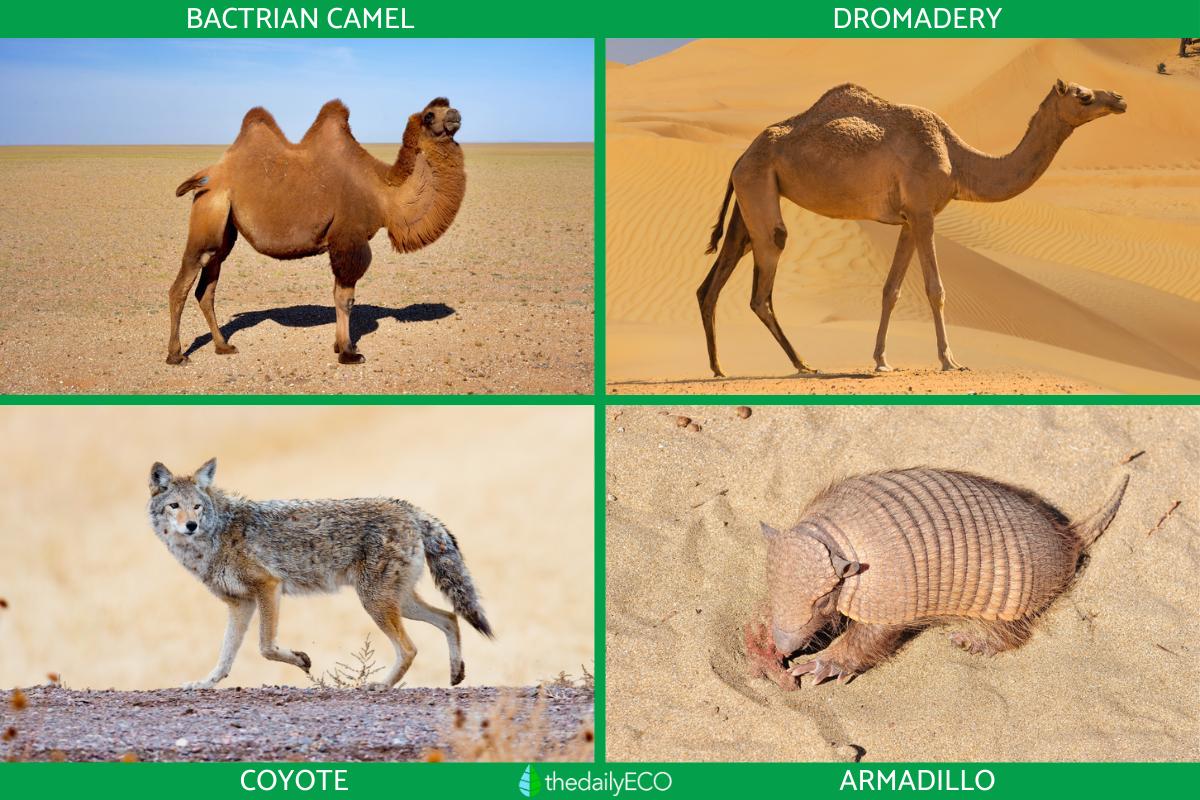
Some examples of the animals found in deserts include the Bactrian camel and dromedary in Asia and Africa, the coyote and armadillo in North America, the gerbil and fennec fox in the Sahara, and the red kangaroo and the emu in Australia. As you can see, many of these are types of mammals, although reptiles and insects are also commonly found in deserts.


If you want to read similar articles to What Is the Climate in the Desert Like?, we recommend you visit our Environment (other) category.