What Is the Humboldt Current?

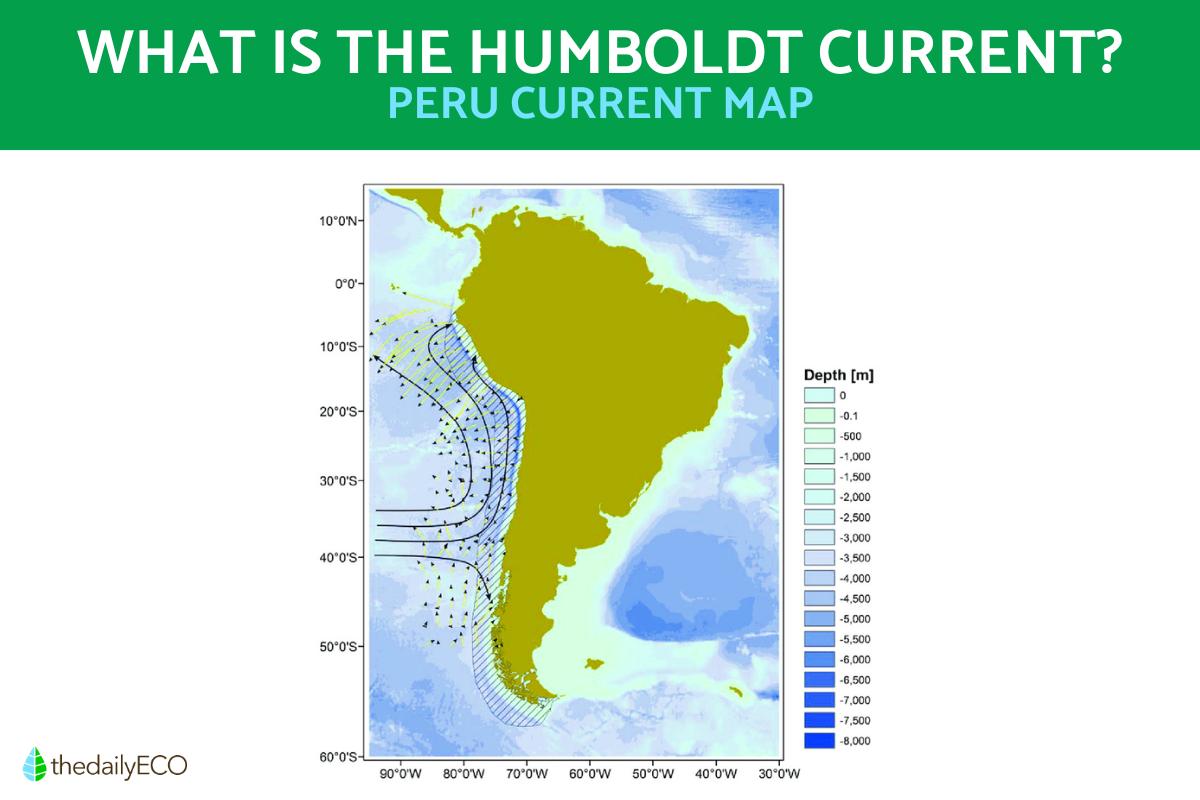
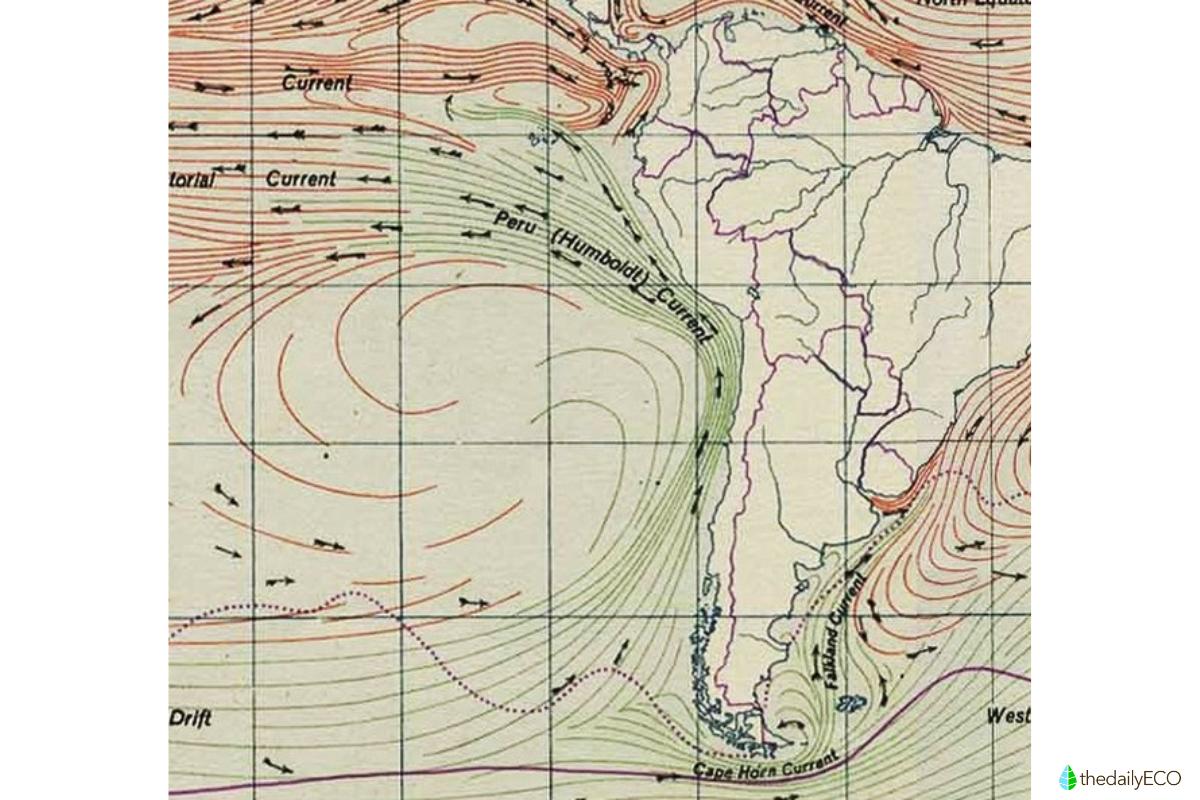
Also know as the Peru Current, the Humboldt Current is an oceanic current in the Pacific that extends from Chile to Ecuador, including the Galapagos Islands. Its origin lies in the combined effects of the Earth's rotational movement and the centrifugal force exerted by the oceanic water masses of the equatorial region. One of its main engines driving this oceanic movement is the South Equatorial Current, a current driven westward by the action of the trade winds. This current affects both marine ecosystems, as well as regional and global climate patterns. In ecological terms, it forms one of the richest fishing areas in the world due to the abundance of nutrients it provides its waters.
At thedailyECO, we explain more in our article asking what is the Humboldt Current? We explain how this current is formed, how it affects ocean waters and what are its ecological impacts. We also provide maps so you can see the direction of the Humboldt Current for yourself.
What is the Humboldt Current?
Also known as the Peru Current, the Humboldt Current is a cold ocean current of great importance to the world as a biosphere. It flows along the western coast of South America, extending in the eastern South Pacific from Chile to Ecuador. It includes the Galapagos Islands which are noted for their rich biodiversity. Discovered by Spanish scientist José de Acosta and named after the German naturalist Alexander von Humboldt who first described it, this current plays a crucial role in the climate and marine ecosystems of the region.
The Humboldt Current originates from the outcropping of very cold, nutrient-rich deep waters. This occurs through a phenomenon known as upwelling. This has transformed the region into one of the most productive and fertile on the planet.
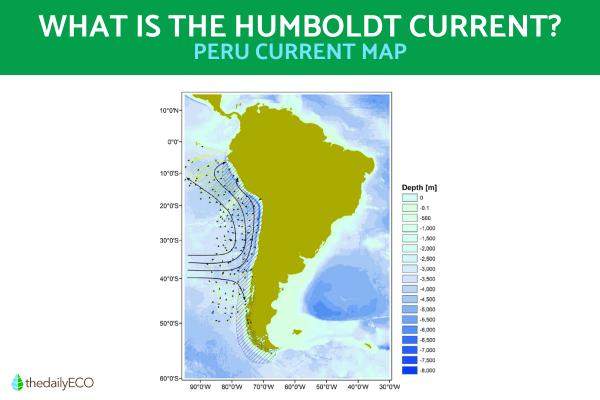
The Humboldt Current map below shows its movement in a typical January. Learn more about how our planet's ecosystems are classified and connected with our article on what is an ecoregion?

Characteristics of the Humboldt Current
The Humboldt Current has particular characteristics which makes it such an ecologically important phenomenon. These characteristics include the following:
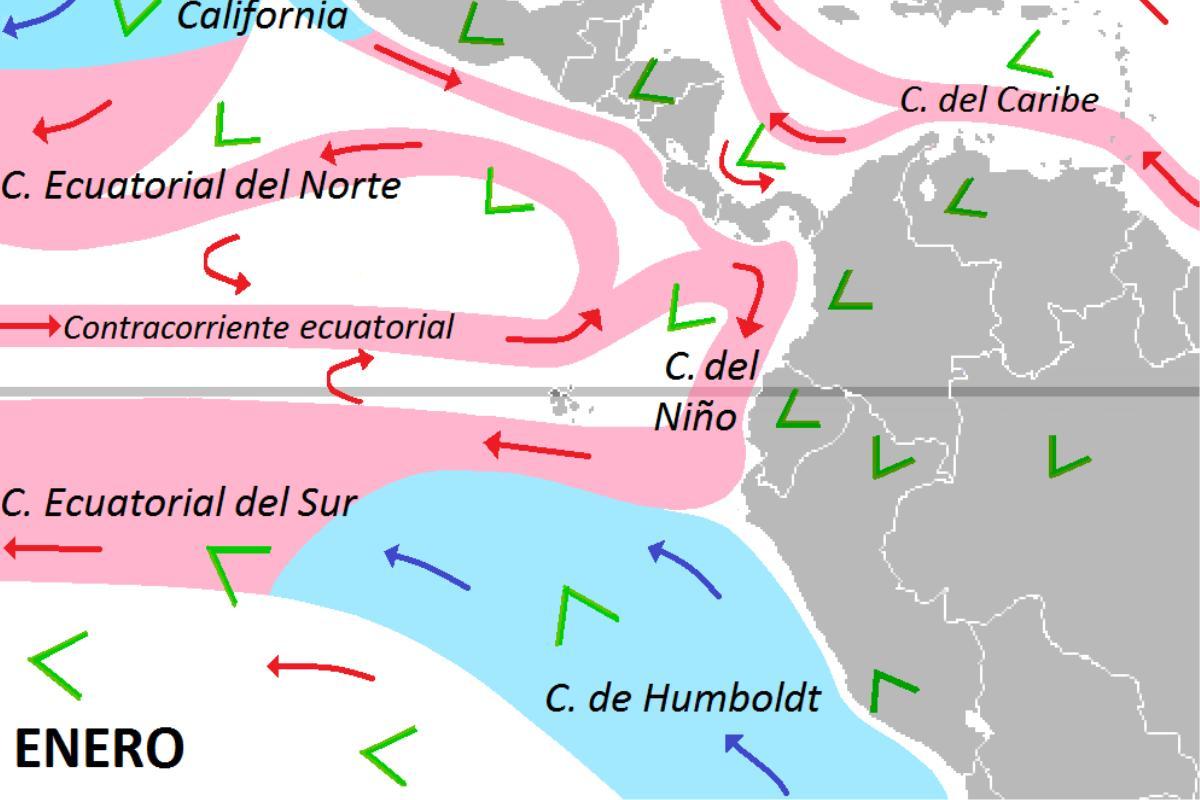
- Origin and trajectory: the Humboldt Current system is born from the bifurcation of the Antarctic Circumpolar Current (42º South Lat.) and flows northwards joining the warm South-Equatorial Current (4º South Lat.). Its area of influence includes the Gulf of Guayaquil, the Galapagos Islands and the Chilean fjords south of Chiloé Island. Learn more about the latter geographical feature with our article on how fjords are formed.
- Productivity of the marine ecosystem: the Humboldt Current Large Marine Ecosystem (HCLME) is one of the richest marine systems in terms of biological productivity, supporting one of the largest fishing areas. This is mainly due to the phenomenon of upwelling, i.e. the emergence of deep waters towards the surface driven by southerly winds. These generally transport waters with a high content of nitrates and low content of dissolved oxygen.
- Climatic influence: the Humboldt Current plays a fundamental role in shaping the climate along the coasts of South American countries. This cold current is responsible for particular climatic phenomena, such as the formation of dense coastal fogs, known locally as camanchacas in Chile and garúas in Peru. These fogs are characteristic of the regions where the current flows, contributing to a significant decrease in temperatures, which are lower than what would practically be expected at these latitudes. In addition, it influences the reduction of precipitation, generating relatively cold coastal deserts, such as the Atacama Desert in Chile and the Sechura Desert in Peru.
- El Niño: the cyclical episodes of the climatic phenomenon known as El Niño is a product of the warming of the surface waters of the Pacific. They interfere with the climate generated by this current, causing climatic instabilities. These manifest themselves in floods as well as landslides and decreases in oceanic biodiversity. In this link you can learn more about the causes and consequences of the El Niño Phenomenon.
- Threats: various investigations have shown a decrease in trophic levels within the HCLME caused by intense fishing exploitation that could be altering predator-prey interactions and the ecosystem services it provides. The ecological integrity of this ecosystem also faces increasing threats due to pollution caused by population growth in coastal areas and poor management of urban, agricultural, industrial and mining waste. The effects of pollution are severely manifested in bays with little water renewal, highlighting the urgent need to address these pressures to preserve the health and sustainability of the HCLME.
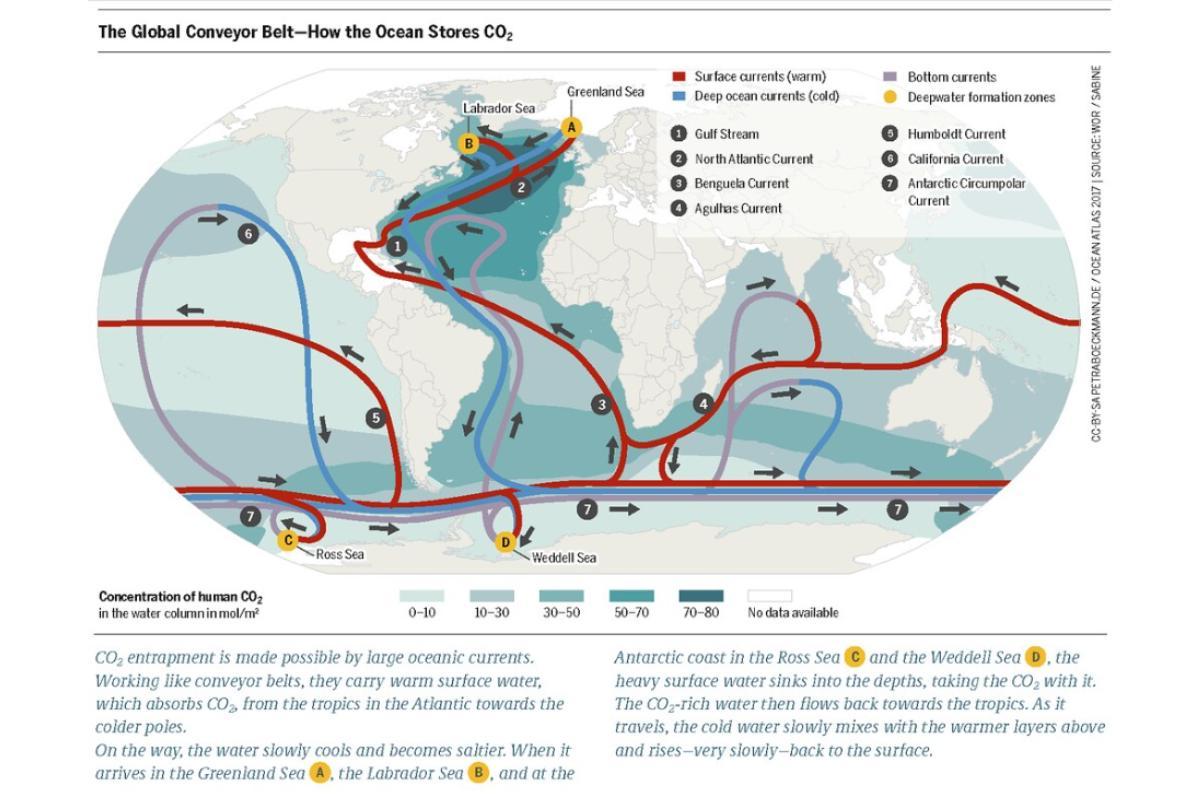
You can see the pathways of the Humboldt Current by taking a look at the map below which shows the global oceanic conveyor belt. You can also learn more about how ocean currents are formed with our article on what drives deep ocean currents?

How is the Humboldt Current formed?
The formation of the Humboldt Current is the result of a series of interconnected physical and geographic processes acting together. Its origin lies in the combined effects of the Earth's rotational movement and the centrifugal force exerted by the oceanic water masses of the equatorial region. These elements contribute to the distribution and circulation of ocean currents globally.
One of the main drivers of the Humboldt Current is the South Equatorial Current. This current is driven westward by the action of the trade winds. These are prevailing winds that blow towards the equator from both hemispheres due to high-pressure belts from the subtropics.
Upon encountering the South American continental mass, the Humboldt Current is deflected to the south and east. It cools and submerges there, before being driven north by the dynamics of the Earth's rotation through the Coriolis effect. The latter phenomenon causes currents to shift to the left in the southern hemisphere, guiding the northerly direction of the Humboldt Current along the western coast of South America.
You can learn more about these meteorological phenomena with our article on what is the causes of the Coriolis effect?

Consequences of the Humboldt Current
The consequences of the Humboldt Current are vast and varied. They affect marine ecosystems, as well as regional and global climate patterns. In ecological terms, the Peru Current promotes one of the richest fishing areas in the world, being the main support for local economies and communities. This is due to the abundance of nutrients that support a vast diversity of marine life, including phytoplankton, zooplankton, fish, birds and marine mammals.
In terms of climate, the current has a moderating effect on coastal temperatures, keeping them lower than they would otherwise be. This contributes to the formation of extensive coastal deserts, such as the Atacama Desert. They so do by limiting the amount of precipitation. Learn more about precipitation with our article on what is a torrential downpour?
Changes in the intensity or direction of the current can alter these patterns. Such changes are possibly influenced by climate change. The results affect both marine biodiversity and climatic conditions. Human activities dependent on these natural systems are thereby also affected.
Understanding how the oceans function can help us to better understand Earth's overall biosphere, as well as how it influences human activity. Learn more with our articles on whether the Pacific and Atlantic oceans meet, as well as what is the blue economy?
If you want to read similar articles to What Is the Humboldt Current?, we recommend you visit our Environment (other) category.
- Graco, MI, Ledesma, J., Flores, G., & Girón, M. (2007). Nutrients, oxygen and biogeochemical processes in the Humboldt Current upwelling system off Peru. Peruvian Journal of Biology, 14(1), 117-128.
- Salgado, H., González, C., Sueiro, JC, & De la Puente, S. (2015). Estimation of the Total Economic Value (TEV) of the ecosystem goods and services of the Large Marine Ecosystem of the Humboldt Current (GEMCH). GEF-UNDP Humboldt Project, 127.