What Is the Foehn Effect? - Foehn Wind Definition


The Foehn effect is related to a dry, warm wind that moves along the downward side of a mountain. It occurs when an air mass encounters this mountainside and is forced to ascend up it. This natural phenomenon occurs in most mountainous regions of the world, although it is a localized effect. Foehn winds can also occur on the downward sides of valleys. If you want to know more about this weather phenomenon, thedailyECO asks what is the Foehn effect? We look at a Foehn wind definition, as well as how it occurs. We also provide diagrams of how the Froehn effect works.
What is the Foehn effect?
The Foehn effect is a process that is results a Foehn wind. It is a phenomenon that occurs in certain mountainous regions of the world, particularly in mountains with very high altitudes.
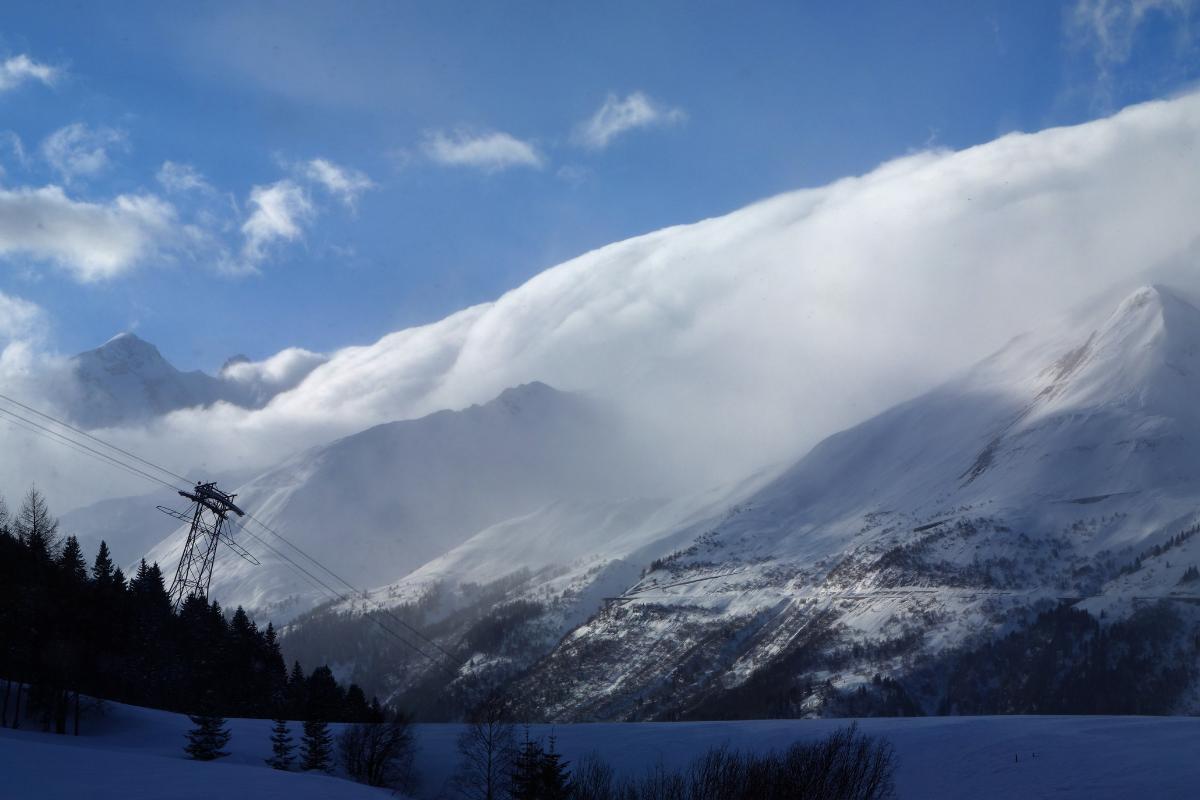
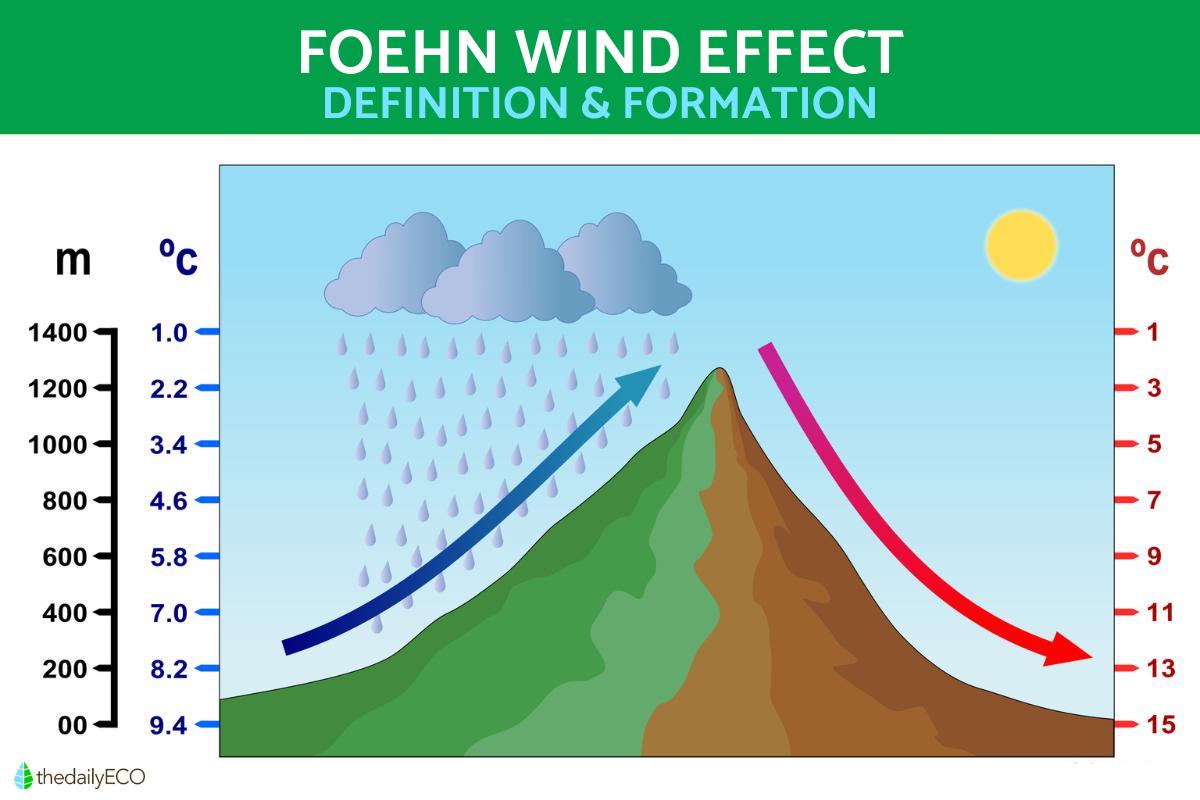
The Foehn effect occurs when a current of cool and moist air encounters a very large obstacle with a massive downward slope and is forced to overcome it. It is for this reason it occurs on mountains. As the air mass rises, it cools further. If the air contains enough humidity, then the water vapor can condense. This water vapors forms a visible cloud which then releases precipitation in the form of rain.
Once the rain has been released by the cloud created by the Foehn wind, the air mass is lighter and will descend down the mountain and become warmer. The Foehn effect is an example of how topography and air movement can lead to noticeable changes in weather conditions on different sides of a mountain or range. This phenomenon can have a significant impact on climate and precipitation.

Why does the Foehn wind warm up when descending if warm air rises?
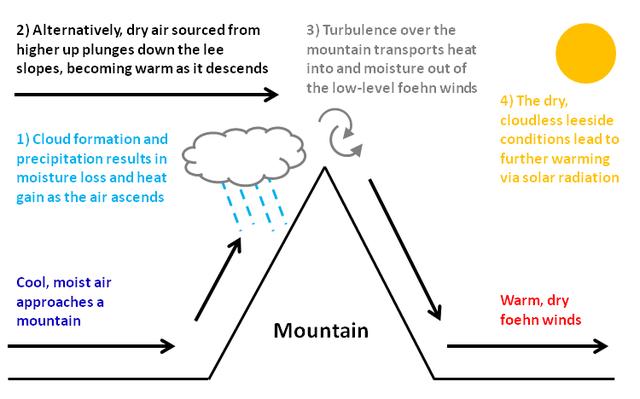
The warming of descending air in the Foehn effect may seem counterintuitive, given the general principle that warm air rises. However, several factors contribute to the warming of descending air in this specific weather phenomenon:
- Adiabatic heating: as air rises and cools on the windward side of a mountain range, it undergoes a process called adiabatic cooling. Conversely, when air descends on the leeward side, it experiences adiabatic heating. Adiabatic means that the temperature change occurs without the addition or removal of heat from the surroundings. When air compresses as it descends, its molecules become more tightly packed, leading to an increase in temperature. This is why the descending air warms up.
- Rain shadow effect: the process is often associated with a rain shadow effect. On the windward side of the mountains, the cooling air can lead to the condensation of moisture, cloud formation and precipitation. By the time the air descends on the leeward side, it has lost much of its moisture content due to these processes. Dry air can heat up more quickly than moist air, further contributing to the warming effect.
- Mechanics of atmospheric pressure: the movement of air from high-pressure areas to low-pressure areas plays a role in the Foehn effect. As air rises on the windward side, it moves from a high-pressure area to a lower-pressure area at higher altitudes. Conversely, as it descends on the leeward side, it moves from a lower-pressure area to a higher-pressure area at lower altitudes. Compression due to this pressure difference results in warming.
In summary, the warming of descending air in the Foehn effect is primarily due to adiabatic heating and the mechanics of atmospheric pressure changes associated with the movement of air over mountains. You can see these mechanics illustrated in the diagram below.

How the Foehn effect occurs
Also known as the Föhn effect, the Foehn effect occurs in several stages as an air current encounters and moves over a mountain. Each of the stages of the Foehn effect is described step by step below:
- Moist air flow: a flow of moist air approaches a mountain range. This air usually contains moisture in the form of water vapor.
- Rising of air on the windward (upward) side: as the air mass encounters the mountain, it is forced to rise due to the topography, which causes the air mass to cool adiabatically.
- Condensation and precipitation: when the air temperature drops sufficiently, the water vapor in the air condenses to form vertically developing cloudiness due to orographic forcing. From the cloud that has formed in the windward direction, precipitation can occur.
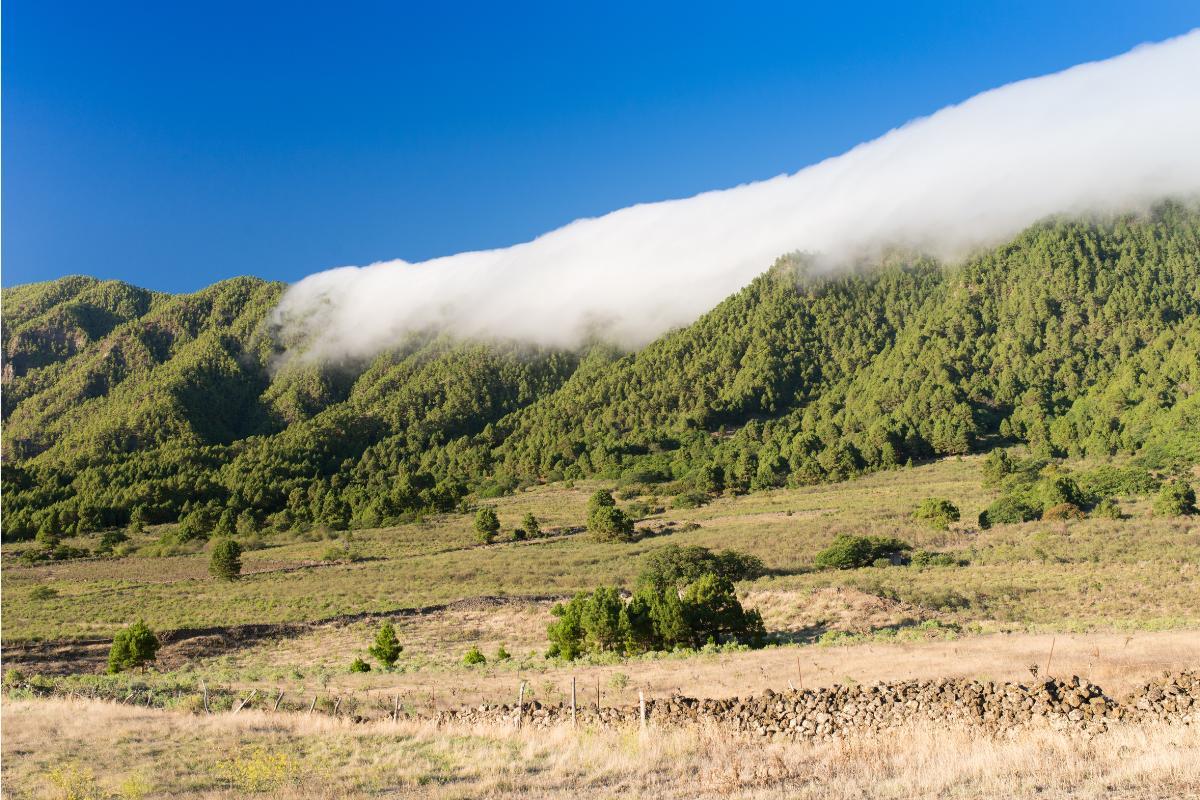
- Descent of air on the leeward side (downward): once the air has reached the top and crossed the mountain, it will be drier. This is because it has lost moisture due to precipitation. The air current will begin to descend on the leeward side and will be reheated by adiabatic compression.
- Adiabatic heating: descending air is heated due to adiabatic compression, meaning its temperature increases as it is compressed. As air warms, its ability to retain moisture increases, causing the air to become drier.
- Foehn wind: in this final stage, the air reaching the leeward side of the mountain is characterized by being warm and dry. This is the phenomenon which constitutes the Foehn effect. On this side of the mountain, weather conditions can become significantly warmer and drier compared to the windward side.

What are the effects of the Foehn effect?
The Foehn effect can have several effects on nature and the environment in the areas where it occurs. These effects can be both positive and negative. They mainly depend depend on local conditions and magnitude. Below are some examples of how the Foehn effect can affect nature:
- Impact on vegetation: the Foehn effect can increase temperatures and reduce humidity on the leeward side of mountains, potentially affecting vegetation in different ways. On the one hand, it favors the growth of plant species adapted to hot and dry climates, but it can also cause the disappearance of vegetation that is more adapted to cold and humid conditions.
- Wildfires: hot, dry and windy conditions associated with the Foehn effect can increase the risk of wildfires. Dry vegetation and the increased availability of flammable material due to falling leaves and dead branches can contribute to the spread of wildfires in these areas. Learn more with our article on how to stop wildfires.
- Impact on fauna: the alteration of climatic conditions can affect local fauna, since some species are not able to adapt to climatic changes. This can influence the distribution of species and the interactions between predators and prey.
- Water resources: the Foehn effect can rapidly melt snow on leeward slopes, which can affect runoff patterns and freshwater availability in local rivers and streams.
- Effect on soil erosion: strong winds associated with the Foehn effect can increase soil erosion, reducing soil quality and fertility. Learn more with our article on the horizon layers of soil.
Now that you know what the Foehn effect is and how it is produced, you may also be interested in other weather phenomena with our article on what is haze weather?
If you want to read similar articles to What Is the Foehn Effect? - Foehn Wind Definition, we recommend you visit our Meteorological phenomena category.