Why the Study of Cells Is So Important

All living organisms are composed of cells which are responsible for their functioning of their biological processes. Although they themselves are made of atoms, cells are considered the basic building block for all life. We know about their existence thanks to microscopy, the technical field which allows us to visualize the behavior of cells. You may not be aware of cytologists such as Antonie van Leeuwenhoek, Nettie Stevens or Georgios Papanikolaou, but it is thanks to their pioneering work that science has dramatically change humanity's course.
At thedailyECO, we look at why the study of cells is so important. Moreover, in understanding the importance of cell biology, we can see how it is applied to make our lives better.
What is cell biology?
In its most basic sense, cell biology is the study of cells. Also known as cellular biology or cytology, it is a complicated discipline which has a very basic aim. The aim of the study of cells is to understand their structure, function and behavior. Since they are building blocks of life, cells have within their microscopic structures the keys to understanding life on both micro- and macrocosmic planes.
Within cells, a series of vital processes occur. These processes allow the organism to both develop and to function. When these cells no longer function or function well, it leads to a detriment to the organism and eventual death. Some examples of cellular processes include:
- Metabolism
- Protein folding
- Extracellular communication
- Secretion of substances
- Excretion of components that are no longer useful
- Assimilation of growth substances
- Cell division
All these processes are studied by cell biology and are directly related to the cellular components. Each type of cell has its own use and function, as do the individual organelles which make up each cell. Despite their tiny size, cells control the state of any organism at a given time.
The cellular components vary according to the type of cell since there are different types of cells. Some of the most common cell types are:
- Eukaryote
- Prokaryote
- Animal cell
- Vegetable cell
- Fungal cell
- Protist cell
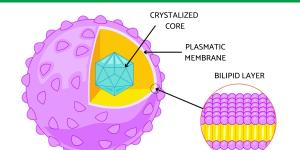
The word for someone who studies cells is ‘cytologist’. As each cell type has particular characteristics, cell research has various specializations. Some cytologists will spend their entire careers trying to better understand the functions of specific cell organelles. These include the cell membrane, nucleus, Golgi apparatus, peroxisomes, ribosomes, mitochondria, chloroplasts, vacuoles, lysosomes, cell wall and microtubules.
You can learn more about the differences between cell types with our comparison between plant and animal cells.
What are the applications of cell biology?
It is too easy to see the study of cells as a purely academic endeavor. Some may even think it is a boring subject which has little in terms of practical application. Nothing can be further from the truth. It is thanks to cell biology that many of us are still alive. Only by understanding how life works can be improve living. Some of the most important practical applications of the study of cells include:
Medicine
Thanks to our understanding of cells, it has been possible to discover pathological tissues. One of the most damaging is cancer. This is caused by disordered cell multiplication, from which it has been possible to create treatments that attack these diseased cells. Cytology is the specific branch of cell biology that uses staining and labeling of cells to find out how they are behaving.
In embryonic development, cells have an important role. Cell multiplication varies according to the stage of the zygote. This is useful information for both doctors and veterinarians in the field of reproductivity. Related to this is the study of reproductive cells which seeks to address the causes of infertility. For example, there are sperm count tests where it is analyzed whether the motility or the volume are adequate for the individual to be considered fertile.
There are numerous diseases related to blood, which is also made up of cells. Specific blood cells include platelets, red blood cells and white blood cells. When there are abnormalities in these cells, pathologies occur. These include insufficient production in bone marrow aplasia or particular problems such as erythroblastopenia. Knowledge of blood cells can help detect pathologies and develop therapeutic solutions.
Biotechnology
The immune system works thanks to specific cells, such as lymphocytes (for humoral immunity) and T cells (for cellular immunity). These cells respond to external stimuli that may endanger the body. Cellular responses determine the immune response. It is thanks to cellular technology that vaccines have been developed using the principle of antibody development to prevent disease.
The study of cells is also important to know the cellular functioning of other biological groups. Microbiology is the field of science where fungal and prokaryotic cells are also studied. These cells can be harnessed in biotechnology for various purposes. For example, the production of food with lactic acid bacteria to produce cheese and yogurt or to create pathogen-defense methods, such as antibiotic drugs.

Difference between cellular and molecular biology
Cells make molecules needed for different functions. It is this which is the key to understanding the difference between cell biology and molecular biology. Although they are related, they study different aspects of the cell.
- Molecular biology: studies the composition, function and structure of cellular molecules.
- Cell biology: studies the mechanisms of the cell that occur in its organelles.
Cellular molecules that can be studied are divided into inorganic compounds, small organic molecules and macromolecules:
- Inorganic compounds: include water and mineral salts.
- Small organic molecules: sugars, fatty acids, amino acids and nucleotides. When united, they form more complex molecules.
- Macromolecules: are composed of these small molecules, which form high molecular weight polymers such as polysaccharides, lipids and phospholipids. The most important macromolecules are proteins and nucleic acids in the form of DNA and RNA. They are also the basis of the study of molecular biology because the physical and metabolic characteristics of all living beings emerge from them.
Learn more about how molecules affect living beings with our article on the differences between DNA and RNA.
Importance of cell biology for humans
Knowledge of cells is essential to know how organisms work. This can be achieved thanks to cell biology. It is necessary to understand the functional units of life to know how life works. The main contributions to humanity generated from the knowledge of the cell have been originated by molecular biology. Its understanding and management have allowed:
- Therapeutic treatments
- Disease and pathology prevention
- Production of new types of proteins
- Plant and animal phenotypic modifications
- Increase in food production
This branch of biology has been useful for discovering the origin of various living beings. For example, the analysis of thale cress (Arabidopsis thaliana) lead to its complete genome being sequenced. In doing so, the evolution of flowering plants has been better mapped, which will help improve agricultural development.
Another important application of molecular biology that needs to be mentioned again is in medicine, with the use of mice as models. We share genes with these animals, such as the KIT gene that regulates pigment cells. From this it has been possible to modify genes in mice to experiment how they respond to change and thus discover the processes in humans.
The tissues of the human body are made up of cells. With this knowledge, therapies have been developed to regenerate tissues in the best way. For example, there are bone regeneration practices where implants are inserted that promote cell renewal. This is particularly useful in cases of fracture. Remodeling occurs by bone cells called osteoclasts and osteoblasts.
The genetic modification of plants has been crucial to our food system. The climatic conditions have been in constant change and the plants have undergone this accelerated process. For this reason, genes have been modified so that crops can survive at different temperatures and even resist pests. This has managed to alleviate the famine as food production has increased considerably, especially to the benefit of underdeveloped countries.
A recent worldwide example of how the study of cells can benefit the world is the COVID-19 pandemic. It is thanks to the study of B cells that helped a vaccination against this virus be developed[1]. Similar achievements in HIV/AIDs research and development of antibiotics against tuberculosis have made treatable diseases which were once considered a death sentence.

Why is the study of cells controversial?
For the most part, there is little controversy in the study of cells. As with any empirical scientific endeavor, cell biology should be investigated without bias and under the general guidelines of research ethics. This does not mean there have not been ethically dubious investigations throughout the history of cell study, but mostly it is a form of scientific investigation which has global support.
Perhaps the most controversy which has arisen in the study of cells is due to stem cell research. This is due to the methods of stem cell extraction, sometimes resulting in animal death. Another major issue is the use of embryonic stem cells which use human embryo cells which need to be destroyed to carry out research.
Some claim this is the same as abortion, but these embryos are from days-old blastocysts which are fertilized in a laboratory and were never implanted in a womb. They are not a fetus and have no recognizable features of faculties of a human person. It is a collection of 180 to 200 cells which are located in a petri dish[2].
The controversy is mainly derived from religious and conservative opposition. The broad consensus of scientists and researchers do not see an ethical dilemma. On the contrary, the benefits of stem cell study are incredibly important as they can help fight disease and improve fertility for those who want to have children.
If you want to read similar articles to Why the Study of Cells Is So Important, we recommend you visit our Biology category.
1. Chen, S., Guan, F., Candotti, F., Benlagha, K., Camara, N. O. S., Herrada, A. A., James, L. K., Lei, J., Miller, H., Kubo, M., Ning, Q., & Liu, C. (2022). The role of B cells in COVID-19 infection and vaccination. Frontiers in immunology, 13, 988536.
https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2022.988536
2. Harvard Stem Cell Institute. (2007). Examining the ethics of embryonic stem cell research. Retrieved from:
https://hsci.harvard.edu/examining-ethics-embryonic-stem-cell-research
- Orengo, D. (2011). Fundamentals of Molecular Biology. Barcelona: Editorial UOC.
- Alberts, B., Bray, D., Hopkin, K., Johnson, A., Lewis, J., Raff, M., Roberts, M., & Walter, P. (2004). Introduction to cell biology. Madrid: Panamerican Medical Editorial.
- Fernández, I., Alobera, M., & Blanco, L. (2006). Physiological bases of bone regeneration I. Histology and physiology of bone tissue. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal, 11, E47-51.