What Is Considered a Soft Coral?


Soft corals are a mesmerizing and diverse group of marine organisms that captivate the imagination with their unique beauty and intriguing characteristics. Unlike their stony counterparts, these corals do not build rigid calcium carbonate skeletons, leading to their name "soft corals." Instead, they showcase an array of flexible, fleshy structures, which create an enchanting display in marine ecosystems.
The article by thedailyECO explains the concept of soft corals, delving into their various types, distinctive characteristics, and feeding habits.
What are soft corals?
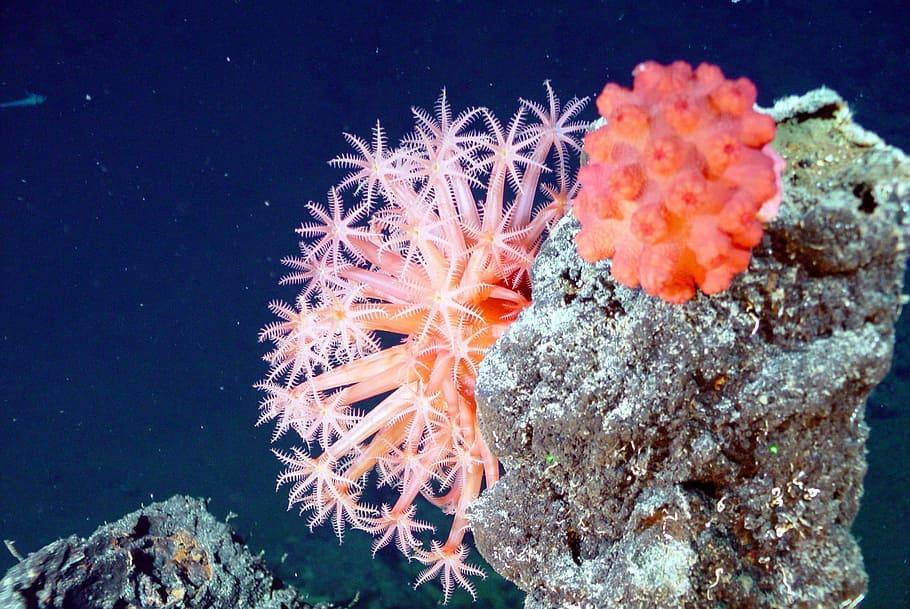
Soft corals, also known as alcyonarian corals, are a fascinating group of corals that stand apart from their stony counterparts due to their unique characteristics.
Belonging to the Octocorallia subclass, the majority of soft corals fall under the Alcyonacea order, although the Pennatulacea order is sometimes included within this classification as well.
While soft corals lack the calcium carbonate skeleton that defines stony corals, they possess comparable support structures within their tissues called spicules. These tiny structures are made of calcite, a form of calcium carbonate, and serve both as a support system and a defense mechanism against potential predators.
Soft corals have a colonial configuration, where multiple polyps work harmoniously, each contributing to the collective functioning of the group. The defining characteristic of these polyps is the presence of eight pinnate tentacles. The corals exhibit a fleshy appearance, their polyps embedded in soft tissues, which sets them apart from the stony corals' rigid exoskeletons.
Unlike some marine organisms that are capable of movement, soft corals remain firmly anchored to the substratum, relying on the water currents to bring them sustenance. Though they do not directly participate in reef-building like stony corals, they are integral components of the marine reef ecosystem. Inhabiting the reefs, they play a crucial role in hosting a diverse array of species, contributing to the overall biodiversity and balance of the ecosystem.
Do not miss this other article that explains what an aquatic ecosystem is.

Types of soft corals
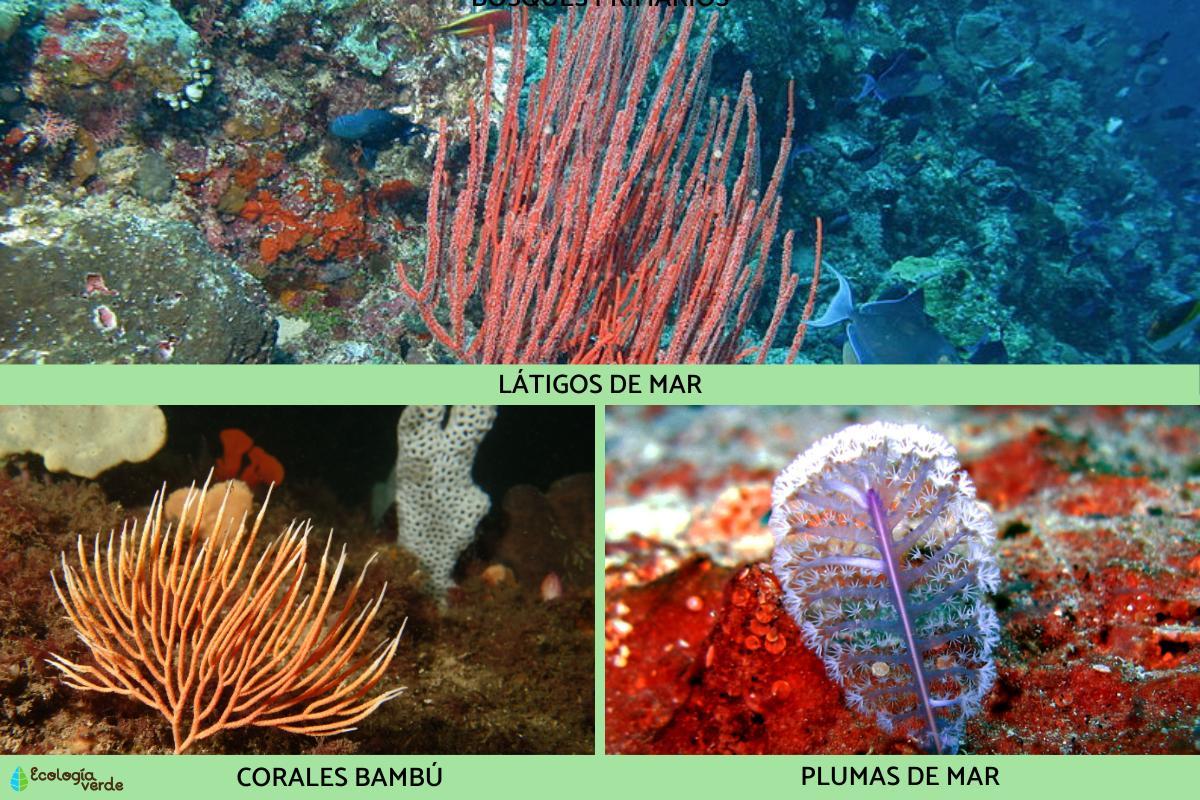
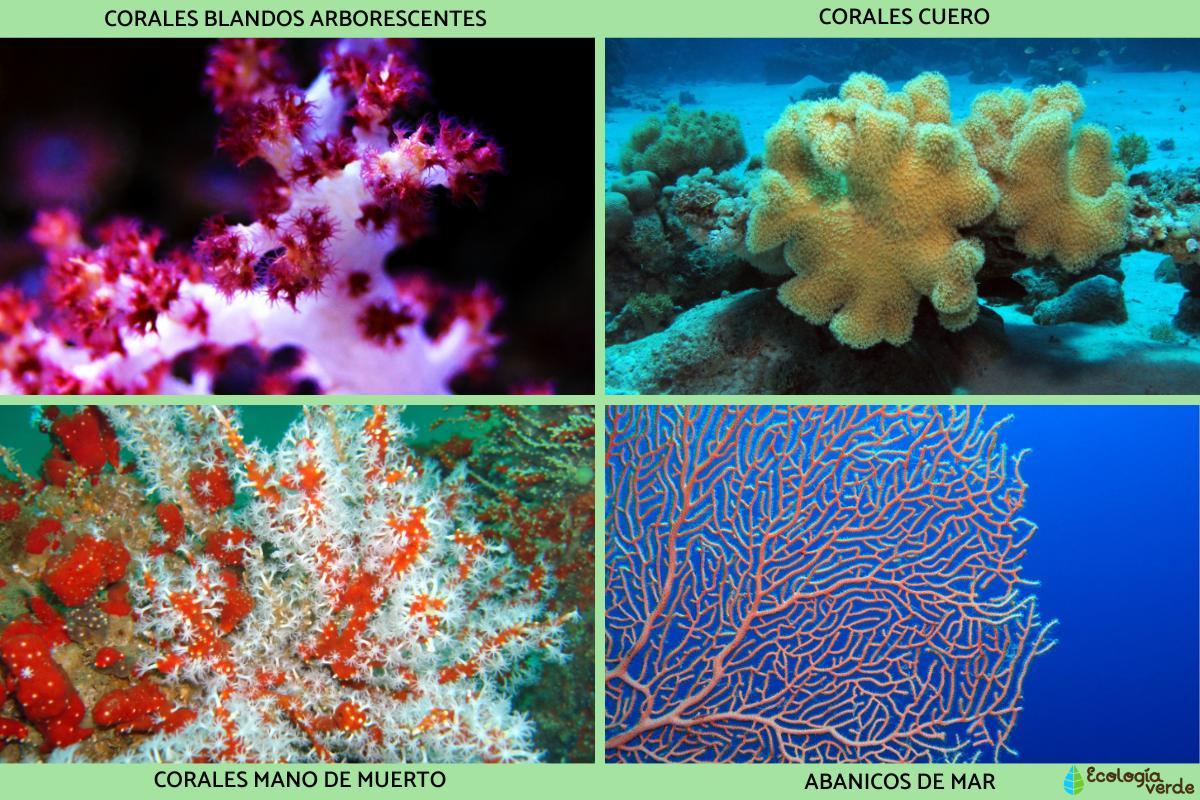
Coral types exhibit remarkable diversity and can be grouped based on various characteristics such as suborders, families, genera, or even close relations with other orders outside of Alcyonacea. Here are some of the most popular and intriguing coral types:
- Kenya Tree Coral (Capnella spp.): known for its tree-like appearance with small polyps covering numerous branches. It's flexible and fast-growing, making it popular in reef aquariums.
- Toadstool Leather Coral (Sarcophyton spp.): this soft coral has a mushroom-shaped appearance with a wide, flat cap and thick stalk. It's hardy and easy to care for.
- Colt Coral (Cladiella spp.): features captivating branching structures with bright-colored polyps. It's adaptable to various lighting conditions.
- Finger Leather Coral (Sinularia spp.): this coral has elongated, finger-like lobes and sways gracefully in water currents, coming in various colors.
- Green Star Polyps (Pachyclavularia spp.): known for its rapid growth and vibrant green polyps, it forms a carpet-like growth over rocks and substrates.
- Xenia Coral (Xenia spp.): this coral pulsates rhythmically, displaying feathery polyps and offering an enchanting sight in reef tanks.
- Cabbage Leather Coral (Sinularia dura): named for its large, cabbage-like appearance, it has a crinkled surface and bold color variations.
- Clove Polyps (Clavularia spp.): these soft corals come in stunning and diverse coloration, forming dense colonies in reef tanks.
- Weeping Willow Coral (Nepthea spp.): known for its long, slender branches resembling a willow tree, adding elegance to aquariums.
- Leather Coral: leather corals are a group of soft corals with various appearances, known for their adaptability and attractive features.
These soft corals represent just a few of the numerous captivating species. Each brings its unique beauty and characteristics, enhancing the diversity and charm of reef tanks. Do not miss the following article, where we explain what gorgonian corals are.


Feeding of soft corals
Indeed, corals possess a fascinating dual feeding mechanism, alternating between heterotrophic and symbiotic feeding. This combination of feeding strategies is a key factor in their classification as animals rather than plants.
Heterotrophic feeding
The first type of feeding employed by corals is heterotrophic feeding. In this process, corals depend on external sources for nutrition. Each soft coral is adorned with numerous polyps, each equipped with tentacles that create water currents. These tentacles attract tiny particles of plankton towards the central mouth of the polyp. Once the plankton is captured, the coral's tentacles facilitate the transportation of the particles towards the polyp's mouth, where they are ingested and serve as a source of nourishment.
Symbiotic association with zooxanthellae algae
Additionally, many soft corals engage in a symbiotic relationship with zooxanthellae algae. These microscopic algae reside within the coral's tissues. Through photosynthesis, the zooxanthellae algae convert sunlight into metabolites, such as sugars and other organic compounds. These valuable nutrients are then used by the coral for its nourishment. In return, the coral provides the algae with inorganic compounds and a protected environment in which to thrive.
This symbiosis between soft corals and zooxanthellae algae is of paramount importance as it serves as the primary source of energy for the coral. The partnership is more common in species that inhabit shallow waters, where sunlight is abundant and accessible for the photosynthetic activities of the zooxanthellae. This remarkable feeding adaptation contributes significantly to the ecological significance and beauty of soft corals in coral reef ecosystems.
Be sure to read this other article where we explain what symbiosis in biology is.
If you want to read similar articles to What Is Considered a Soft Coral?, we recommend you visit our Biology category.
- Abel, E., Riedl, R. (1986). Fauna and flora of the Mediterranean Sea: a systematic guide for biologists and naturalists. Spain: Omega.
- Beatty, R., Beer, A., & Deeming, C. (2010). The book of nature. Great Britain: Dorling Kindersley.
- Jahajeeah, D., Bhoyroo, V., & Ranghoo-Sanmukhiya, M. (2020). A review of soft corals (Octocorallia: alcyonacea) and their symbionts: distribution of clades and functionality . Western Indian Ocean Journal of Marine Science, 19(1), 123-141.