What Is the Heat Urban Island Effect?


As cities continue to grow and develop, an increasing concern arises: the rising temperatures in urban areas. The heat island effect refers to the phenomenon where urbanized regions experience significantly higher temperatures compared to their surrounding rural areas. By understanding the heat island effect and its implications, we can work towards creating cooler and more sustainable urban environments.
In this article from thedailyECO, we will explore the causes, consequences, and potential solutions to the heat island effect.
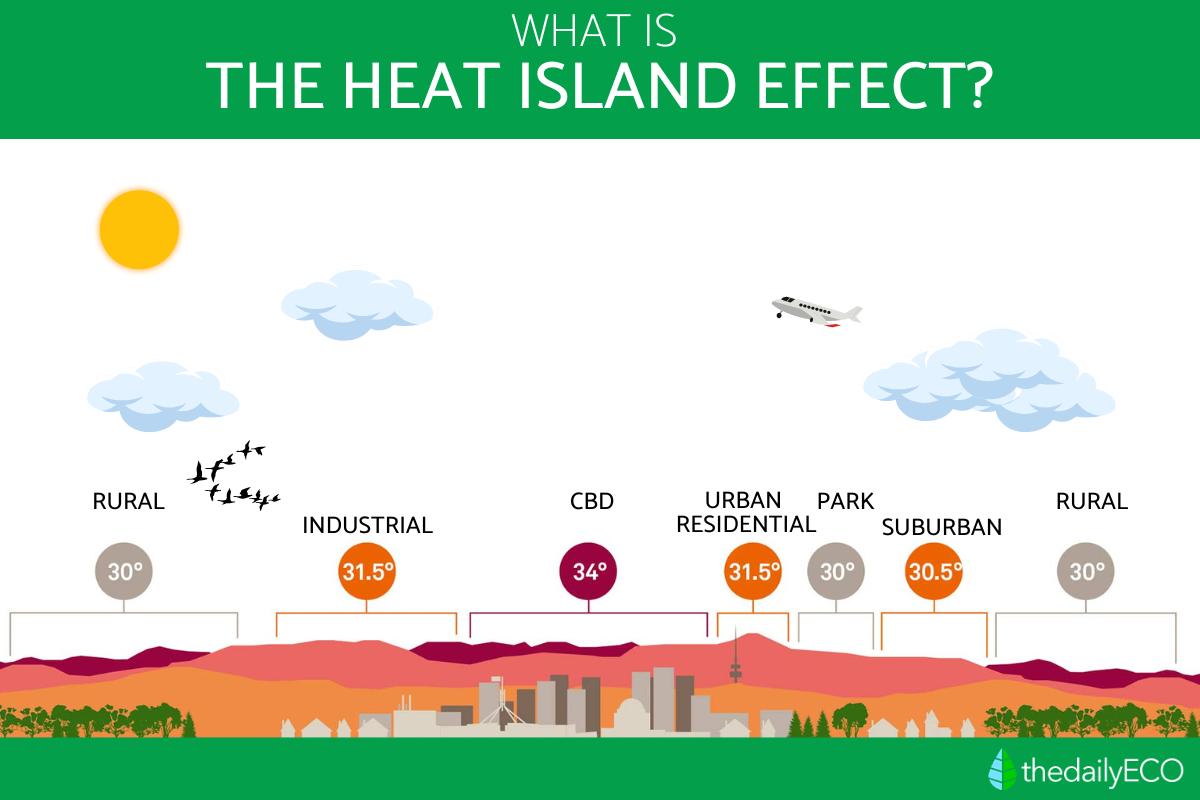
What is the urban heat island effect?
When we refer to infrastructure, we're talking about man-made elements like buildings, streets, sidewalks, and asphalt. These surfaces have a higher capacity to retain heat compared to open, natural spaces such as fields or forests. Additionally, the lack of vegetation in cities reduces the natural cooling effect through water evaporation.
Human activities in urban areas also contribute to the urban heat island effect. The use of heating or air conditioning systems, power generation, industry, and transportation all generate heat as by-products. Furthermore, greenhouse gas emissions and other pollutants trapped in cities contribute to the warming of the air.
The combination of these factors creates a localized "bubble" of heat over urban areas, resulting in temperatures several degrees higher than nearby rural areas. This effect has various negative impacts on the urban environment and the well-being of its residents.
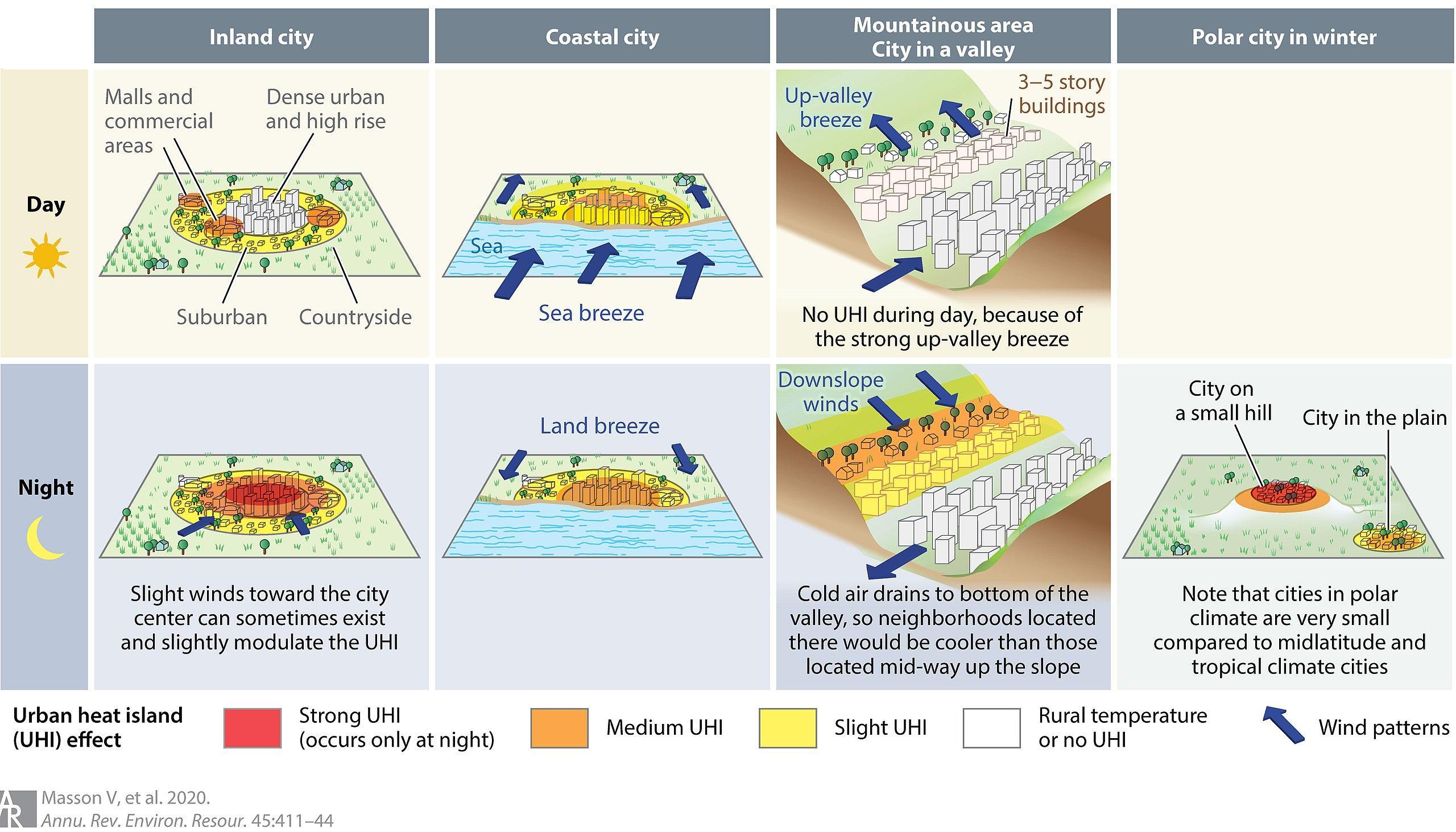
The urban heat island effect is prevalent in densely populated cities that prioritize construction over maintaining a natural ecological balance. It is also influenced by factors like limited cloud cover and sunny days, which encourage warm air to linger over specific areas for longer periods.
However, it's important to note that not all cities experience the heat island effect. The geographical location and the presence of mountainous structures in different cities can impact the occurrence of this phenomenon.
Be sure not to miss this other article that delves into the causes behind the occurrence of heat waves.

Causes of the urban heat island effect
The heat island effect is caused by a combination of factors, including:
- Urban geometry: the layout and design of cities can contribute to the heat island effect. Tall buildings, narrow streets, and the arrangement of structures can create urban canyons that restrict airflow and trap heat within the urban area.
- Surface composition: the materials used in urban areas, such as asphalt, concrete, and dark-colored surfaces, have a high heat absorption capacity. These materials absorb solar radiation during the day and release it slowly at night, keeping the urban environment warmer.
- Lack of vegetation: the reduction of vegetation in cities, including trees, parks, and green spaces, is another significant factor. Vegetation provides shade and evaporative cooling, helping to lower temperatures. Urbanization and the removal of vegetation reduce the cooling effects of evapotranspiration.
- Human activities: various human activities in urban areas contribute to the heat island effect. These include the use of air conditioning and heating systems, industrial processes, power generation, and transportation. These activities release excess heat, adding to the overall temperature of the urban environment.
- Greenhouse gas emissions: the emission of greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide and methane, from human activities in cities contributes to the heat island effect. These gases trap heat in the atmosphere, leading to a warming effect in urban areas.
It's important to note that the severity of the heat island effect can vary depending on the size and density of the urban area, local climate conditions, and other geographical factors.
Discover more about renewable and non-renewable energies, including their key characteristics and distinctions, by exploring this other article.

Consequences of the urban heat island effect
The heat island effect can have several consequences on urban environments and the well-being of people living in these areas. Some notable consequences include:
- Increase in the energy demand and costs: the higher temperatures in urban areas result in increased demand for cooling, particularly air conditioning. This leads to a higher energy consumption and greater strain on the electrical grid, resulting in increased energy costs for individuals and businesses.
- Health issues: the heat island effect can have significant health implications. Prolonged exposure to high temperatures can lead to heat-related illnesses, including heat exhaustion and heatstroke. Vulnerable populations, such as the elderly, children, and those with pre-existing health conditions, are particularly at risk.
- Poor air quality: the heat island effect exacerbates air pollution in urban areas. The stagnant air and increased energy usage contribute to the accumulation of pollutants, such as particulate matter and ozone, leading to reduced air quality. This can have detrimental effects on respiratory health and overall well-being.
- Water management challenges: urban heat islands also impact the water cycle. The increased temperatures accelerate evaporation rates, leading to higher water demand for irrigation and potentially stressing water resources. Additionally, the increased runoff from impervious surfaces during rainfall events can overload stormwater systems, leading to flooding and water pollution.
- Ecological impact: the heat island effect disrupts the natural balance and biodiversity in urban areas. The reduction of vegetation and habitat loss negatively impact wildlife populations. Urban ecosystems may struggle to support native species and ecological processes.
Don't miss out on this informative article that delves into the definition of environmental degradation, accompanied by compelling examples of its causes and effects.
Solutions to the urban heat island effect
Addressing the urban heat island effect requires implementing various solutions and strategies to mitigate the elevated temperatures in urban areas. Some effective approaches include:
- Urban greening: increasing the amount of vegetation in cities through planting trees, creating green spaces, and incorporating rooftop gardens. Vegetation provides shade, reduces surface temperatures through evapotranspiration, and improves air quality.
- Cool roofs: using reflective materials or coatings on rooftops to reduce solar heat absorption. Cool roofs reflect more sunlight and emit less heat, resulting in lower surface temperatures and decreased energy consumption for cooling.
- Green infrastructure: implementing green infrastructure practices such as bioswales, green roofs, and permeable pavements. These features help to manage stormwater, reduce runoff, and provide cooling effects through evaporation.
- Urban design: incorporating urban design strategies that promote natural ventilation and airflow. This includes designing buildings and streetscapes to allow for better air circulation and creating open spaces that facilitate cooling breezes.
- Heat-resistant materials: utilizing heat-reflective or heat-resistant materials in urban infrastructure, such as roads, sidewalks, and parking lots. These materials can help reduce the heat island effect by minimizing heat absorption and retention.
- Sustainable transportation: encouraging sustainable transportation options such as walking, cycling, and public transit to reduce vehicle emissions and associated heat generation.
- Policy and planning: incorporating heat island mitigation strategies into urban planning and development policies. This may include incentivizing green infrastructure, implementing heat island mitigation requirements for new construction, and integrating climate resilience considerations into urban planning processes.
By implementing a combination of these solutions, cities can effectively mitigate the urban heat island effect, create more livable environments, and enhance the resilience of urban areas in the face of climate change.
Lastly, don't forget to check out this other article where we explore the distinction between temperature and heat.
If you want to read similar articles to What Is the Heat Urban Island Effect?, we recommend you visit our Climate change category.
- National Geographic. Urban Heat Island. Available at: https://education.nationalgeographic.org/resource/urban-heat-island/
- Reduces Urban Heat Island Effect. EPA. United States Environmental Protection Agency. Available at: https://www.epa.gov/green-infrastructure/reduce-urban-heat-island-effect