El Niño Phenomenon - What It Is, Causes and Consequences


El Niño, meaning "the little boy" in Spanish, is a climate pattern characterized by a significant warming of the surface waters in the central and eastern equatorial Pacific Ocean. This warming, which typically occurs every two to seven years, is not a mere regional affair; it's a global game-changer, influencing weather patterns from the Americas to Asia and beyond. El Niño's influence extends beyond precipitation, affecting temperatures, storm tracks, and even the delicate balance of marine ecosystems.
In this article by thedailyECO, we'll delve into the intricacies of El Niño, unraveling its causes, tracing its consequences, and understanding its role in shaping our planet's climate.
What is the El Niño phenomenon?
El Niño, meaning "the little boy" in Spanish, is a climate pattern characterized by a significant warming of the surface waters in the central and eastern equatorial Pacific Ocean.
This warming, which typically occurs every two to seven years, can have far-reaching effects on weather patterns around the globe.
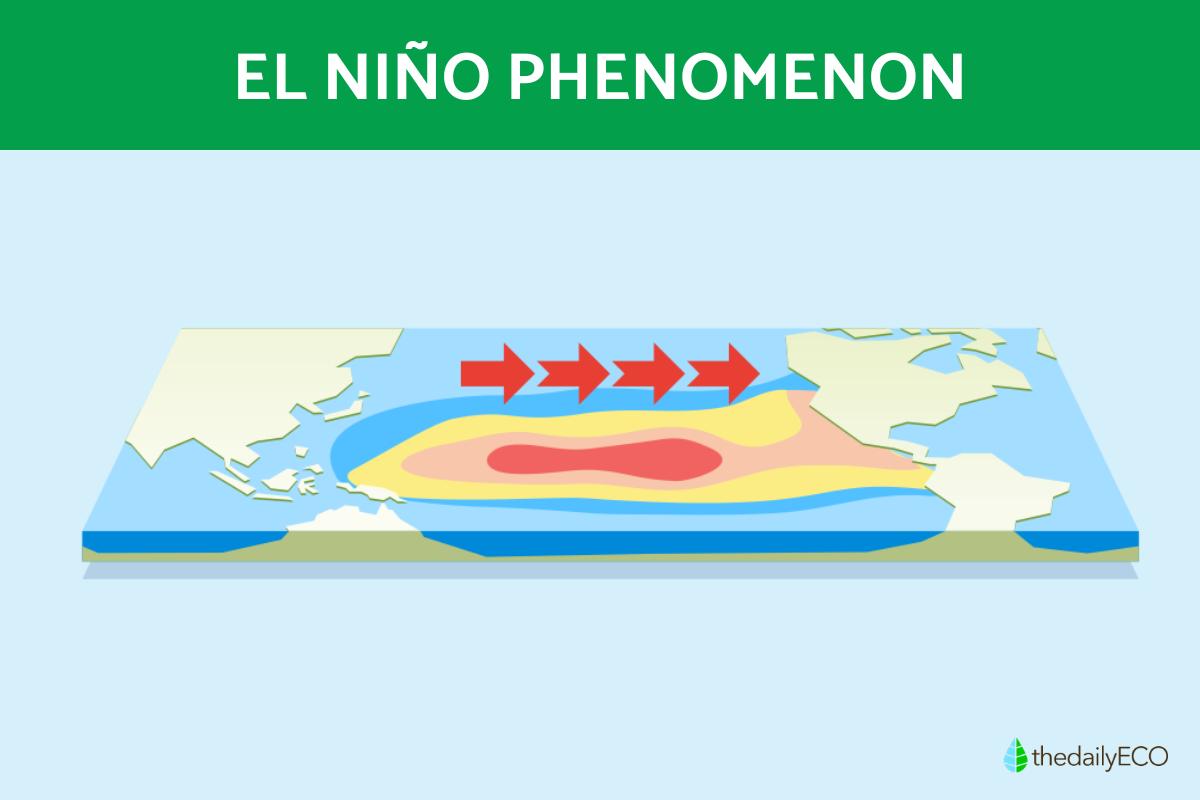
During an El Niño event, the normally strong easterly trade winds that blow across the Pacific weaken or even reverse direction. This disruption in the trade winds allows warm water from the western Pacific to surge eastward, leading to a rise in sea surface temperatures in the central and eastern Pacific. This warming, in turn, alters atmospheric circulation patterns, influencing precipitation and temperature patterns worldwide.
Gain insights into flood mitigation strategies, from sustainable land management practices to resilient infrastructure design, to safeguard communities against future inundation.

Causes of the El Niño phenomenon
The causes of the El Niño phenomenon are rooted in the Earth's climate system, specifically the interaction between the ocean and the atmosphere in the tropical Pacific region. These causes encompass:
- Variations in sea surface temperature: El Niño initiates with the unusual warming of the surface waters of the equatorial Pacific Ocean. Typically, trade winds blow from east to west in this area, pushing warm waters westward and accumulating them in the western Pacific region. During an El Niño event, these trade winds weaken or even reverse, enabling warm waters to move eastward.
- Change in atmospheric circulation: the warming of water in the equatorial Pacific region alters global atmospheric circulation. Warm, moist air ascends in the eastern Pacific, setting off a chain of effects. This includes a reduction in atmospheric convection in the western Pacific, potentially leading to droughts in areas like Australia and Indonesia. Simultaneously, it triggers more intense rainfall patterns in South America, contributing to flooding.
- Interaction with other weather patterns: El Niño does not operate in isolation and can interact with other weather patterns, such as the North Atlantic Oscillation and the South Atlantic Oscillation. These interactions can either magnify or alleviate the effects of El Niño in different parts of the world.
The El Niño phenomenon is part of a natural cycle, occurring approximately every 2 to 7 years, along with its counterpart, La Niña. Natural variability in the atmosphere and ocean plays a pivotal role in the occurrence of these events.
You might be interested in this other article where we explore the interplay between reflective surfaces and sunlight absorption, and discover how albedo plays a crucial role in shaping Earth's climate.
Consequences of the El Niño phenomenon
El Niño can lead to a wide range of consequences, disrupting conventional weather patterns and transforming landscapes. It's not limited to one region; its global impact stretches across the world, affecting diverse ecosystems and species, including humans.
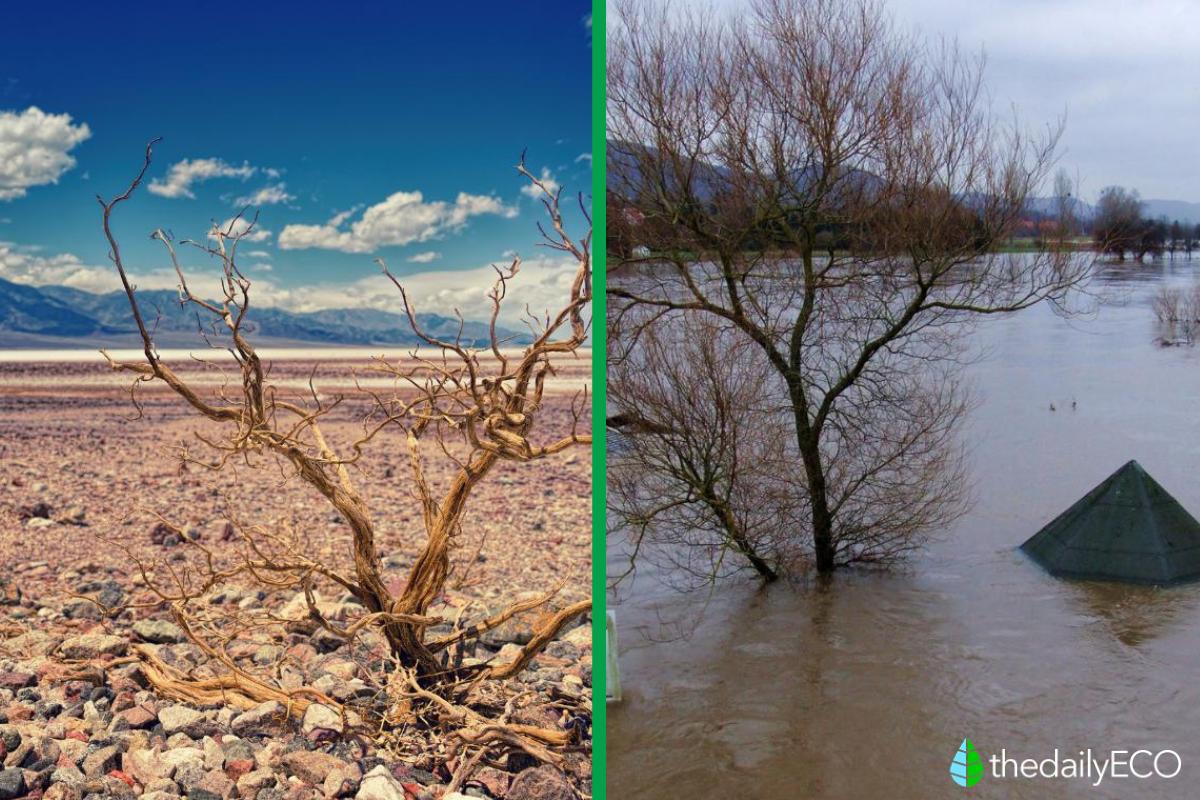
In some regions, El Niño can turn deserts into flooded zones. This drastic change in weather patterns can lead to severe flooding, erasing arid landscapes and creating unexpected water bodies.
Conversely, El Niño can trigger droughts and sometimes wildfires in typically humid tropical forests. This paradoxical effect can be observed in some of the world's wettest regions.
The repercussions of El Niño are not confined to a single location. Its influence spans the globe, impacting various regions from Canada to New Zealand, encompassing both northern and southern hemispheres and extending from east to west.
El Niño-induced alterations in ocean circulation patterns can disrupt marine ecosystems. It can bring heavy rainfall to areas unaccustomed to such precipitation, which can be beneficial in some cases, such as providing much-needed water to typically arid regions like the Peruvian coast. However, when rain turns to snow in mountainous areas, it can result in destructive flooding and landslides.
These shifts in weather patterns and their far-reaching consequences demonstrate the profound impact of El Niño on both terrestrial and aquatic environments.
Challenge your perception of hot and cold by delving into the fascinating world of thermodynamics, where temperature and heat play a pivotal role.

Differences between the El Niño and La Niña phenomena
El Niño and La Niña are opposite phases of the El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) phenomenon, and they bring distinct changes to global weather patterns. Here are the key differences between El Niño and La Niña:
Sea surface temperature
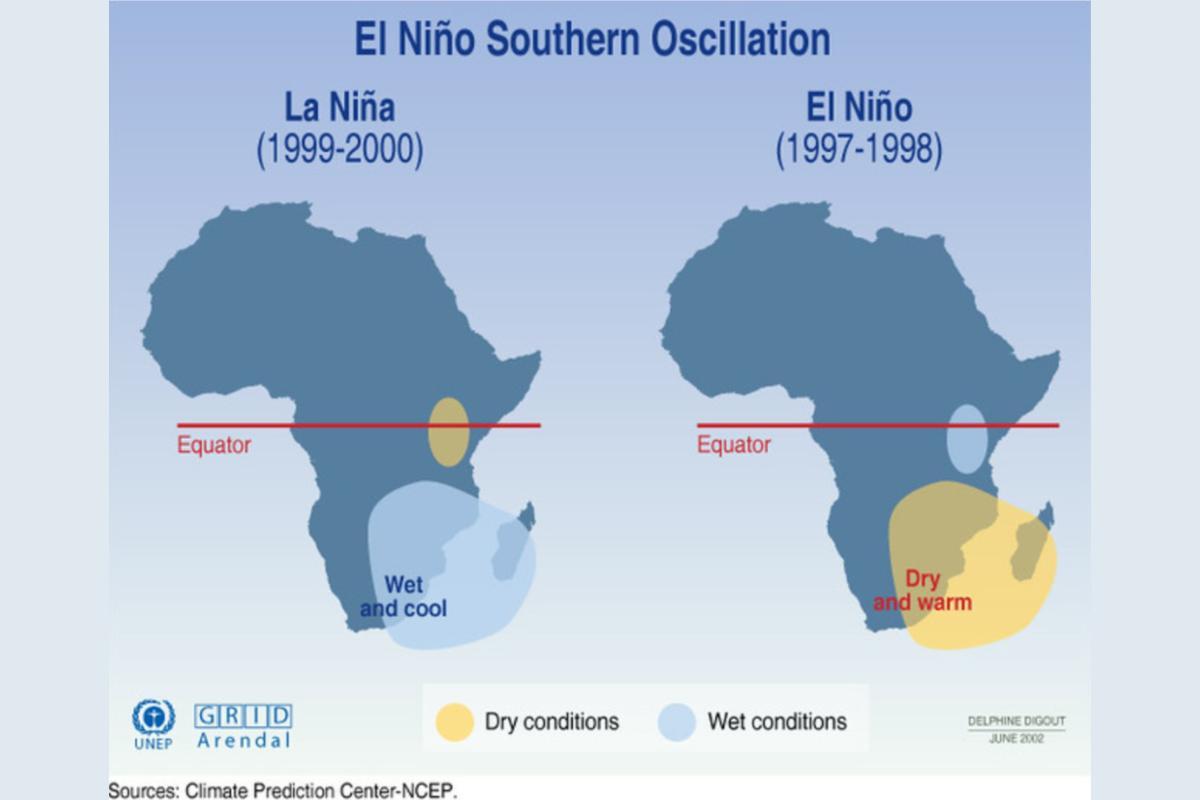
- El Niño: during El Niño, there is a warming of the sea surface temperatures in the central and eastern tropical Pacific Ocean. Warmer waters extend towards the western coast of South America.
- La Niña: in La Niña, sea surface temperatures in the central and eastern tropical Pacific become cooler than normal. This cooling effect is more pronounced in the eastern Pacific.
Atmospheric circulation
- El Niño: El Niño is characterized by weakened or reversed trade winds in the tropical Pacific. This can disrupt normal atmospheric circulation patterns, affecting weather across the globe.
- La Niña: La Niña features stronger than usual trade winds in the tropical Pacific. This typically leads to more stable atmospheric conditions.
Weather effects
- El Niño: El Niño often brings wetter conditions to the western coast of South America, leading to flooding and landslides. It can also result in droughts in some regions, such as Australia and Indonesia. In the United States, it can bring milder winters and increased precipitation to the southern states.
- La Niña: La Niña tends to bring drier conditions to the western coast of South America, which can lead to droughts. It is associated with more rainfall in the western Pacific and increased hurricane activity in the Atlantic.
Global Impact
- El Niño: El Niño's effects are felt globally, impacting weather patterns, agriculture, and ecosystems in various regions. It can result in extreme weather events like hurricanes and heavy rainfall.
- La Niña: La Niña also has a global impact, but its effects are often opposite to those of El Niño. It can lead to increased hurricane activity and more predictable weather patterns in some regions.
Frequency
- El Niño: these events occur irregularly, typically every 2 to 7 years, and can last for several months.
- La Niña: these events are the opposite phase of El Niño and occur at varying intervals, often following El Niño events.
In summary, El Niño and La Niña represent opposite phases of the ENSO cycle, resulting in contrasting sea surface temperatures, atmospheric circulation, and weather patterns across the world.
Do not miss this other article where we explain the intricacies of climate and weather, two intertwined yet distinct concepts that govern our planet's atmospheric tapestry
If you want to read similar articles to El Niño Phenomenon - What It Is, Causes and Consequences, we recommend you visit our Meteorological phenomena category.