La Niña Phenomenon - What It Is, Causes and Consequences


Did you know that a cooler Pacific Ocean can trigger flooding in Southeast Asia and droughts in the American Southwest? This paradoxical scenario is a consequence of La Niña, a climate phenomenon impacting weather patterns around the world. La Niña is one phase of the El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) cycle, a natural fluctuation in Pacific Ocean temperatures and atmospheric conditions.
The following article by thedailyECO dives deep into the La Niña phenomenon, exploring its causes, consequences, and how it differs from El Niño.
What is the La Niña phenomenon?
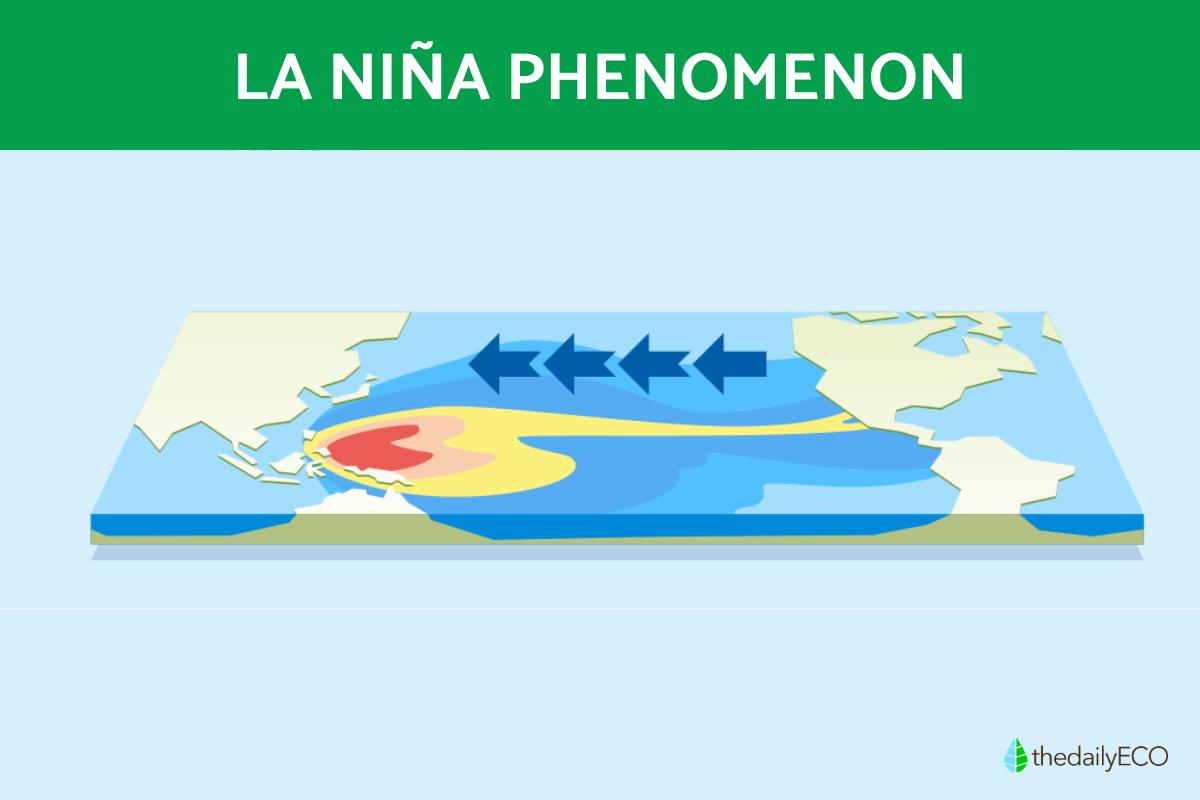
La Niña, translating to "the little girl" in Spanish, is a climate phenomenon occurring in the tropical Pacific Ocean.
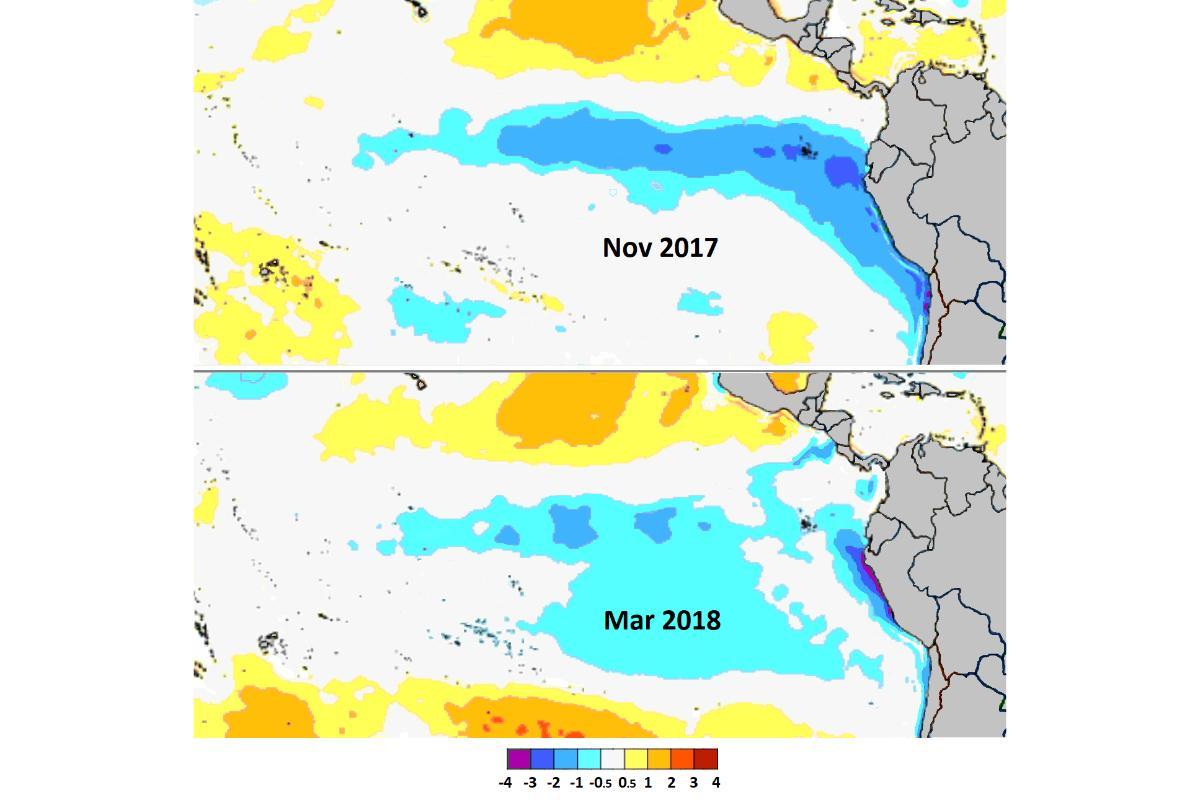
It represents the cooler phase of the natural cycle known as the El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO), contrasting with its warmer counterpart, El Niño. This cycle encompasses two distinct phases: El Niño, marked by warmer-than-average sea surface temperatures, and La Niña. These fluctuations in Pacific Ocean temperatures can disrupt typical weather patterns, leading to increased chances of intense storms in some regions and heightened risk of droughts in others. During La Niña, sea surface temperatures dip below average levels in the central and eastern equatorial Pacific.
The name was coined by fishermen along the coast of Peru, who noticed that the phenomenon often coincided with the appearance of cold, nutrient-rich waters, which they associated with the Christ child (El Niño) and the opposite, colder phase, which they termed "La Niña" or "the little girl." This naming convention reflects the contrasting nature of the two phases.
La Niña is triggered by strengthened trade winds. These powerful east-to-west winds blow across the Pacific, pushing warm surface water westward. This cool down in the east happens because the warm water piles up in the western Pacific due to the stronger winds.
As surface water cools, a fascinating phenomenon called upwelling occurs. Colder, nutrient-rich water from the ocean depths rises to the surface, replacing the displaced warm water. This upwelling can influence marine ecosystems by providing a nutrient boost for plankton growth, potentially impacting fisheries in some regions.
How frequently does the La Niña phenomenon occur?
La Niña events typically occur irregularly, with intervals that can vary widely. On average, they tend to happen approximately every 2 to 7 years. However, the frequency and intensity of La Niña occurrences can be influenced by various factors, including oceanic and atmospheric conditions, and therefore may not adhere strictly to a regular schedule.
To delve deeper into El Niño, a phenomenon often compared to La Niña, you can read our other article.

What causes the La Niña phenomenon?
La Niña phenomenon arises from a complex interplay of several mechanisms:
Intensified trade winds
Prevailing east-to-west winds, known as trade winds, typically transport warm surface waters westward across the Pacific. During La Niña, these trade winds become significantly stronger and more persistent, further propelling warm surface water towards the western Pacific and leading to a buildup of warm water in that region.
Surface water cooling
The intensified trade winds act like a giant conveyor belt, pushing warm surface waters westward. This results in a cooling effect in the central and eastern equatorial Pacific, contrasting sharply with the warming witnessed during El Niño events.
Upwelling
The cooling of surface waters triggers a fascinating phenomenon known as upwelling. Colder, nutrient-rich waters from the deep ocean depths rise to the surface, replacing the displaced warm water. This upwelling process contributes to a surge in nutrients, potentially impacting marine ecosystems and fisheries by fueling plankton growth and potentially enhancing fishing opportunities in specific regions.
Explore another interesting article where we delve into the formation and characteristics of the polar vortex.
Consequences of the La Niña phenomenon
The La Niña phenomenon has various consequences that ripple across the globe, these include:
Altered precipitation
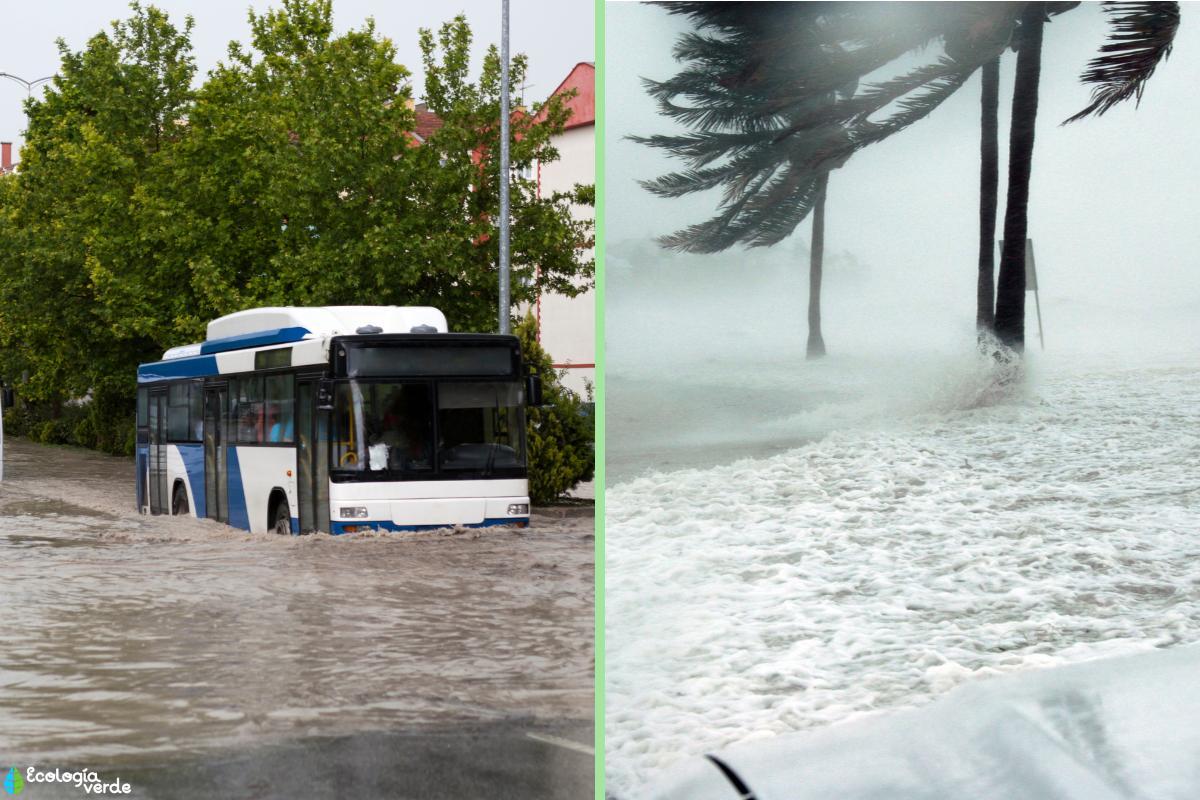
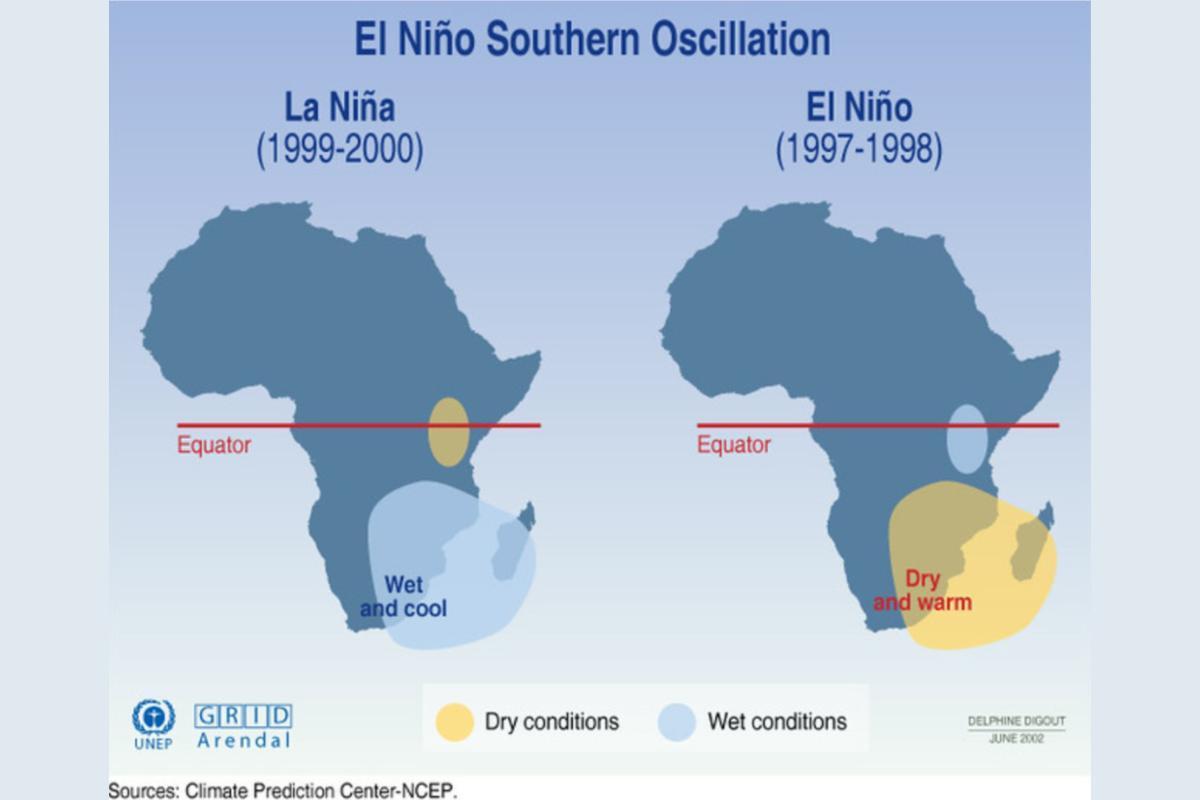
La Niña often leads to increased precipitation in some parts of the world, like Australia, Southeast Asia, and parts of South America, which can cause flooding.
Conversely, other regions, such as the southwestern United States and northern South America, experience drier conditions and potential droughts and water shortages.
This can have significant economic consequences for agriculture, with potential crop failures in drought-stricken regions and disruptions to harvest schedules in flood-prone areas. Water management becomes crucial, with regions needing to implement strategies for flood control or water conservation depending on their situation.
Influenced hurricane activity
La Niña can enhance hurricane activity in the Atlantic Ocean, posing increased risks to coastal areas. This can lead to societal disruptions due to evacuations, damage to infrastructure, and potential loss of life. Communities along the coast need to be prepared for these heightened risks.
Shifted temperature patterns
La Niña can cause changes in temperature patterns around the globe, with some regions experiencing colder temperatures and increased climate variability. This variability can manifest as more frequent extreme weather events like heatwaves, cold snaps, or erratic rainfall patterns.
These disruptions can impact various sectors, with increased energy demands for heating or cooling, challenges for construction and outdoor activities, and potential disruptions to ecosystems. Not to mention that extreme weather events like heatwaves and cold snaps can have adverse health impacts, particularly on vulnerable populations.
The consequences of La Niña can often have cascading effects, impacting interconnected systems and creating complex challenges.
Do not miss this other article on what the difference between temperature and heat is.

Differences between the La Niña and El Niño phenomena
As mentioned before, The El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) cycle encompasses two distinct phases: El Niño and La Niña. While they share some similarities, their effects on global weather patterns are quite different. Here's a breakdown of their key differences:
During El Niño events, the equatorial Pacific experiences warmer-than-average sea surface temperatures.This typically leads to increased precipitation along the west coast of South America, while other regions, like the western Pacific, may experience drier conditions. Weakened trade winds allow warm surface water to pile up in the central and eastern Pacific, leading to warmer temperatures.
In contrast, La Niña events are characterized by cooler-than-average sea surface temperatures in the equatorial Pacific. Compared to El Niño, La Niña often leads to reduced precipitation along the west coast of South America, with potential for increased rainfall in other regions, such as Southeast Asia and Australia. Stronger trade winds blow from east to west across the Pacific, pushing warm surface water westward and contributing to cooler temperatures in the east.
Overall, La Niña and El Niño represent opposing ends of the ENSO spectrum, influencing global climate patterns in contrasting ways.
While La Niña is a large-scale phenomenon impacting global weather, other regional factors like the cold drop, a meteorological phenomenon characterized by cool air masses at high altitudes, can also influence specific weather patterns.Read about it in this other article.

If you want to read similar articles to La Niña Phenomenon - What It Is, Causes and Consequences, we recommend you visit our Meteorological phenomena category.