What Is a Whorl in Biology?


In the botanical world, the concept of whorls unveils a captivating pattern of arrangement found in plants. Whorls refer to the concentric groupings of leaves, branches, or flowers that emerge from the same level or node along the plant's stem. These remarkable formations not only contribute to the structural integrity of plants, but also play a crucial role in their reproductive processes.
In this article from thedailyECO, we explain what whorls are and also explore their various components and their respective functions.
What are flower and leaf whorls?
In the world of plants, the concept of whorls is an intriguing phenomenon that sheds light on their structure and classification. Whorls can indeed be observed in both leaves and flowers, providing valuable insights into plant anatomy and organization.
Leaf whorls
When examining the arrangement of leaves along the stem, we can classify them into two main types.
- Alternate leaves: are positioned individually along the stem.
- Whorled leaves: form clusters or emerge from the same node, creating a visually captivating spiral pattern.
Flower whorls
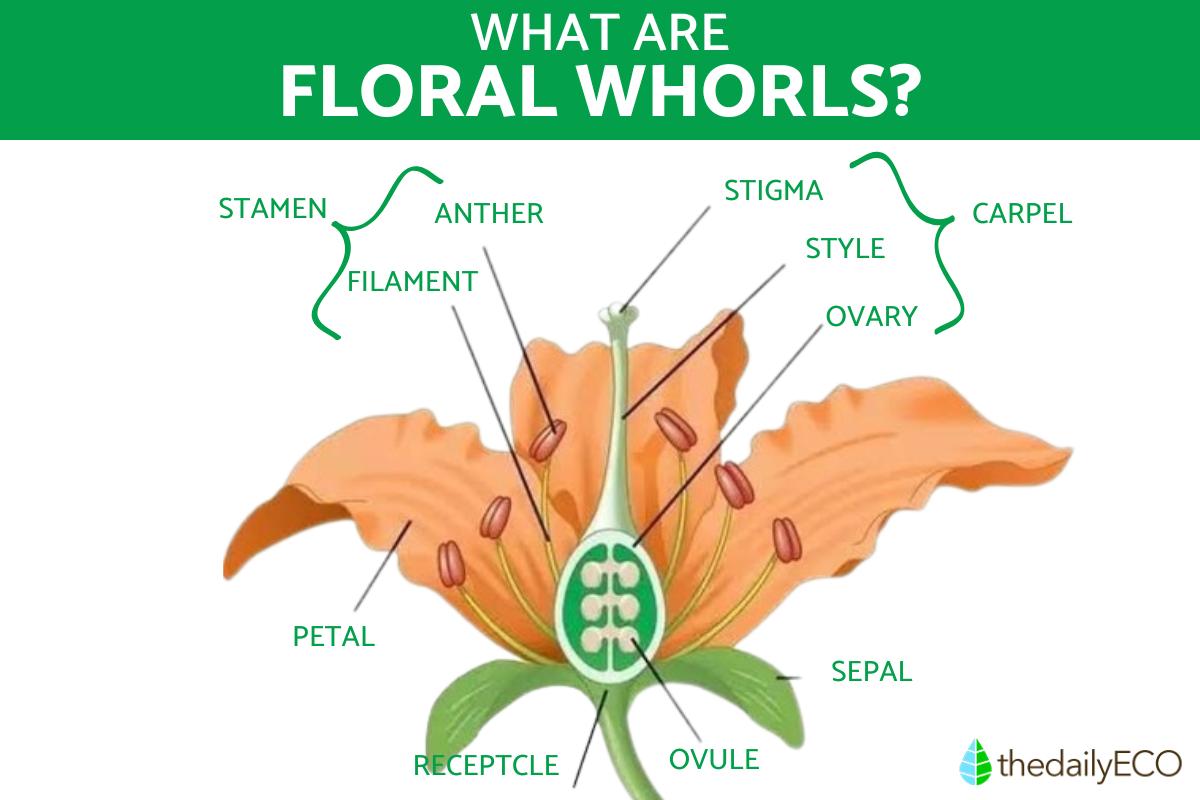
Flowers, the remarkable reproductive structures of flowering plants, do originate from modified leaves that undergo transformation as the plant matures. These modified leaves do give rise to various parts of a flower, including the peduncle (flower stalk), calyx (sepals), corolla (petals), androecium (male reproductive organs), and gynoecium (female reproductive organs). Collectively, these parts do indeed form what we refer to as floral whorls.
Similar to leaves, flowers can indeed be classified based on their whorls. Some flowers, referred to as naked flowers, lack a perianth, which is the protective covering of a flower.
In contrast, dressed flowers, known as clamídeas, do possess a perianth. The perianth indeed consists of the calyx and corolla, which serve to safeguard the reproductive organs within the flower.
Flowers can further be categorized as:
- Monoclamydeous if they have only a calyx.
- Diclamydeous if they have two distinct whorls within the perianth.
Additionally, certain flowers may indeed exhibit homoclamydeous characteristics, where both the corolla and calyx are similar in appearance, while others may display heteroclamydeous traits, indicating differentiation between the corolla and calyx.
For more detailed information, don't miss this additional article that explains the perianth and its vital functions.

What are floral whorls and their components?
In this section, we will explore the floral whorls, which are the structures that constitute a flower. These whorls can be classified into two groups:
- Androecium and gynoecium: these floral whorls can exist independently or coexist within a flower.
- Calyx and corolla: these leafy structures collectively form what is known as the perianth.
Androecium
The androecium represents the male reproductive organ of the flower. It consists of stamens, each composed of a filament and an anther at its end. The anther is responsible for storing pollen. Stamens can be united or free, and they can be grouped in various ways, including:
- Monadelfous stamens: united by the filaments in a single bundle.
- Diadelphous stamens: arranged in two bundles.
- Polyadelphous stamens: arranged in more than two bundles.
- Syngenesious stamens: united by the anthers in a single bundle.
- Didynamous stamens: comprising two long stamens and two short stamens.
- Tetradynamous stamens: comprising four long stamens and two short stamens.
Gynoecium
The gynoecium represents the female reproductive organ, where enclosed structures give rise to seeds. It is composed of carpels and includes the ovary, style, and stigma. The gynoecium can be classified as:
- Monocarpous: formed by a single fused carpel leaf.
- Pluricarpous: formed by several carpel leaves, further classified into syncarpous (carpel leaves fused) and dialycarpous (carpel leaves free).
Calyx
The calyx is formed by sepals, modified leaves that are typically green and serve a protective function. Sepals can be differentiated based on their arrangement:
- Polysepalous: when sepals are free and not fused.
- Gamosepalous: when sepals are fused.
Sepals can also be classified based on their duration, either ephemerous (shedding after flower opening and fertilization) or fugacious (persisting and accompanying the fruit).
Corolla
The corolla consists of petals, which are modified leaves with attractive shapes and colors that facilitate pollination. Similar to the calyx, the corolla can be categorized as either dialypetalous (petals are free) or gamopetalous (petals are fused) based on their arrangement.
Don't miss out on this other article where we explore the differences between angiosperm and gymnosperm plants.

Other parts of the flower
Now that you are familiar with floral whorls and their classifications, let's explore other important components of a flower:
- Peduncle: The peduncle is the lowermost part of the stem that supports the flower. It acts as a slender stalk, connecting the flower to the stem. A flower with a peduncle is known as a pedunculate flower, while a flower without a peduncle is referred to as a sessile flower. The peduncle is typically green, cylindrical, and its size varies across different plant species.
- Receptacle: The receptacle, also called the floral axis, is an enlarged structure located above the peduncle. It serves as the base to which the other floral whorls are attached. These include the calyx, corolla, androecium, and gynoecium, forming the complete flower structure. The receptacle provides support and serves as a platform for the arrangement and development of the various floral organs.
You might find this article interesting as well, as it delves into the world of gymnosperms, discussing their defining features and how they differ from angiosperms.
If you want to read similar articles to What Is a Whorl in Biology?, we recommend you visit our Biology category.