Environment
425 articles

The jet stream is a high-altitude, fast-moving ribbon of air that encircles the Earth, influencing weather patterns and climate across continents. It steers storms, shifts temperatures, and creates distinct weather zones. Formed by temperature differences between the polar and tropical regions, the jet stream...

Also known as a udometer, hyetometer or, most commonly, a rain gauge, a pluviometer is used to measure the amount of liquid precipitation which falls in a specific location during a given period. This liquid precipitation is mostly in the form of rain. knowing rainfall measurements is of great importance...

An anemometer is an instrument used to measure wind speed. This device is essential in various fields such as meteorology, aviation, energy production, navigation and even certain outdoor sports. Its operation varies depending on the type, but all models collect key information to analyze wind intensity....

An altimeter is a device that measures altitude, meaning the vertical distance between a given point and certain fixed level. In most practical uses, this fixed level is sea level. Its use is essential in various activities such as aviation, mountaineering and outdoor sports. In these capacities, accurate...

Also known as soil contamination or land pollution, soil pollution is a type of environmental degradation which affects the natural substrate of the Earth. This degradation is the result of chemical substances being released which harm the land to varying degrees, endangering ecosystems and human health...

Amyloplasts are specific plastids present in plant cells, specifically they are organelles responsible for functions such as starch synthesis and storage. Amyloplast organelles have a double membrane, composed of a smooth outer membrane and an inner membrane that invaginates to form tubules. The inner...

Porpoises are marine mammals of the Phocoenidae family. Although very similar in appearance to dolphins, they are genetically different and are more closely related to other cetaceans. Most live in ocean habitats, but there are some which are known to live in brackish waters and one which is known to...

Thunderstorms are one of nature’s most powerful and dramatic weather phenomena, often marked by flashes of lightning, rumbling thunder, and heavy rain. But have you ever wondered what causes these intense storms to form? Understanding the science behind thunderstorms can help us better appreciate their...

Industrial wastewater, a byproduct of various manufacturing processes, poses a significant threat to our environment if not properly treated. Containing harmful pollutants such as chemicals, heavy metals, and other toxic substances, this wastewater is generated by a wide range of industries, from factories...

Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) refer to the combined content of all inorganic and organic substances, including minerals, salts, metals, and other compounds, dissolved in a liquid—usually water. These particles are so small that they pass through a typical water filter, distinguishing them from suspended solids...

A barometer is an instrument used to measure atmospheric pressure, a fundamental metric for predicting changes in the weather. While they may be less common in homes than they once were, barometers are still vital pieces of equipment to help assess atmospheric conditions. In this article from thedailyECO,...

Ctenophores, commonly known as comb jellies, are marine invertebrates that, despite their jelly-like appearance, they are distinct from jellyfish. They belong to their own unique phylum, Ctenophora. Characterized by rows of cilia, or comb-like structures, these creatures use these for movement, creating a...

Climate change is a major factor contributing to the increasing frequency and intensity of hurricanes globally. As the Earth's temperature rises, weather patterns are shifting, leading to significant changes in the dynamics of these powerful storms. Understanding the complex relationship between climate change...
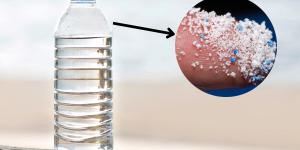
Microplastics are plastic particles that are less than 0.2" (5 mm) in size which can come from different sources. Regardless of their origins, their presence in the world's water has been exponentially increasing. Since they are found in water, they can even enter human tissue if they are sufficiently...

The various types of global climates are categorized by different factors and systems. These can be dependent on their ecosystem type, location, altitude and other determinants. The continental climate is a category of climate which is determined by the Köppen climate classification. This is a system based...

A mountain climate is the localized climate of a mountainous area. Due to the greater altitude, the atmospheric conditions are altered, resulting in lower temperatures and significant climate variability. Temperature and precipitation patterns change significantly at different altitudes. For this reason,...

The Last Universal Common Ancestor, or LUCA, represents the most recent shared ancestor of all life on Earth. LUCA is not a single organism but rather a hypothetical entity from which all modern organisms—bacteria, archaea, and eukaryotes—descend. Understanding LUCA provides crucial insights into the...

Cirrocumulus are a type of cloud that forms at high altitudes, generally more than 6,000 meters above sea level. They are composed of small ice crystals. They are characterized by their appearance in groups of small white clouds that are organized in regular patterns, often being compared to fish scales....

Atmospheric pressure, the force exerted by the weight of the air above us, plays a crucial role in weather patterns, aviation, and even our daily lives. Measuring this pressure helps scientists and meteorologists predict weather changes and understand atmospheric behavior. But how exactly is atmospheric...

The Earth's atmosphere is in constant motion, driven by the uneven heating of the planet's surface by the sun. This dynamic movement, known as general atmospheric circulation, shapes global wind patterns, influences climate zones, and affects weather systems around the world. Understanding these circulation...

Also known as flooded forests, freshwater swamp forests are characterized by periodic flood by bodies of water such as rivers or lakes. While this flooding can be seasonal, it can be more frequent in certain areas. Their duration and the depth of the flooding can also vary according to region and the...

Stomata are tiny, but vital structures found on the surfaces of plant leaves and stems, playing a crucial role in the processes of gas exchange and transpiration. These microscopic pores allow plants to absorb carbon dioxide for photosynthesis while releasing oxygen and water vapor. However, not all stomata...

Chromoplasts are a type of cell organelle that are present exclusively in certain plants, algae and other eukaryotes. Specifically, they are a type of plastid. They are responsible for pigment generation in plants, meaning they give color to flowers and other parts. In addition, their functions include...

Also known as tropical dry forests, dry forests are a relative description. While rainforests have periods throughout the year when there is more rainfall, high rainfall occurs throughout the year. In a dry forest, there are distinct wet and dry seasons with periods of little to no rain. As with rainforests,...

World Car Free Day is celebrated on the 22nd September as part of a global movement that promotes sustainable mobility and the reduction of the use of private cars. This day aims to reduce the environmental impact produced by these means of transport. In turn, the hops is not only to improve people's...

Leucoplasts are small rounded structures that belong to the plastid family. These are membrane-bound organelles which are found in certain cells, mainly plants and algae. The functions of leucoplasts include lipid synthesis, carbohydrate storage and starch production. There are three types to carry out these...

Granivorous animals are those that carry out seed predation as their main form of nourishment. This means they search for seeds and grains to acquire the nutrients they need for survival. Without them, they will be unable to survive. There are other animals which will supplement their main diet with seeds,...

A sclerophyllous forest is an ecosystem characterized by the presence of vegetation adapted to Mediterranean climate conditions. This is largely defined by its dry summers with hot temperatures and wet winters which are relatively mild. The flora and fauna of these ecosystems have specific adaptations to...

Hot springs can be found all around the world, with notable concentrations in Latin American countries, as well as in Europe and Asia. These natural formations are popular tourist attractions due to the numerous health benefits they offer. he warm, soothing waters of hot springs help to relax both the...

Examining the concept of an endorheic basin is important for understanding how water is distributed and used in different regions of the world. This is very important for geographical and hydrological studies. An endorheic basin is defined as a region in which rainwater and river water have no outlet to...

Sea level rise is a serious and urgent result of climate change, mainly caused by melting polar ice caps and glaciers, as well as seawater expanding as it heats up. As global temperatures keep rising, sea levels are increasing at a rapid pace, threatening coastal communities, natural habitats, and important...

Bodies of water, ranging from expansive oceans to winding streams, are crucial elements of our planet. They are categorized by their size, origin, and physical properties, and play a fundamental role in sustaining life on Earth. These bodies of water are integral to ecological health, human well-being, and...

Monsoon climates are characterized by distinct wet and dry seasons driven by seasonal wind shifts. This climatic pattern is prevalent in regions near the equator, particularly in South Asia, Southeast Asia, West Africa, and parts of Australia. Monsoon climates have a profound impact on agriculture, as the...

A chaparral is a biome characterized by dense and shrubby vegetation which have a Mediterranean climate. The latter means they have dry summers and went winters. This type of biome is most associated with the United States, but there are chaparrals outside of the US such as in the Mediterranean basic, Chile,...

There is a lot of waste we can see piling up in landfills and even in areas where it is illegally discarded. Such waste is varied in nature, including decomposing organic matter, chemical spills, oxidized metals and plastics both macro and micro. Different types of waste decompose at different rates...

Clams, mussels, oysters, and scallops are just a few examples of fascinating creatures belonging to the bivalve family. These aquatic invertebrates are distinguished by their unique two-part shells, which protect their soft bodies. Whether they inhabit freshwater lakes or salty oceans, bivalves play a crucial...

Hydrology is the scientific discipline that studies the water cycle on Earth, including its distribution and movement, as well as its physical and chemical properties. This discipline covers the analysis of precipitation, water runoff, soil infiltration, river currents, aquifer recharge, evaporation and...

We know that different ecosystems can vary greatly in terms of biodiversity and geographical features. However, we can define ecosystems by certain characteristics. For example, a marine ecosystem is defined by saltwater and a desert ecosystem is defined by a lack of precipitation. One of the most defining...

Nature is a complex interplay of competition and cooperation. While survival often hinges on outcompeting others, many species have evolved mutually beneficial relationships. Unlike the predator-prey dynamic where one thrives at the expense of another, mutualism represents a win-win scenario, with both...

Fynbos is the term for a type of vegetation characteristic of the southwestern region of South Africa, known for its extraordinary biodiversity and adaptations to its Mediterranean climate. This ecosystem is part of the Cape Floral Kingdom. It is one of the world's six floral kingdoms and is home to a rich...

Life as we know it thrives within specific parameters, but Earth is also home to extraordinary organisms that defy these limitations. Among them are halophilic bacteria, microbes that not only survive but flourish in environments saturated with salt. From the depths of salt mines to the sun-baked surfaces...

Have you ever stopped to think about how some animals in the vast ocean manage to find sustenance? Unlike the known powerful predators with razor-sharp teeth, many aquatic creatures rely on a much more delicate approach – filter feeding. These fascinating animals are the ultimate opportunists, extracting...

Glial cells are structural, metabolic and trophic support cells for neurons. They are found in both the central nervous system and in the peripheral nervous system. For any function in an organism to be carried out, specialized cells are required. Despite being part of the central nervous system, glial cells...

Woody plants are a diverse and essential group of flora characterized by their durable, lignified stems and trunks. Defined by their robust internal structure, called secondary xylemthey, they differ significantly from their soft-stemmed herbaceous counterparts. These plants form the backbone of many...

Hydrography is the science responsible for the study and mapping of the Earth's bodies of water, both above and below the Earth's surface. This science provides essential data for navigation, resource management and prevention of natural disasters. Its findings are not only used by experts, but it helps...

Supercells are a particular type of thunderstorm distinguished by a persistent, rotating updraft called a mesocyclone. This rotating updraft plays a crucial role in propelling supercells to become the powerhouses of severe weather. Unlike regular thunderstorms, supercells have the potential to produce...

Have you ever witnessed a dramatic lightning show, only to find not a single drop of rain? This phenomenon, known as a dry storm, might seem counterintuitive, but it's a surprisingly common occurrence in dry and hot regions. Unlike regular thunderstorms that bring rain, dry storms only tease the dry...

Berries are more than just a tasty treat. They're a fascinating example of co-evolution, a partnership between plants and animals that benefits both sides. As animals munch on the berries, they also help spread the plant's seeds far and wide. And forget the image of berries as all small and round. They...

Also known as the horse family, equines are part of the taxonomic family Equidae. In the order Perissodactyla, they are four-legged mammals which are defined by robust bodies, placental birth, herbivorous diet and herd living. There are various types of equines, all with their own specific characteristics....

Air might seem like a simple, invisible blanket around our planet, but it's actually a fascinating mix of gases that play a crucial role in keeping us alive and shaping the Earth. Mostly made up of nitrogen and oxygen, air is not just essential for breathing; it also helps regulate temperature, protects...
