Difference Between Haploid and Diploid Cells


The difference between haploid and diploid cells concerns the chromosomes found within the nucleus of cells. Nuclei of eukaryotic cells contain the genetic information that results in how an organism is formed and functions. This information is packed very compactly into structures known as chromosomes. Chromosomes have a shape reminiscent of the letter X. They are composed of chromatin complex and proteins through which DNA is wound. Different cells have different numbers of chromosomes with this specific amount being known as the cell's ploidy. A diploid cell has a pair of these sets of chromosomes, while the haploid cell has one. Organisms in which there are more than two homologous chromosomes are called polyploids.
If you want to learn about the difference between a haploid vs. diploid cell, thedailyECO explains this in depth. We compare these two types of cells by their similarities and differences, as well as how they behave during reproduction. We also provide diagrams to explain these differences more clearly.
What is a haploid cell?
A haploid cell is one that has a single copy of each type of chromosome in its nucleus. This means there are no homologous chromosomes (i.e. of the same structure) in this type of cell. Haploid cells are the result of a meiotic cell division. Since they present a copy of the cell's genetic material, they can only perform mitosis to reproduce.
To take humans as an example, we have 23 pairs of chromosomes in each cell. 22 of these chromosomes are diploid somatic cells and the remainder is the haploid sex chromosome. In addition to the sex cells of humans, there are haploid life forms that reproduce asexually. These include some algae, fungi, wasps, ants or male bees (drones).
In the case of male drone bees, they are haploid organisms. This is because the eggs from which they originate are not fertilized. The number of chromosomes in their cells is half that of the queens or workers. This means they have 16 chromosomes that come entirely from the mother.
Take a look at our related article to discover more about the different types of cells.
Photo: Comparative tables
What is a diploid cell?
The product of the fusion between two haploid cells from two parents gives rise to the diploid cell. For this reason, diploid cells have two copies of each type of chromosome. In the human body, most of the cells are diploid. These are the somatic cells, i.e. cells that are not involved in reproduction. These include the cells that are used to create organ tissues, such as intestinal wall cells and neurons.
Most animals and some plants are diploid organisms. Some examples of diploid cells in animals and plants include common house mosquitoes (Culex pipiens) that have 3 pairs of chromosomes, the potato (Solanum tuberosum) that has 31 and the Eurasian carp (Cyprinus carpio) which has 51 pairs of chromosomes in its cells.
There are many plants whose life cycle is marked by presenting these two types of haploid or diploid cells, but they do so at different stages. An organism in the diploid stage undergoes meiosis where haploid spores originate. In turn, these will divide by mitosis and give rise to multicellular haploid organisms. From the latter, haploid male and female cells will emerge that will fuse, giving rise to the resultant diploid organism.
Both plants and animals can have haploid or diploid cells. However, this does not mean the cells of these organisms are all the same. Learn about their differences with our article on the differences between animal and plant cells.

Main differences between haploid and diploid cells
Although we have provided definitions of both haploid and diploid cells, we can better understand them both my making a comparison between them. For this reason, we summarize by looking at the main differences between haploid and diploid cells:
- The haploid cell has a single copy of chromosomes and the diploid cell has two copies.
- With the exception of human sex cells, most animal cells are diploid. Only some algae or fungi are haploid for most of their life cycle.
- A haploid cell is the result of mitosis of another haploid cell or meiosis of a diploid cell.
- A diploid cell is the result of the fusion of two haploid cells.
Do humans have diploid or haploid cells?
With these differences between haploid vs. diploid cells explained, it is understandable for us to wonder about the cells in our own body. All cells in the human body are diploid (somatic), with the exception of reproductive cells (gametes). Since these gametes are required from reproduction of the organism, they join chromosomes to create one complete set.
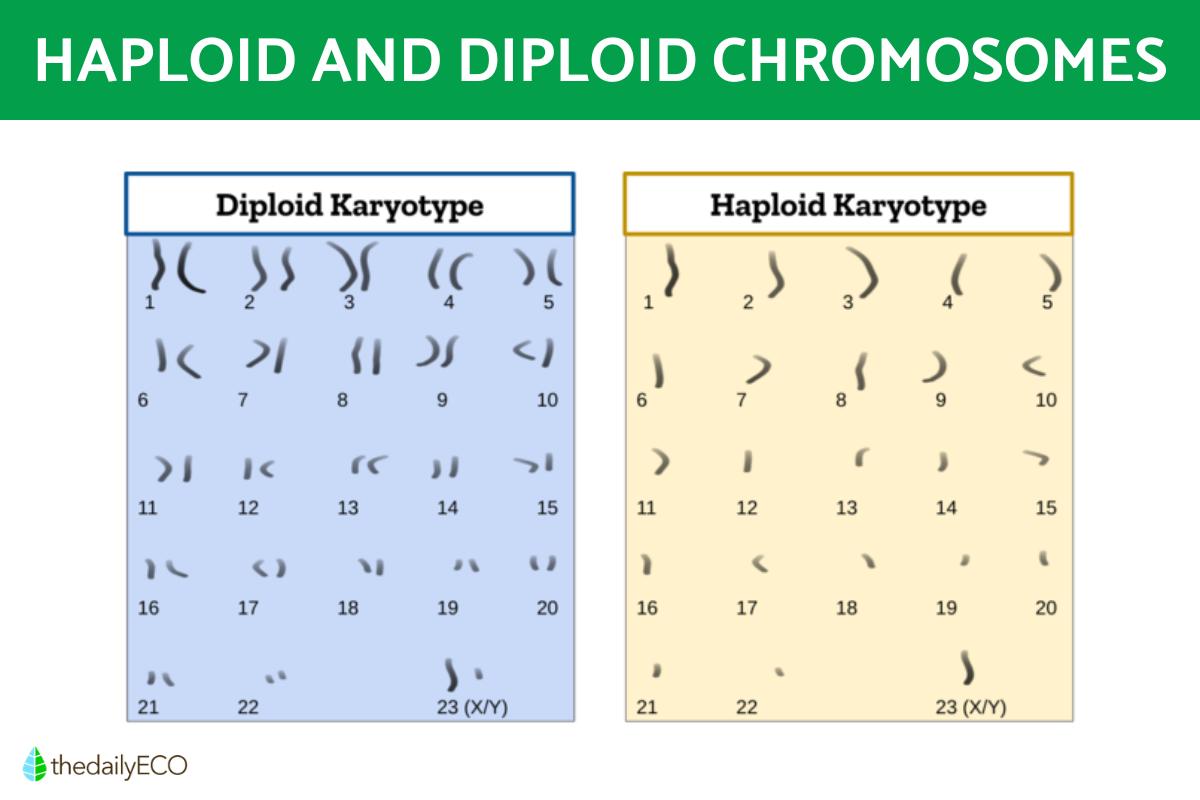
We can see the complete sets of chromosomes with the diagram below which shows the karyotypes of diploid and haploid organisms, i.e. their chromosomal sets.

Main similarities between haploid and diploid cells
Although there are key differences between haploid and diploid cells, it is important to remember there are certain key similarities. They include:
- Both are cells present in eukaryotic organisms (i.e. those that have cells with a well-defined nucleus).
- They originate through the process of cell division.
- In the nucleus of these cells is the genetic material in the form of chromosomes.
Learn more about the difference between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells in our related article.

Cellular reproduction: mitosis and meiosis
The cell cycle of diploid eukaryotic cells is divided into two main phases:
- Interphase: where the cell prepares for cell division
- Mitosis: the actual cell division itself
This is the same for haploid cells responsible for sexual reproduction, except the type of cell division is known as meiosis. This is the process of cell division where one diploid cell separates and gives rise to four haploid cells. Each of these daughter cells contains a copy of each chromosome of the parent. In the diagram above, you will see that haploid cells briefly become diploid cells because the zygote is necessarily diploid.
In mitosis, the process that results in two daughter cells identical to the mother. For this to be possible, the cell has had to previously replicate its genetic material so that the daughter cells receive an exact copy.
Although the cell cycle of eukaryotes can vary depending on whether we are talking about a single-celled organism, a plant or a fungus, there is a certain pattern that remains common. At the beginning of the cycle two haploid cells have different genetic information in each. They fuse and give rise to a diploid cell with a mixture of genetic material from the two parents.
It is common for mitosis to occur at some point in the cell cycle, giving rise to haploid cells. Finally, the successive mitosis that originates in the organism from its haploid or diploid cells gives rise to the development of multicellular organisms.
This is a very basic definition of the difference between mitosis and meiosis in cell division. With this in mind we can say that mitosis only occurs in diploid cells and meiosis only occurs in reproductive cells. In this way, meiosis is the process by which human embryos form.
If you want to read similar articles to Difference Between Haploid and Diploid Cells, we recommend you visit our Biology category.
- Teresa Audesirk, Gerald Audesirk, (2003) Biology: Life on Earth . Ed. Prentice Hall.
- Bruce Alberts, Dennis Bray (2006). Introduction to cell biology (2006). Pan American Medical Ed.
- Neil A. Campbell, Jane B. Reece (2007). Biology . Pan American Medical Ed.
- Hypertexts in the area of Biology. Meiosis and sexual reproduction : http://www.biologia.edu.ar/cel_euca/meiosis.htm
- Valega, O. Apiservices. Inbreeding in bees : https://www.apiservices.biz/es/articulos/ordenar-por-popularidad/1145-consanguinidad-en-las-abejas