Difference Between Mitosis and Meiosis in Cell Division

The difference between mitosis and meiosis in cell division is to do with the type of cell which is created by each process. Both are important in genetics as they allow for the functioning of various vital processes in cells, ensuring the organism of which they are a part survives. We can say that mitosis and meiosis are types of cell division, a normal part of a cell's life cycle. Cell biology or cytology is the study of these cells and their processes.
Thanks to technological advances in microscopy, we are able to better understand how cells are formed, as well as how they function. Continue reading thedailyECO to discover the difference between mitosis and meiosis with diagrams to explain each process.
Difference between mitosis and meiosis explanation
The main difference between the processes of mitosis and meiosis is determined by the function that each process performs. In a general sense we can say their functions are the following:
- Mitosis: the division of the nucleus of any cell of an organism (somatic cells). It is necessary for the growth and renewal of said cells.
- Meiosis: is carried out only and exclusively by the cells involved in the reproduction process. It has the the aim of exchanging genetic information between the nuclei of two sex cells from different organisms. In doing so, it increases the genetic diversity and survival of the species.
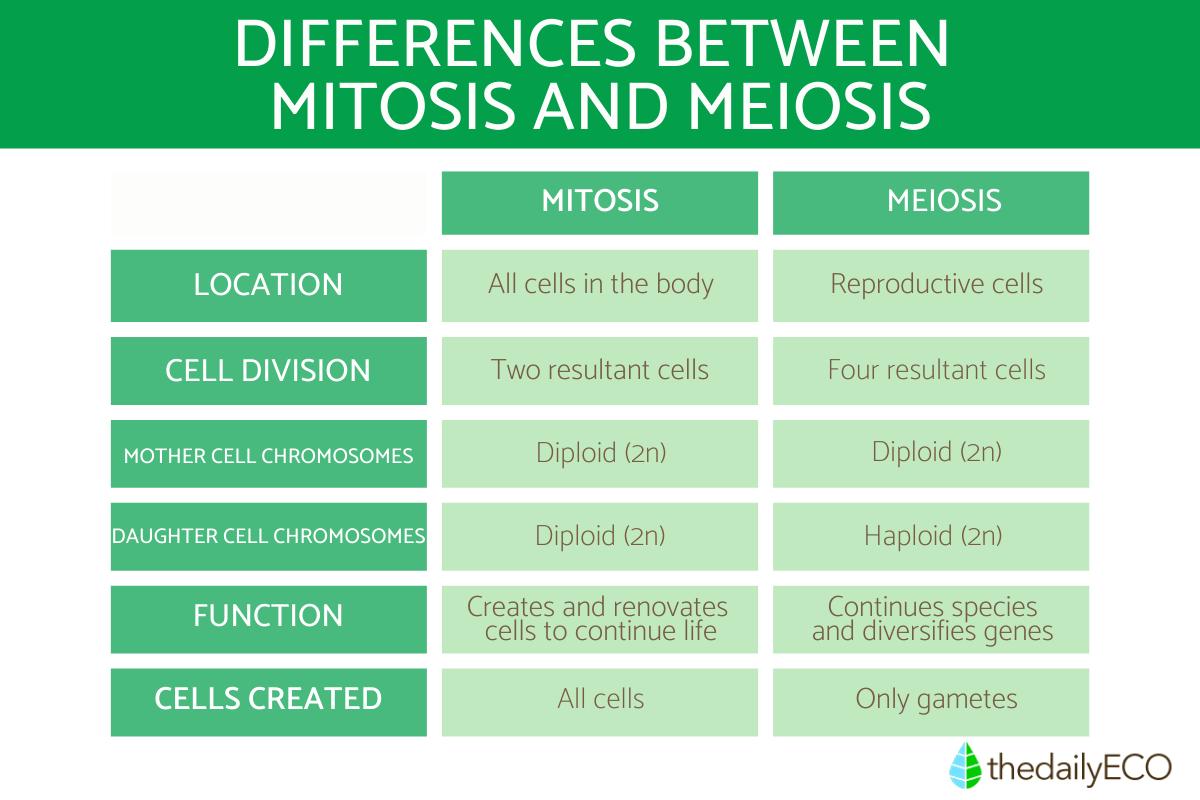
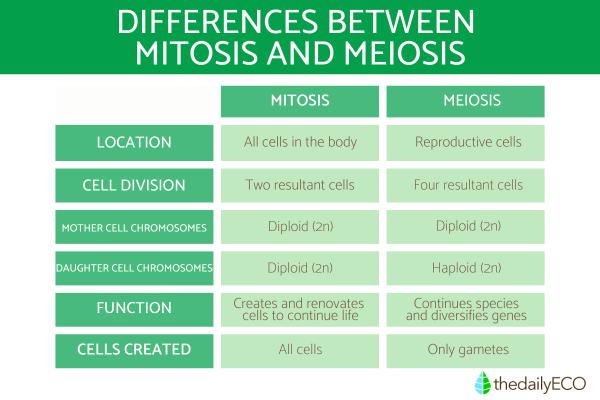
Not only do mitosis and meiosis have different functions, but the type of cell is different. We can see this reflected in the differences between the number and type of chromosomes or genetic material that are involved in these cell division processes. This is the difference between mitosis and meiosis with respect to the types of cells involved:
- Mitosis: short-lived process involving haploid (n) cells with unpaired chromosomes.
- Meiosis: long process involving diploid (2n) cells with paired chromosomes.
As stated in the introduction, one of the main differences between mitosis and meiosis is the type of cell which is created. These two types of cell division create the following types of cells:
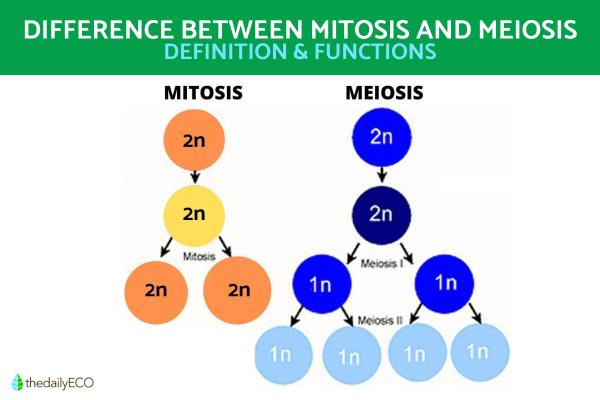
- Mitosis: after a single cell division, two new daughter cells genetically identical to the mother cell are obtained. This happens because the exchange of genetic information between chromatids has not occurred.
- Meiosis: after undergoing two nuclear fissions, the original cell gives rise to four final gametes (sex cells), each having half the number of chromosomes contained in the original cell. In addition, these four new cells have different genetic information, since during the meiosis process they have undergone a genetic exchange. This genetic process is known as crossing over[1].
Learn more about how we know the differences between mitosis and meiosis in our article where we ask why is the study of cells so important?
Similarities between mitosis and meiosis
Although they are different processes, both mitosis and meiosis are types of cell division. The reason we want to create a comparison between mitosis vs. meiosis is due to their similarities, the most important of which include:
- Cell nucleus division process: thanks to both biological phenomena, living beings guarantee their survival. Mitosis does this through the growth and maintenance of their own cells and tissues thanks. Through meiosis, the cells guarantee the diversity and genetic balance between species. With such genetic diversity in the gametes, the consequent organisms are better able to survive.
- Universality: the existence of the processes of mitosis and meiosis is universal, occurring with a greater or lesser frequency in all eukaryotic living beings that exist on the Earth.
Learn more about how these processes affect living beings with our guide to the difference between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells.
Definition and phases of mitosis
To better understand the differences between mitosis and meiosis, it can be helpful to look at each process of cell division individually. In its basic sense, we can say the definition of mitosis is:
The biological process by which the somatic cells of eukaryotic living organisms divide their cell nucleus and the genetic information available to them.
In this way, living organisms guarantee their survival, thanks to the correct growth and maintenance of all their cells. Both animal cells and those of plants, fungi and other eukaryotic microorganisms carry out the amazing process of cell mitosis.
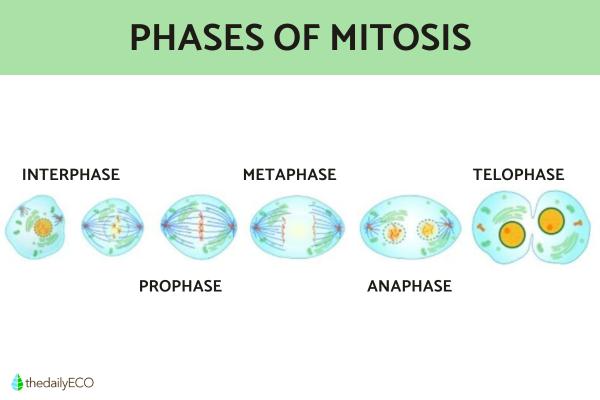
To achieve an equitable distribution of DNA or genetic material, there are five main phases of mitosis. They are the following:
- Interfase
- Prophase
- Metaphase
- Anaphase
- Telophase
The final result of mitosis is to obtain two daughter cells with identical genetic information. These are identical both between them and with respect to the mother cell. In this way, mitosis constitutes a type of asexual reproduction in which no more than a single stem cell is involved. You can learn more about these different processes with our guide to asexual reproduction in plants and animals.
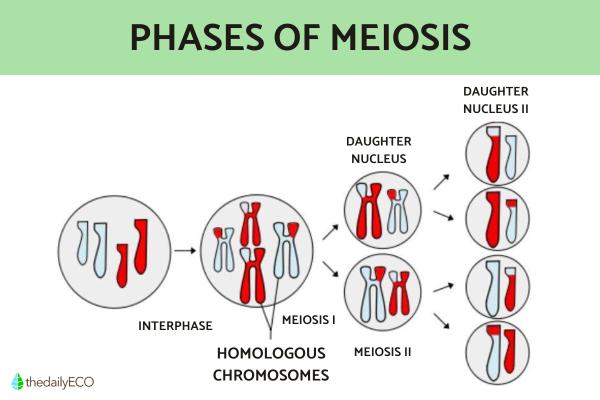
Definition and phases of meiosis
Meiosis is the most important process responsible for guaranteeing genetic diversity among individuals of the same species. This amazing biological process is necessary to carry out sexual reproduction between organisms of different sexes. In this way, meiosis is responsible for producing the male (sperm) and female (ovules) sex cells necessary for sexual reproduction. The result is the creation of new individuals genetically different from their parents.
During the complex genetic process of meiosis, two successive divisions of the cell nuclei are carried out. This is because the process is long and entails the completion of the following stages of meiosis:
Meiosis II
- Prophase I
- Metaphase I
- Anaphase I
- Telophase I
meiosis II
- Prophase II
- Metaphase II
- Anaphase II
- Telophase II
After the division and exchange of genetic material, the four cells resulting from the meiotic process are characterized by being haploid, i.e. there are a single copy of the genetic material). In doing so they provide new genetic information which is enriched and more varied. This can help the organism adapt better to their environment, have a better chance of fighting disease and provide many benefits science is yet to discover.
Now that you know well the difference between mitosis and meiosis, you can learn more about these processes with diagrams of the cell division cycle.
If you want to read similar articles to Difference Between Mitosis and Meiosis in Cell Division, we recommend you visit our Biology category.
1. Lorenz, A., & Whitby, M. C. (2006). Crossover promotion and prevention. Biochemical Society transactions, 34(Pt 4), 537–541.
https://doi.org/10.1042/BST0340537
- Murray, A. W., & Szostak, J. W. (1985). Chromosome segregation in mitosis and meiosis. Annual review of cell biology, 1, 289–315.
https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.cb.01.110185.001445