What is the Cytoskeleton and Its Functions?


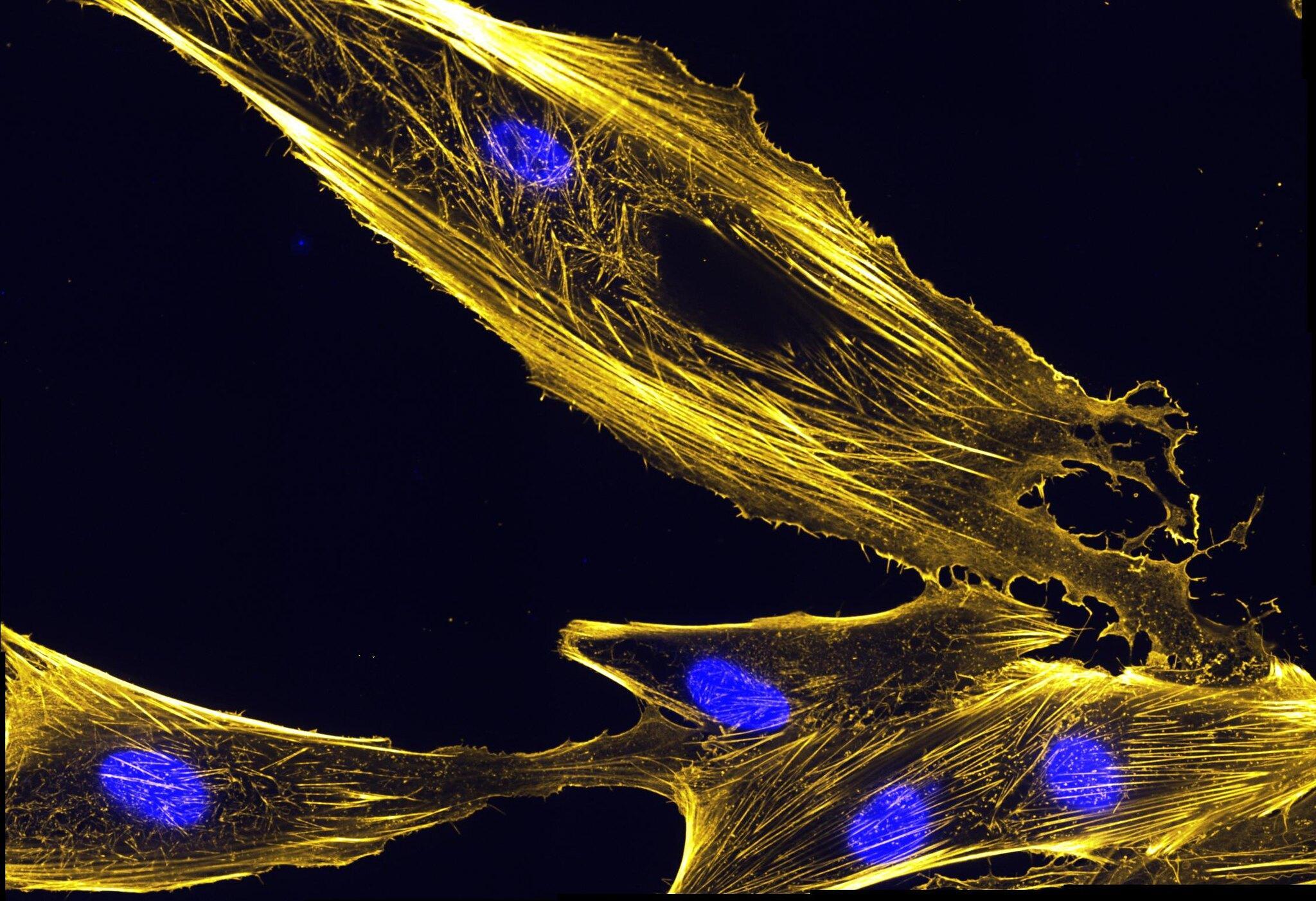
The cytoskeleton is a network of filaments that is part of the cytoplasm. Its characteristics are flexibility, firmness and a three-dimensional shape. Its function is the support, motility and regulation of biochemical processes in the cell. The structure is divided into microtubules, microfilaments, intermediate filaments and cilia or flagella.
Cells are the basic unit that makes up living beings. Within them are organelles of specific function from which all the larger functions of the organism are derived. The cytoplasm is the internal medium of cells, formed by a liquid matrix that serves to support the organelles and allow exchange. Within the cytoplasm is the cytoskeleton, a substructure that has its own important role within the cell. To learn more, thedailyECO provides a definition of the cytoskeleton by asking what is the cytoskeleton and its functions?
What is the cytoskeleton?
A basic definition of the cytoskeleton is a network of filaments made of proteins which function as a support matrix for the various components of a cell.
The cytoskeleton is found within the cellular cytoplasm. This is the medium that contains all the cellular organelles. It is one of the two components that make up the cytoplasm. The other is cytosol, the watery substance which helps keep the organelles in suspension. It is found in both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells, cells which have and do not have a true nucleus, respectively.
Learn more about what are eukaryotic cells in our related guide.
Characteristics of the cytoskeleton
Now that we have provided a basic understanding, we can look in more detail at the characteristics of the cytoskeleton in cells:
- One of the most important characteristic of the cytoskeleton is that it has a three-dimensional shape. This allows it to provide structure and volume to the cytoplasm, as well as the cellular organelles. This allows them to fulfill their various functions.
- It is formed as a geodesic structure, meaning opposing forces stabilize the entire assembly.
- It is flexible, but firm, thanks to the particular characteristics of the proteins that make it up its constituent parts.
Learn more about what are the different types of cell organelles for which the cytoskeleton is so important.

Cytoskeleton function
The cytoskeleton is structured in such as way that it can fulfill the following functions:
- Organizes the cell: the cytoskeleton is the matrix on which the organelles sit, so one of its functions is that each of them is held in its place. It was previously believed that the organelles floated alone in the cytosol. Over time it was discovered that the cytoplasm not only consisted of the liquid substance called cytosol, but also had the matrix of fibers called the cytoskeleton.
- Supports the cell: being made of fibrous proteins, the cytoskeleton helps give rigidity to the cell. This is particularly convenient in animal cells that lack a cell wall, as plant cells do.
- Allows orderly movement within the cell: although the organelles are fixed thanks to the cytoskeleton, it is also flexible to allow the small movements that occur inside the cell, such as that of the cytoplasmic current within plant cells. The movements within the cell are called cell motility.
- Regulates biochemical processes within the cell: through cell motility, the cytoskeleton allows there to be a flow of components manufactured within the organelles. These can be moved within the cell as part of the biochemical processes necessary to carry out their functions.

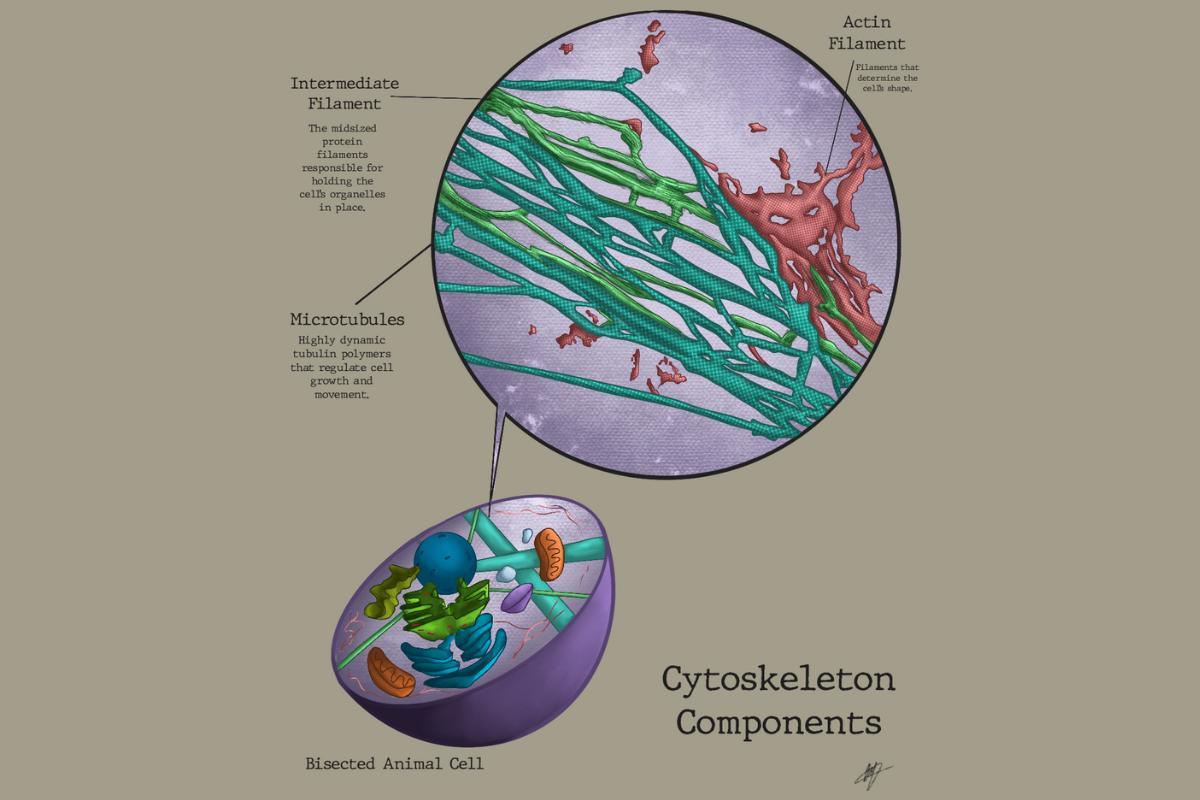
Cytoskeleton structure
The cytoskeleton is made of proteins, each with different characteristics and functions. It varies depending on the type of cell. The differences in structure according to the type of cell are detailed below.
Cytoskeleton in eukaryotic cells
The parts of the cytoskeleton in eukaryotes are the following:
- Microtubules: are made up of a protein called tubulin, which is found in its alpha and beta forms. They are flexible and hard in character. They have the ability to appear and disappear, according to the needs of the cell. They help move organelles, organize meiotic and mitotic spindles during cell division for chromosome placement and transport substances within the cell. They measure 25 nanometers in diameter.
- Microfilaments: are made of a protein called actin. When associated with myosin protein fibers they carry out muscle contraction. Actin is located at the margins of the cell, arranged in a helix made up of two filaments. Its function is to support the cell. They measure 3 to 8 nanometers in diameter.
- Intermediate filaments: are formed by different fibrous proteins, which vary depending on the tissue where the cells are located. They are only found in animal cells. They are the strongest fibers of the three mentioned. They serve to give firmness to the cells, in addition to helping to form networks. They measure 12 nanometers in diameter.
- Cilia and flagella: some eukaryotic cells have extensions that are used to movement. These come from microtubules, using the mobilization of fluid on the surface of a tissue to contract and create movement. In general, cilia measure between 250 nanometers in diameter, as do flagella. They differ in that flagella are longer and are present in smaller quantities than cilia.
Cytoskeleton in prokaryotic cells
In the past, the existence of different structures in the cytoskeleton of prokaryotes was not known. It was previously believed that they only existed in eukaryotic cells. However, today we know that there is a cytoskeleton in prokaryotes. It has functions analogous to those of eukaryotes, but is made up of the following proteins:
- MreB and ParM: similar to actin.
- WACA family proteins: a group of several proteins which serve to perform functions in the biogenesis and assembly of cilia and flagella in unicellular organisms.
- Crescentin: equivalent to the intermediate filaments.
- FtsZ: similar to tubulin.
Now that you know what is the cytoskeleton and its functions, you may want to know more about the cellular processes which it is able to support. You can do so with our article on the difference between mitosis and meiosis in cell division.
If you want to read similar articles to What is the Cytoskeleton and Its Functions?, we recommend you visit our Biology category.
Campbell, N.A., Reece, J.B. (2007). Biology. Argentina: Editorial Médica Panamericana SA.