What Is Cytoplasm and Its Function?


Cytoplasm is a vital component of cells, but it is important to know it is not an organelle. Its function is important to organelles as it holds these cellular structures in place within the cell. Cytoplasm is composed of complex network of proteins known as the cytoskeleton and cytosol, the latter being a type of intracellular fluid.
The organisms of living beings function thanks to their cells. They are the basic structural units of all organisms, with each one containing substructures which carry out various functions to keep the organism alive. Among these structures is the cytoplasm, a supportive material which is vital for the cell as a whole. We discover more in our thedailyECO article on what is cytoplasm and its function? We do so by providing a definition of cytoplasm and explaining its structure in more detail.
What is cytoplasm?
We start by providing a basic definition of cytoplasm. The cytoplasm is the internal environment of cells. It is not an organelle like the other parts that make up the cell, but rather it is an aqueous medium for these organelles. With the exception of the nucleus, these organelles are considered constituent parts of the cytoplasm.
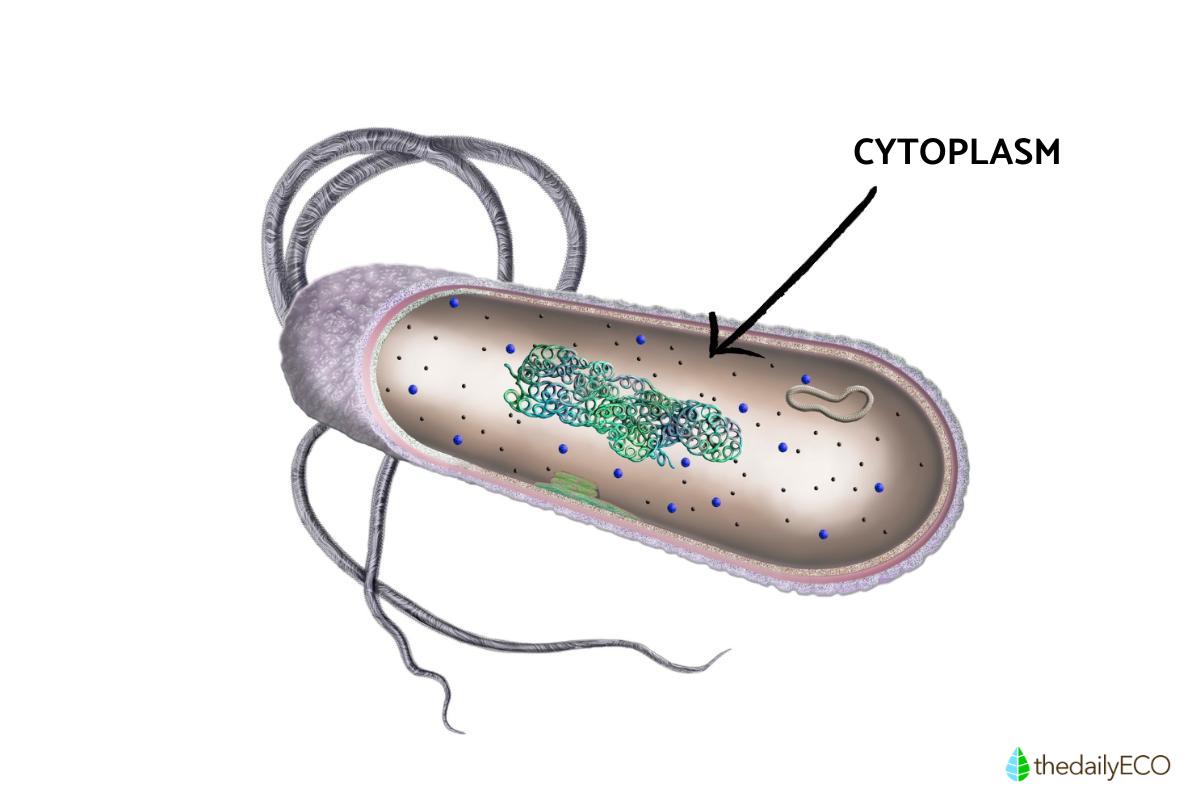
Cytoplasm is found both in eukaryotic cells (those with a true nucleus) and prokaryotic cells (those without a true nucleus). It is essentially everything within the cell membrane (plasma membrane) which is not the nucleus in eukaryotic cells. In prokaryotic cells, the cytoplasm encompasses the entire cell content within the cell membrane.
Discover more about what are cell organelles and their function.
Characteristics of the cytoplasm
Now we have a definition of cytoplasm, we can understand it better by looking at the following cytoplasmic characteristics:
- The cytoplasm is liquid in consistency and has no specific shape. This liquid consistency is described as a colloidal solution or dispersion, i.e. it contains particles dispersed within it. These particles are sugars, mineral salts with ions, lipids, amino acids to form proteins, nucleotides, vitamins and transfer RNA. It is made up of 70% water, with the remainder consisting of the aforementioned biomolecules.
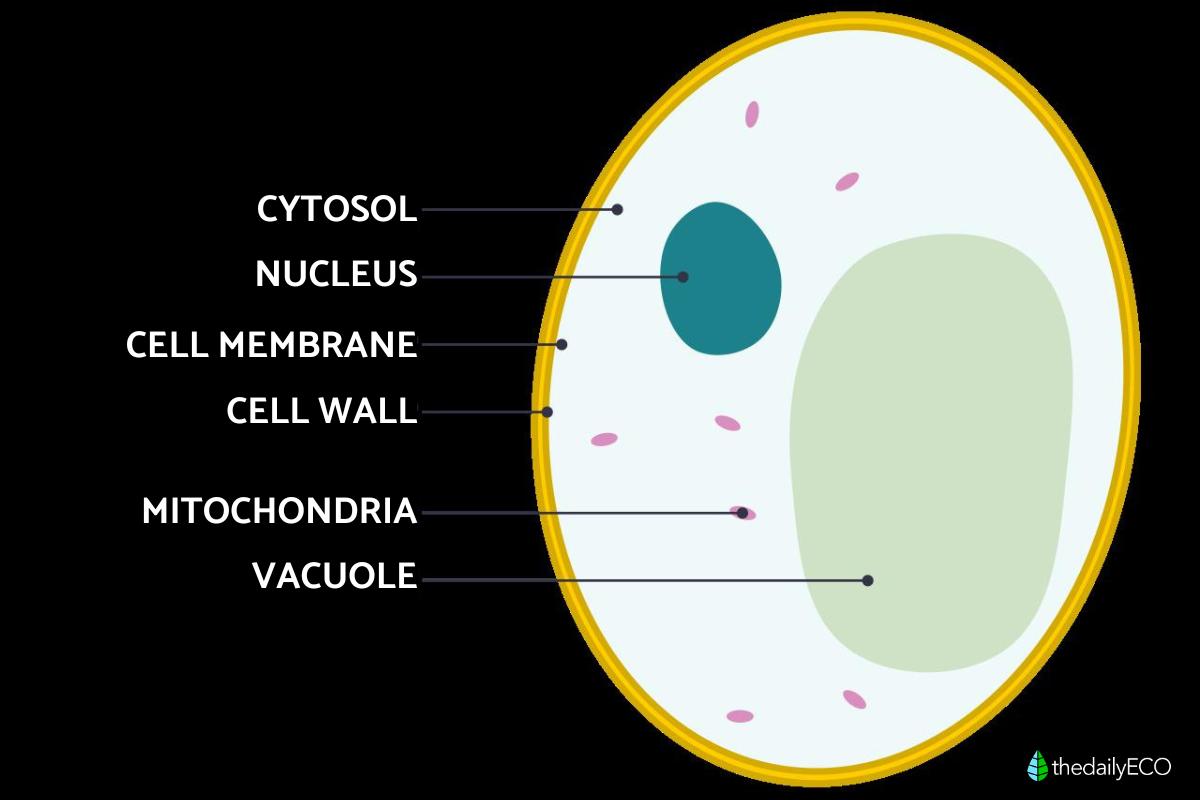
- The cytoplasm is delimited by the inner surface of the cell membrane. It is compartmentalized into what we call organelles. Each of these cellular organelles has particular characteristics and its own functions. You can see the location of the cytoplasm within a cell in the cytoplasm diagram below.
- The cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells is different from the cytoplasm of prokaryotic cells which can be observed in their structure. In eukaryotic cells the cytoplasm is between the cell membrane and the nuclear membrane. On the contrary, in prokaryotic cells it is includes everything in the cell membrane due to the absence of a nucleus.
- Another important difference between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells is that in prokaryotic cells almost all metabolic reactions occur in the cytoplasm. In eukaryotes, some occur in the cytoplasm but others occur in the organelles.
- Prokaryotic cells are also differentiated from eukaryotic cells by the organelles that are immersed within the cytoplasm. In the prokaryotic cell there are the nucleoid, plasmids, ribosomes, inclusion bodies, thylakoids in photosynthetic organisms and accessory organelles. In eukaryotic cells the organelles present arranged in the cytoplasm are the nucleus, ribosomes, mitochondria, rough endoplasmic reticulum, smooth endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, peroxisomes and accessory processes.
We can find out more about important processes within cells in our explanation of the difference between DNA and RNA molecules.

Cytoplasm function
With these characteristics in mind, we can look more closely at the function of cytoplasm within living cells:
- The main function of the cytoplasm is to contain the cellular organelles, providing them support so they can carry out their functions. Thanks to the cytoplasm the organelles do not float, but are held and contained in their place.
- A large part of the cellular metabolic processes and biochemical processes essential for the life of organisms occur in the cytoplasm, such as glycolysis (i.e. breakdown of glucose to produce energy). This is how the cytoplasm plays a role in cellular transport, since the components formed within the organelles use the cytoplasm as a pathway for molecules.
- The cytoplasm also serves as a transport medium for all the products that are manufactured within the cell. Since they have to move from one place to another, it is the cytoplasm that fulfills this function.
- It also serves to organize cell division, especially thanks to the cytoskeleton that orders the organelles during the formation of a new cell. You may be interested in this article about the phases of the cell cycle which explains these processes in more detail.
- Other important processes that occur within the cytoplasm are cellular respiration, cell signaling and protein synthesis.
Learn about some of the many processes which are carried out within cells by reading our explanation of the differences between anabolism and catabolism.
Cytoplasm structure
The cytoplasm consists of two main components which are the following:
- Cytoplasmic matrix, cytosol or hyaloplasm: the colloidal solution composed of liquid and dispersed particles. Among them we have the biomolecules already mentioned and cytoplasmic inclusions. The latter are dispersed and inert inconstant structures that serve as food reserves, products of cellular excretion or even pigments. It is made up of 70% water.
- Cytoskeleton: a network of filaments formed by proteins that holds organelles. If they did not exist, these cellular components would float within the cell without order or support. Cells are not always immobile, since organelles, chromosomes and cellular contents tend to move. This is achieved thanks to the flexibility of the cytoskeleton that allows such movement.
There are differences between the prokaryotic and eukaryotic cytoskeleton. The eukaryote is made up of microtubules made of tubulin, microfilaments of myosin and actin, and intermediate filaments made of various proteins. The cytoskeleton of prokaryotes is made up of classified proteins called MreB and ParM, WACA proteins, crescentin and FtsZ. The functioning of the proteins of prokaryotes and eukaryotes are analogous to each other, fulfilling the same purposes of support and movement.
We can also differentiate specific areas within the cytoplasm which are of differing consistencies. These are the following:
- Ectoplasm: it is the region closest to the internal cellular membrane, i.e. it is the outermost part of the cytoplasm. It has a dense gel-like consistency. It is rich in filaments that give it such consistency. It serves to give more support to the ends of the cell.
- Endoplasm: is the innermost part of the cytoplasm, where the organelles are. It has a more liquid consistency in relation to ectoplasm.

Difference between cytoplasm and cytosol
Although the terms cytoplasm and cytosol sound quite similar, they are two different things. Cytosol is the aqueous solution with dispersed elements and is part of the cytoplasm. This means that the cytosol is one of the many components of the cytoplasm. Conversely, the cytoplasm incorporates the entire cytosol together with the cytoskeleton.
Now that you know what is cytoplasm and its function, don't miss this article on the different types of cells and their function.
If you want to read similar articles to What Is Cytoplasm and Its Function?, we recommend you visit our Biology category.
- Murialdo, R. (2009) Human biology. Argentina: Editorial Brujas.