Environment
Explore the Environment category to uncover deep ecological insights, analyze human impacts, and engage with innovative strategies to safeguard Earth's ecosystems.
425 articles

New
New
A canyon is a geographical formation characterized by a deep and relatively narrow valley with steep walls. Canyon formation occurs primarily by the erosive action of a river over millions of years. This landform is a type of relief that can be found in different parts of the world. They are particularly...

New
New
Bracts are a part of a plant which can be quite confusing, especially in certain plant species. Often they can look like a leaf, but sometimes they look like the petals of a flower. This is because they can be of various colors, textures, shapes and sizes. While some may look like petals, they are not....
New
New
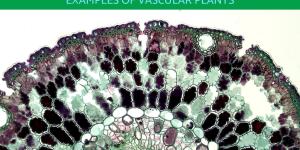
Non-vascular plants are the oldest plant species on planet Earth. It wasn't until 400 million years ago that vascular plants first developed their definitive vascular structures. Also known as tracheophytes, vascular plants have now become the dominant type of plant on our planet with around 350,000...

New
New
Every ecosystem has different food chains which helps us to understand the biocenosis of the living organisms within it. This refers to the interactions of living organisms in a given geographical area. Energy transfers between producers and consumers within the food chain, but not all are equal in...

New
New
When we classify fruits, we may think of them in terms of consumption. For example, an aubergine is technically a type of fruit, but we eat it like a vegetable. Different fruits can be eaten in different ways, but botanical classification is not necessarily the same as culinary. In botany, fruits are...

New
New
There are various ways in which plants can be classified, but all fall under the category of being either a vascular or non-vascular plant. This is an important distinction because the presence or lack of a vascular system influences the properties of the plant. Most plants which are consumed by humans...

In geography, a plateau is a large geological structure which has a flat or gently undulating structure at least 500 meter above sea level. This highland landform is also known as a tableland or high plain. This is because they are a flat surface at heigh which mimics the basic structure of a table,...
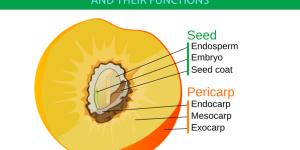
The fruit is a part of all angiosperms, commonly known as flowering plants. This is because the fruit is the mature ovary of the plant which is located in the flower and which produces seeds. Non-flowering plants do not have ovaries, so their seeds are exposed. Fruits are necessary for the reproduction...
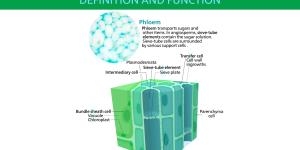
Plants have different tissues which carry out the necessary functions which allow them to grow and survive. Not all plants have the same tissues to carry out these processes. One of the most important ways to distinguish between different plants is whether they are vascular or non-vascular. Vascular plants...

Gullies in geography are landforms that manifest as deep and narrow channels in unprotected soil. They form due to soil erosion caused by surface water runoff. They are a geographical phenomenon that can be observed in different regions in the world. They are often most associated with vegetation loss, poor...
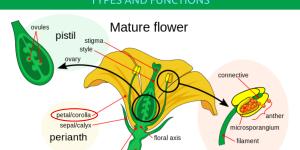
Due to their color, the petals of a plant are often the first thing we notice when looking at them. While they are a part of the flower and play a part in the plant's reproduction, they do not house any of the sexual organs themselves. This means their influence on plant reproduction is indirect. Evolutionary...

There are different types of valleys which differ due to their formation. Although most valleys are formed by erosion or tectonic movements, even these factors can be very different from each other. The resulting valleys take on their characteristic shape due to the nature of this erosion. If we see...

Chemosynthesis is a metabolic process in which inorganic substances are oxidized into organic matter using inorganic compounds. This process is mainly used for the organisms which carry it out or those which directly depend on them. Although it involves oxidization, it does not produce oxygen as a byproduct....

The field of topography is an important aspect of physical geography. It involves the study of the surface of landforms with a particular emphasis on elevation. A hill is a natural landform which is elevated from the area surrounding it. This means they don't have to start at sea level since some may only...

Our planet's ecosystems are composed of living organisms which exist within various biotopes, the specific geographical areas which contain them. Within these biotopes, biocenosis occurs. Biocenosis refers to how all these organisms interact with each other to maintain balance in their respective biotopes....

Climate study is a field within geography. Studied within this discipline are the overarching factors which determine climate and weather patterns around the globe. There are also small-scale phenomena that directly influence the environmental conditions of specific geographical areas. One of these is the...

The Gran Chaco forest is the second-largest forested region in the Americas, second only to the Amazon rainforest. Located in South America, the Gran Chaco spans southern Bolivia, western Paraguay, northern Argentina, and a small part of Brazil. This massive ecosystem covers over 647,000 square miles,...

Carbon sinks are systems that absorb and store carbon dioxide (CO₂) from the atmosphere. Known as sequestration, this is a process which can be carried out naturally or artificially. Their role is fundamental in the context of climate change, as they help reduce greenhouse gas concentrations. This makes...

A river valley is a landform characterized by a depression or basin of land formed by the erosion of a natural stream of water. Valleys are common geographical features, some of which have created some of the most beautiful vistas in nature. They are also very important ecosystems for various plant...

Seracs are large blocks of ice that form on glaciers , especially in areas with steep slopes or uneven terrain. They are formed by the fracture of ice due to internal stresses caused by the movement of the glacier. They are both extremely important in glaciology and dangerous for ecosystems. These blocks...

Relationships between individuals of the same species can be positive or negative. Competition is a negative interaction in which at least one of the competitors is harmed. When individuals of the same species compete for food, territory, reproduction or social dominance, population growth can be affected....

In a biological community, living beings establish various relationships. These include with many biotic and abiotic factors, such as other animal species or even the habitat itself. One of the most important biological relationship is with other members of their own species. This includes those with...

A ravine is an abrupt geographical feature generated on the surface of the ground that is charactertized by relatively steep sides and a narrow space between them. The formation of ravines has various causes, but water erosion is one of the most common. Tetonic activity can also influence ravine formation....

Have you ever wondered why some places on Earth are covered in dense forests while others are barren deserts? Or why certain animals and plants can only be found in specific locations? The answer lies in the fascinating world of terrestrial ecosystem. Terrestrial ecosystems are all around us, from the trees...

Although very different, plants are living beings which have some basic functions which are the same as animals. They need to take carry out cellular respiration and reproduce to maintain their species, as well as many other biological processes. Energy is particularly important because they would not...

While heavy water is a type of water and shares the same chemical elements, the configuration of these elements gives it distinct properties to regular water. It derives its common name from the fact that the normal hydrogen atoms are replaced by the much heavier isotope of hydrogen known as deuterium....

You may be aware that nectar is a substance which attracts various pollinators to flowers such as bees. You may not be aware why plants have nectar in the first place. While nectar is most associated with flowering plants, it can be found in some non-flowering plants. Angiosperms evolved from gymnosperms...

There is an enormous variety of plant species on our planet. They have evolved to adapt to various environments and ecosystems, some inhabiting the most inhospitable environments we can imagine. These adaptations affect various aspects of their life cycle, but some of the most vital affect reproduction....

Our world's ecosystems face many threats, with many scientists claiming that biodiversity loss is so great we are currently experiencing a mass extinction event. This is when the loss of biodiversity occurs at a very high rate and to a widespread degree. There are many causes of such biodiversity loss,...

Artificial intelligence has revolutionized multiple industrial sectors, with further innovation appearing at a staggering rate. The generation of capital, opportunities and solutions to various problems are exciting. They have the potential to benefit societies in many ways, especially in areas such as...

Also known as salt deserts or salt flats, salt pans are vast expanses of land which are covered by a layer of minerals, mostly in the form of sodium chloride salt. They are considered extreme environments since this concentrated amount of salt makes it very difficult for organisms to survive. Salt flats...

Water whirlpools are fascinating natural phenomena that occur in oceans, rivers, and lakes. But what exactly causes these swirling vortexes to form? Whether it's ocean currents, tidal forces, or human-made structures, whirlpools result from the movement of water in unique ways.
In this article by thedailyECO,...

Desert pavements are arid topographical regions which are characterized by a surface covered in rocks, pebbles or gravel with little or no sand. While we might most associated deserts with sand, desert pavements represent a very large portion of this planet's desert areas. Of great importance to their respective...

Limestone pavements are geological formations found in limestone terrain that create an exposed flat topography which has features caused by weathering of the rock. This weathering leads to grooves, cracks and cavities which create blocks known as clints which are separated by fissures known as grikes....

Planet Earth is more than 4.5 billion years old. Life on Earth evolved from initial molecules which eventually became the living organisms we know today which can vary greatly in complexity. While various unknown events helped to form life, others worked to curtail it or at least change its course. Included...

A plasmid is a circular genetic molecule containing DNA that is found within certain cells. It is most commonly found in bacteria, although it has been found in eukaryotic organisms such as certain types of yeast. The main function of plasmids is to act as a vehicle for introducing foreign DNA or genes...

Adaptive radiation is a process in evolution where one original species quickly splits into many new ones, each finding its own way to live in different environments. This usually happens when creatures find themselves in new places with less competition, like on isolated islands or after a big die-off...

Considered cycles of matter, biogeochemical cycles are the natural routes of transformation by which essential elements and compounds move between living organisms, the atmosphere, the Earth's crust and water. These cycles are continuous and are necessary for the regulation of the nutrients essential for life...

Artisanal mining, often practiced in small-scale, informal settings, plays a crucial role in the livelihoods of millions worldwide. However, its environmental impact is profound and far-reaching, affecting ecosystems, water sources, and local communities. From deforestation and soil degradation to toxic...
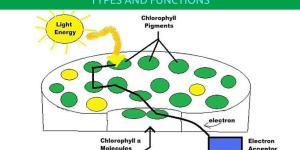
Photosynthesis is a necessary process for most life on Earth, including ourselves. Without it, ecosystems would collapse and only certain prokaryotic organisms which do not rely on it would be able to continue. Photosynthetic organisms include most plants, as well as certain types of algae and bacteria. Although...

Asbestos is a naturally occurring mineral once widely used in construction and manufacturing due to its heat resistance and durability. However, asbestos exposure can have serious health consequences, leading to diseases like mesothelioma, lung cancer, and asbestosis. While its use has been heavily regulated...

Sinkholes are openings in the ground which are caused by the gradual or immediate collapse of the surface. While this can be a general sinkhole definition, there are many different types which can be found both in nature and in urban environments. Some sinkholes are caused by natural processes, but an increasing...

Water springs are one of nature’s most insteresting freshwater sources, emerging naturally from the ground due to underground water pressure. But how exactly do they form, and why are they so important? From supplying drinking water to supporting ecosystems, natural springs play a crucial role in sustaining...
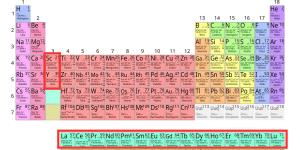
Rare earth metals are a group of 17 chemical elements on the periodic table. They have certain magnetic, electrical and optical properties that make them essential in various industries. Used in the manufacture of electronic devices, renewable energy, military equipment and industrial processes, they are...

Lysosomes are essential organelles that act as the cell’s recycling center, breaking down waste, cellular debris, and foreign invaders. These small, enzyme-filled structures play a crucial role in maintaining cell health by digesting macromolecules and recycling nutrients. Found mainly in animal cells,...

Thylakoids are membranous structures which are contained within chloroplasts and cyanobacteria. They trap light energy and transduce it into the chemical energy forms known as ATP and NADPH. Thylakoids are structures where a lumen space is surrounded by a membrane. They are mainly composed of photosystems...

The terms "flora" and "fauna" represent the living organisms that inhabit our planet. These classifications help scientists and nature enthusiasts alike understand the diversity of life across Earth's many ecosystems. Simply put, flora refers to all plant life while fauna encompasses all animal life. This...

Erosion is a geological process which creates various landforms both above and below the Earth's surface. The mechanical action of various forces causes material to wear away, with different forces affecting this material in different ways. The material which is subsequently produced is them deposited somewhere...

Water condensation is everywhere around us, from the glistening dew drops on grass to the fluffy clouds drifting by. It's the simple yet profound process where water vapor transforms back into liquid water. This fundamental change shapes our weather, drives the global water cycle, and influences our everyday...

A wadi is a dry channel in that only transports water intermittently, usually after intense rainfall in arid and semi-arid regions. Essentially, it is a dry river bed because it was created by water which once passed through the channel. These channels are characteristic of deserts and other similar areas...
